When you make something, you better ensure there’s nothing faulty about the product. If a customer buys your product and it doesn’t work, at best, you’ll lose a customer and at worst, you’ll be served with a lawsuit. Simply put, quality control in manufacturing is important.
Quality control in manufacturing means your customers get what they’ve paid for. A happy customer leads to brand loyalty which creates long-term profits for your company. Let’s learn what quality control is, some of the methods to employ it and the roles of your team to ensure quality control in manufacturing is delivered.
What Is Quality Control (QC)?
Quality control isn’t limited to manufacturing, of course. Quality control is a process that helps deliver products as planned or helps ensure project deliverables meet stakeholder requirements. It requires that the company support an environment where everyone, from management to employees, is executing their jobs as perfectly as possible.
The first thing that must be established is a benchmark or baseline from which to measure the product to make sure that it’s delivered to the project’s quality expectations. Products must also be tested throughout the production process to make sure the production line is operating normally, identify causes of defective products and solve any issues.
Another measure to prevent error is having a system to monitor your production process in real time. ProjectManager is online project management software that delivers real-time data to help you catch problems quickly and resolve them. Use our live kanban board to get a high-level view of your product. Use it to centralize processes, tag team members and ensure quality at every phase. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
To make sure that products are manufactured to the quality standards set by an organization, a quality control management process must be established.
What Is Quality Control Management?
Quality control management refers to the process of establishing the framework that allows an organization to set quality standards, track the performance of their production floor and inspect the quality of their products.
This is done to standardize the manufacturing process and better ensure that each product from the assembly line is consistent and correctly made. Further, specifying which production activities are completed by which employee and capital assets such as equipment or machinery limits errors and helps organizations better understand the causes of manufacturing quality issues.
Quality Control Process
Each organization can establish its quality control process, which means there’s no standard approach. However, here are some basic steps that can help you build your own quality control management process.
- Define quality control standards and manufacturing key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Determine what quality control tools will be used to measure your quality control KPIs
- Define the steps of your quality control inspection process
- Identify who will be responsible for checking the quality of your processes and deliverables
- Make a quality control checklist to standardize the inspection process
- Write a quality control plan that covers the most important aspects of your quality control management guidelines
We’ll learn more about each of the elements of quality control mentioned in these steps in the sections below.
Get your free
Quality Control Template
Use this free Quality Control Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
Quality Control Plan
A quality control plan is a document that describes the procedures, tools, documentation and metrics that will be used to implement the quality control process of an organization. Quality control plans are used in manufacturing, construction project management, software development and many other industries.
Quality Control Tools Examples
Many tools can be used to help you manage the quality of your products. Here are three examples of the most common quality control tools.
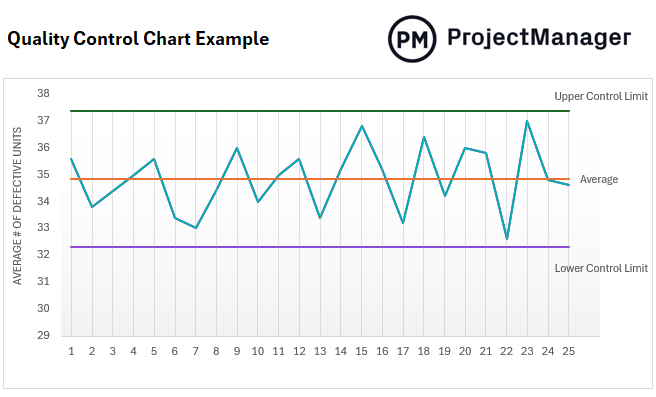
Quality Control Chart
A quality control chart is a graph that helps manufacturers gauge how consistent their production quality is by representing the number of defective products over time to identify patterns that can indicate whether the quantity of defects is constant, or if they fluctuate significantly, which can reveal issues in the production line. This allows organizations to fix those quality issues, be more productive and reduce their cost of quality.
