For a successful project, you need an overall picture of your work performance information (WPI). Performance reporting provides that information by putting performance measurement, quality assurance and accountability data in context.
Performance reports (like a project status report) do more than just show key performance indicators. They can also point out where there’s room for improvement and identify project risks. Project management software can aid in this reporting, but first, let’s look more in-depth at project performance reporting.
What Is Performance Reporting?
Performance reporting is the process of documenting and defining the projects, products or services that a company makes and measuring its success with a reporting system that covers scope, costs, quality assurance, and schedule. Performance reporting is used to determine how well the company is performing and whether it’s meeting its goals and objectives.
To do it, you gather data from specific work and analyze it. Once that analysis is complete, you can make suggestions to improve decision-making in your business processes.
There are different targets for performance reporting. For example, a performance report can focus on one project or team member, but it can also go as broad as the whole company. Performance reports tend to share these common data points:
- Company goals and objectives
- Five-year vision
- Key performance indicators (KPI)
- KPI measurement frequency
- Source of data being monitored
Related: 5 Free Project Report Templates
Why Is Performance Reporting Important?
Performance reporting provides a view into the performance of a business and lets you track your activities and outline your strengths and weaknesses.
A performance report can also be used to benchmark your performance compared to your competitors. This lets you know where you’re falling short and could increase your competitive edge. But performance reporting can also monitor your workforce.
Performance reporting lets you build annual reports and stay compliant if your business is regulated by code and industry rules. But most companies use it to improve their business performance as well as create clear and effective communication.
You can execute and organized gathered data more effectively by using project management software. ProjectManager collects real-time data to make reporting more accurate. The live dashboard automatically calculates this data and displays it in easy-to-read graphs and charts that show project metrics such as time, variance and more. No configuration is necessary. ProjectManager gives you an instant performance report. Try it free today!
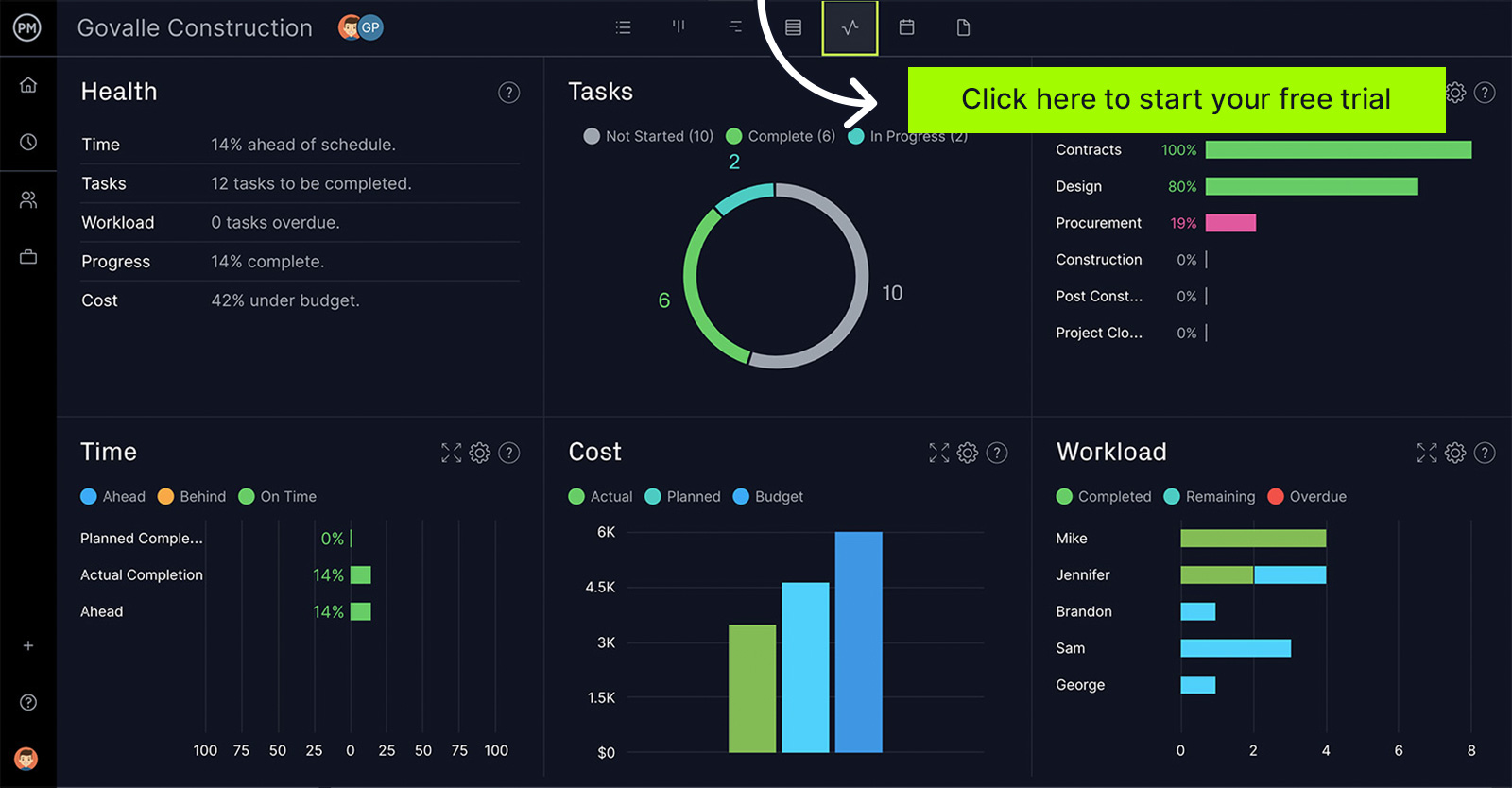
How to Implement Performance Reporting