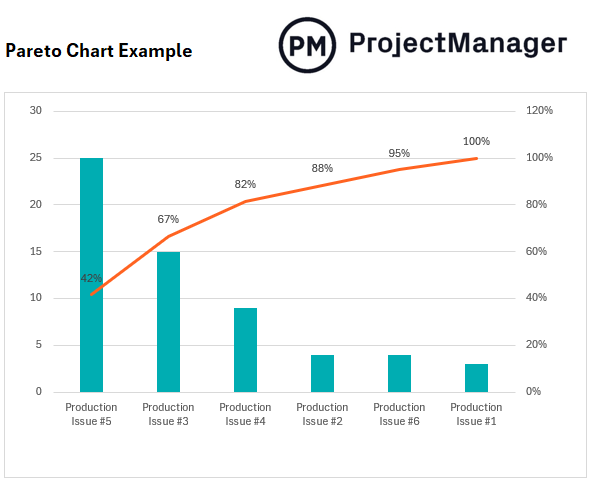
Pareto Chart
A Pareto chart is a bar graph used to represent various causes of production quality issues, in which bar sizes show the total number of defective products and are arranged from longest to shortest from left to right. This helps manufacturers determine the major causes of quality control issues and resolve them.
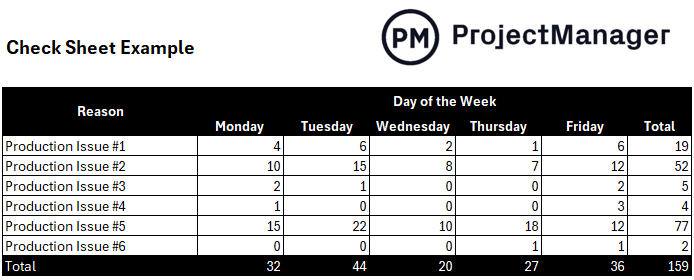
Check Sheet
In manufacturing quality control, a check sheet is a table that allows you to track problems such as defective products and their causes over time. For example, you can create a check sheet to track how many defective products are manufactured daily, weekly, monthly or even quarterly.
Quality Control Template
This quality control template allows you to log any quality issues found as you test the quality of your products, which makes it an ideal tool for manufacturers. Track important details such as who will be responsible for fixing the product quality issue, the date when it was found, its status and the expected date when it will be resolved.

Quality Control vs. Quality Assurance
You’ll hear quality control and quality assurance interchanged, but these are two different things. Quality control is part of the larger quality management process, which focuses on meeting quality requirements.
Quality assurance is also part of the quality management plan and revolves around the activities within that plan that ensure that your product goes through production. It means that you’ve verified that the quality requirements that have been planned will be fulfilled in production.
Quality control takes place during the inspection. As noted, it’s a series of test procedures that make sure the product is safe and effective. Therefore, quality control and quality assurance are different in working together to ensure the quality of the product you’re manufacturing.
There are differences between the two. One, quality assurance is proactive, while quality control is reactive. That’s due to the nature of what they do and when they do it. Quality assurance is process-oriented and preventative while quality control focuses on the product itself and looks for any issues with its quality that will impact the customer.
Types of Quality Control Methods
There are methods of quality control that employ strategic procedures to ensure that the proper maintenance and quality testing in production is taking place. There are several types that we’ll discuss, but all involve training employees, creating standards for the output quality that can be measured to ensure they’re working and periodically testing these quality control methods to make sure there aren’t any inconsistencies.
100% Inspection Method
As the name implies, this method is a thorough assessment of all project items. By quality controlling every aspect of the production, you’re more likely to have better accuracy and remove most imperfections that might mistakenly be passed on to the customer. This method is best suited for those projects where even a slight flaw in the product can cause a recall, such as when processing meat. It is, as expected, a costly measure that doesn’t apply to every product.
Related: 14 Free Manufacturing Templates for Excel
Six Sigma
This quality control method works at improving current processes, products or services by discovering and eliminating defects in order to streamline manufacturing. The aim is that the manufacturing process will have little to no variance. Six Sigma works by defining the problem, measuring the current process and analyzing the root cause of variations and defects to identify the issues. It improves processes by eliminating the root cause of these defects and controlling the process to stay on track.