Performance reporting can vary from company to company. However, in general, the process will follow similar steps. Use these tips to create your own performance report:
- Know Your Audience: Who is your target audience for the report? While executives are the most likely people you’ll deliver reports to, it will also impact the employees at the company. Depending on who the performance report is for, define whether it’s general or specific so that it will be useful for them.
- Define Objectives: The next step is to know what you want the performance report to do. What is the mission statement for your company or the goals and objectives of the project? This lets you evaluate and measure your performance to see if you’re meeting those objectives.
- Write an Executive Summary: The performance report will have a lot of data, which is why you want to start it with an executive summary that gives the reader a short overview of the details. This synopsis is important because it offers a clear and concise summary of the facts.
- Share a Performance Assessment: Here you detail the parts of the business or project that you’re evaluating. This can include the financial status of the company or project, industry comparisons and non-financial quantitative data.
- Make It Visual: Nothing puts people to sleep faster than a tombstone of text. Adding visuals not only pretty up the page, but also provides easily digestible data that can be understood at a glance.
- Don’t Forget to Proof It: Having spelling mistakes, grammatical errors or other typos will diminish the impact of the report and look unprofessional. It’s best to have another person proofread it, as they’re more likely to catch small errors.
Types of Reports
Use a performance report to compare the actual project to the plan. You can do this for various data points. The six common types of performance reports include the following:
- Project Status Report: Captures the state of the project at that point in its life cycle. A status report is a snapshot of the current scope, time, cost and quality of the project.
- Progress Report: Notes what has been completed in the project since the last progress report.
- Forecasting Report: Estimates what is expected to happen in a project, such as future performance and the expected status of the project at that time. This is used for better resource utilization.
- Trend Report: Compares the performance of the project against the same period in the previous report. This can be done monthly, quarterly, semi-annually or annually.
- Variance Report: Charts the difference between the actual vs planned progress of a project.
- Earned Value Report: Integrates scope, schedule and cost performance using earned value management techniques. This report is often part of the project status report.