X-Bar Chart
An X-bar chart is used in quality control to monitor the mean of successive samples of a constant size. The Y-axis tracks the degree to which the deviation of the tested attribute is acceptable. This control chart is used for characteristics that can be measured on a continuous scale. That includes such things as weight, temperature, thickness and so forth. It is, however, rarely used alone and is often coupled with an R-chart, which is used to determine the stability and predictability of a process.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total quality management is an approach to quality control that aims for long-term success by providing customers with satisfaction. The customer comes first and employees must own quality control for their part in the production. This is fostered through the creation and implementation of processes that find successful products and then repeat them. It also looks at system integration to streamline processes. It’s data-driven and is constantly seeking ways to improve.
Statistical Quality Control (SQC)
This method uses statistical data, such as sampling and probability, for quality control. First, a unit of the final product is sampled and tested to determine if the standards for quality have been met. The sample size can be increased to represent more products. Process sampling is also employed with a control chart to map the changes in manufacturing. This identifies tolerable limits in product variations and leads to discovering problems that will be addressed through corrective measures.
Taguchi Method
This quality control method is based on research and development, product designs and reducing defects and failures in the manufacturing process. Developed by the Japanese engineer and statistician Genichi Taguchi, this method focuses more on design than the manufacturing process when dealing with quality control. It aims to remove variances in production before they happen.

Quality Control Roles
While everyone is often employed to maintain the quality of their piece of the larger manufacturing production, specific roles are dedicated to quality control. Let’s look at three of the pivotal roles of quality control.
Quality Manager
This is a supervisory role, one that oversees the product development processes to make sure they’re meeting the quality and efficiency standards that have been set by the company and any regulatory groups. The quality manager works with clients to ensure the final product meets their needs and requirements.
Quality Inspector
Under the quality manager will be a quality inspector who is responsible for making sure the manufactured products meet requirements from the company, regulators, customers, etc. They do this by testing products with tools and making sure the final product follows the guidelines that were developed by the company to ensure the product is safe and meets the needs of the customer without flaws.
Quality Engineer
Sometimes referred to as a QA engineer, QC engineer or senior quality specialist, a quality engineer works to ensure the overall quality of the manufactured product. They’ll test processes, monitor quality standards, create documentation, devise quality tests and define criteria that those tests should meet. They’re also responsible for fixing any problems they might find. They work with design teams, suppliers, manufacturing teams and customers to make sure the products produced are safe, reliable and meet customer expectations.
ProjectManager Helps With Quality Management
All of these quality control roles closely monitor the production processes and work to streamline them for greater efficiency while meeting quality standards. ProjectManager is online project management software that can do this in real time so you can respond to defects faster and resolve them quickly.
Automate Workflow to Streamline Production
Keeping teams focused on the important work ensures greater quality. Our workflow automation allows you to make a trigger that sets an action such as changing the tag, assignee and more instantly. To ensure that quality moves forward in the production line, set task approvals. Now before a status changes, the work is sent to a person with authority to approve it, ensuring quality control.

Manage Risk and Track Issues
Knowing what might go wrong and having a plan to identify and resolve those issues is the basis of risk management. Our risk management feature allows you to track all risks in one place, assess their impact and likelihood, assign an owner and much more. This allows you to manage risks to your production and avoid unexpected impacts on your scope, cost and delivery. Display risk cards showing priority, assignee, and response and add attachments and comments in real time.
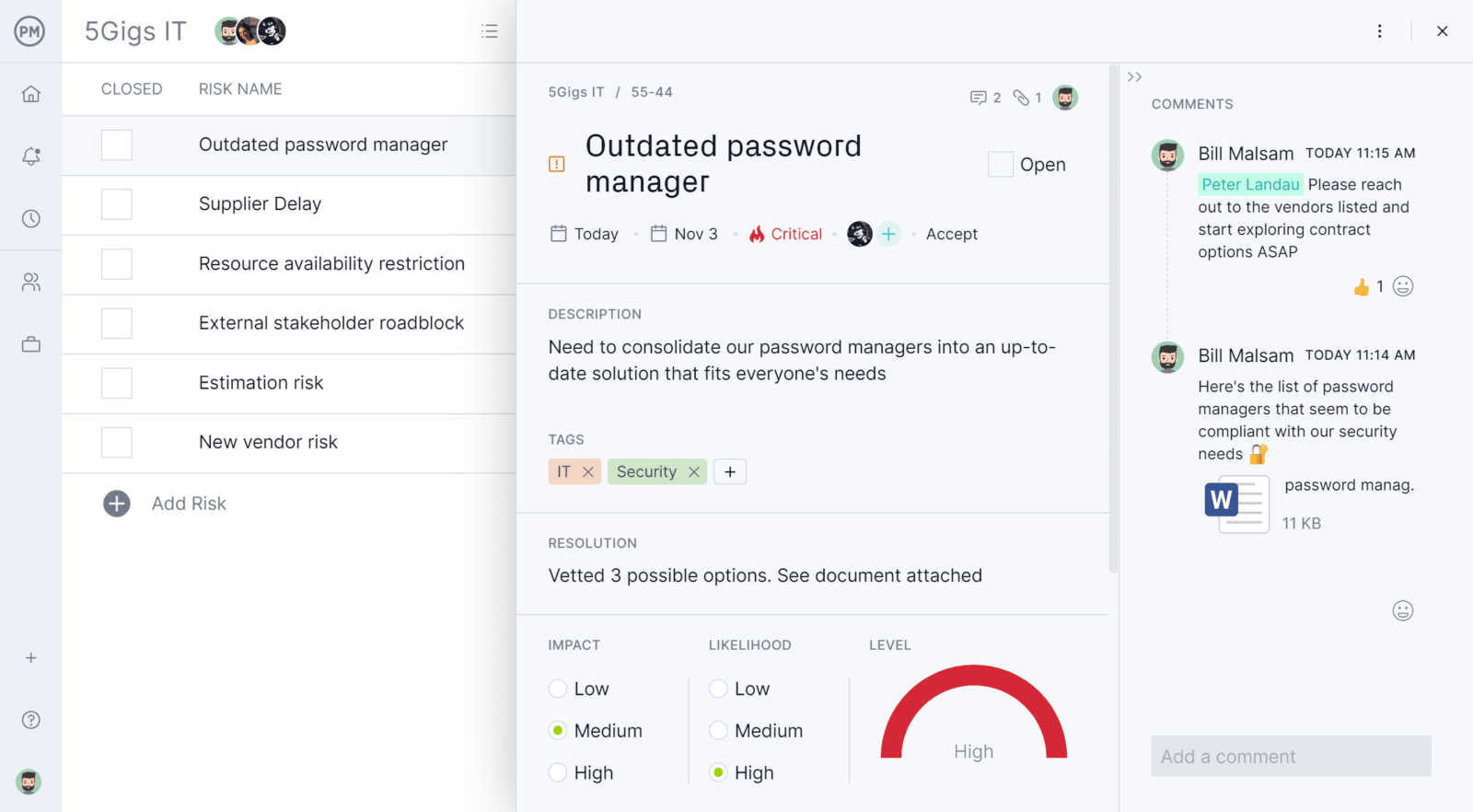
Quality control managers can access customizable reports to get details on production and share updates with stakeholders. Our collaborative platform connects everyone across departments to foster better communication, which helps identify and resolve quality issues better. Our tool helps you plan your manufacturing, manage your resources and maintain the quality your customers want.
Related Content
- Project Quality Management: A Quick Guide
- What Is Quality Planning & Why Is It Important?
- How to Handle Time, Cost & Quality in Project Management
- Meeting Quality Targets on Projects
- Production Planning in Manufacturing: Best Practices for Production Plans
ProjectManager is award-winning software that helps you plan, manage and track quality control. Use multiple project views to allow everyone to work on the tools they want while sharing real-time data for better collaboration and decision-making. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.