Related: Free Status Report Template for Excel
How to Analyze and Act on Performance Reports
Once you have performance reporting set up for your organization or project, the next step is analyzing those reports and taking action. Managers tend to be the ones who are tasked with this job, though often it is outsourced to specialized analysts who understand business intelligence.
The data you need to analyze might be quantitative, such as sales and marketing outcomes, or qualitative, such as responses you get on customer surveys. Whatever type of data you’re analyzing, you need a structure to detail the process, beginning by setting goals and ending with an action plan.
It’s important that you determine a duration for your analysis, whether that’s a month, quarter or annual report on the project or company. This timeframe should be long enough for you to identify trends in the data. Having reports that can filter data that doesn’t pertain to your analysis is helpful.
When you review the data, look for what relates to the goal of your analysis. Next, identify and document the trends you see, especially what is most important and aligns with your analysis goals. Then, you’ll want to summarize the findings and develop an action plan to help you improve your performance.
How to Disseminate the Information
Once you’ve done all the work of performance reporting and analysis, you need to pass on that information.
The reports must be made public. Stakeholders are obviously going to have an interest in what the performance reporting revealed. But in order to make the necessary improvements that the data lead you to, your team must be informed as well.
The results of your performance reporting analysis should be tailored for your audience. Whether a memo, email or even a report on the report, you have to decide the best vehicle to deliver the data to your audience. In order to better enact your action plan, you might also want to call a meeting.
How ProjectManager Helps with Performance Reporting
ProjectManager is cloud-based software that tracks the progress of your project in real time. ProjectManager helps you organize tasks and resources to schedule your project. It also has features to measure performance and share that insight with your stakeholders and team to drive improvements.
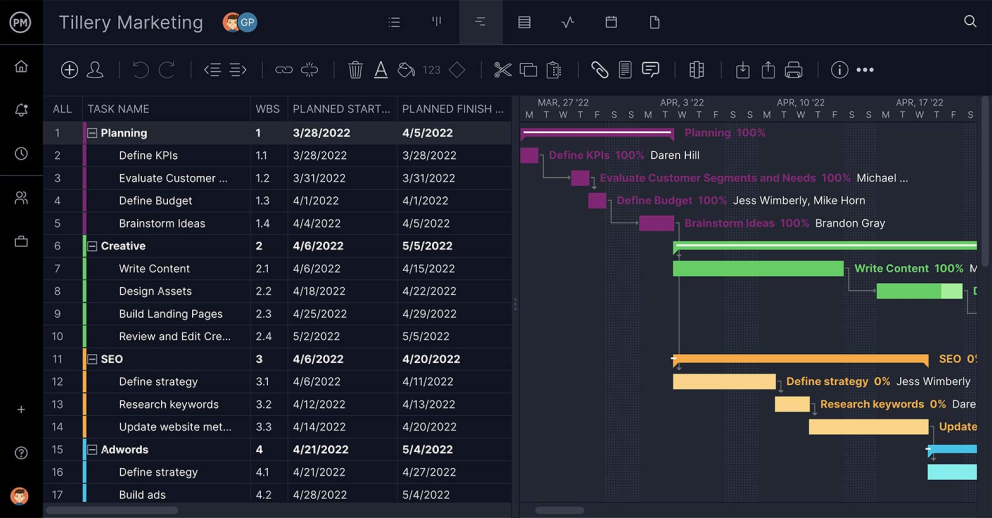
Create Project Schedules on Gantt Charts
Before you can measure performance, you need to set a baseline. When you’re creating a project schedule, ProjectManager’s Gantt chart lets you link dependencies, filter for the critical path and set a baseline. The Gantt will allow you to check the planned versus actual effort and create reports to measure the project variance.
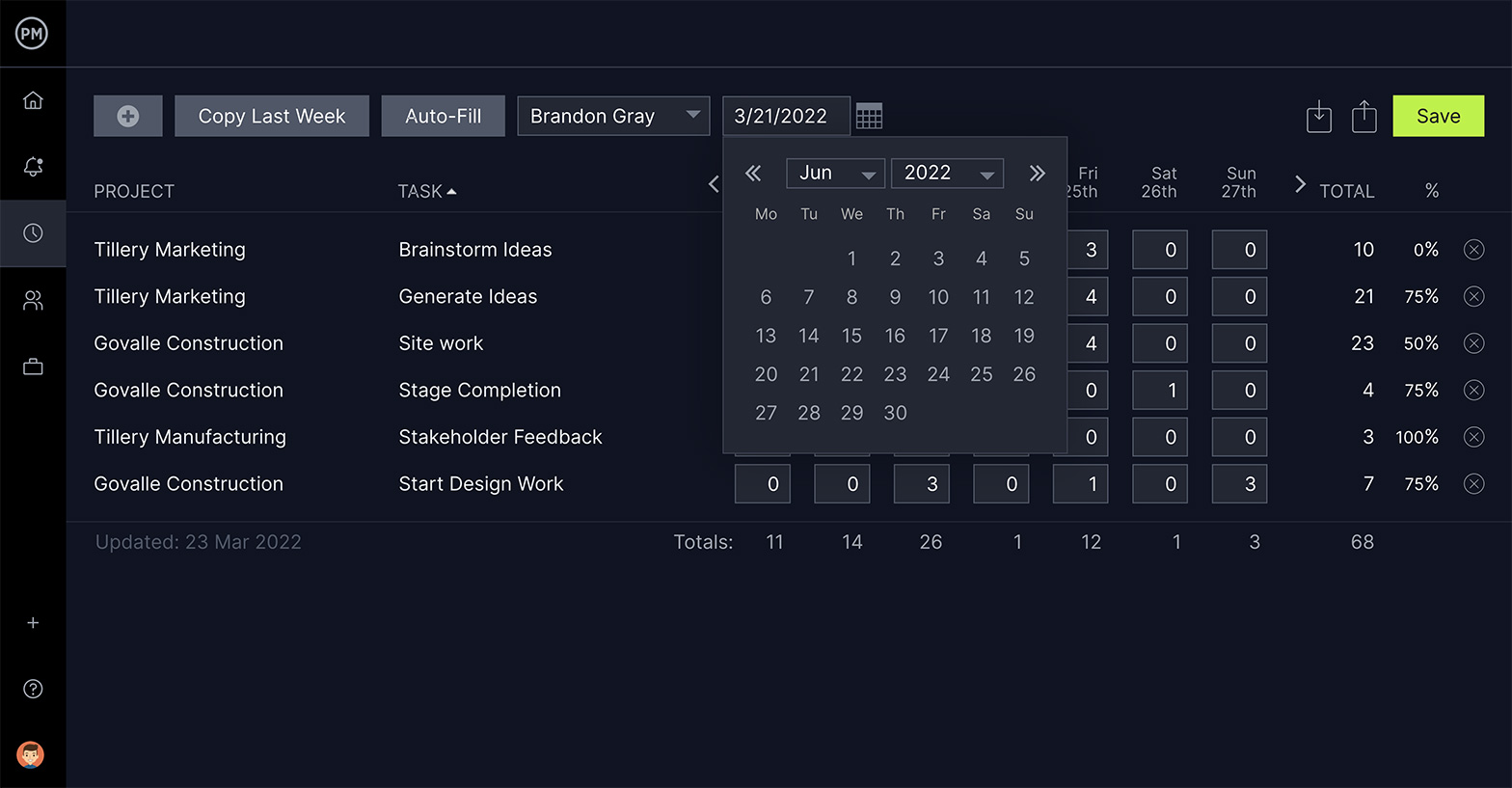
Track Time Accurately on Timesheets
If you’re measuring the performance of individual team members, ProjectManager’s secure timesheets give you data on how long it takes them to complete their tasks. Timesheets also can auto-fill repeating assignments and further streamline the payroll process, locking timesheets once they’re submitted for greater security.
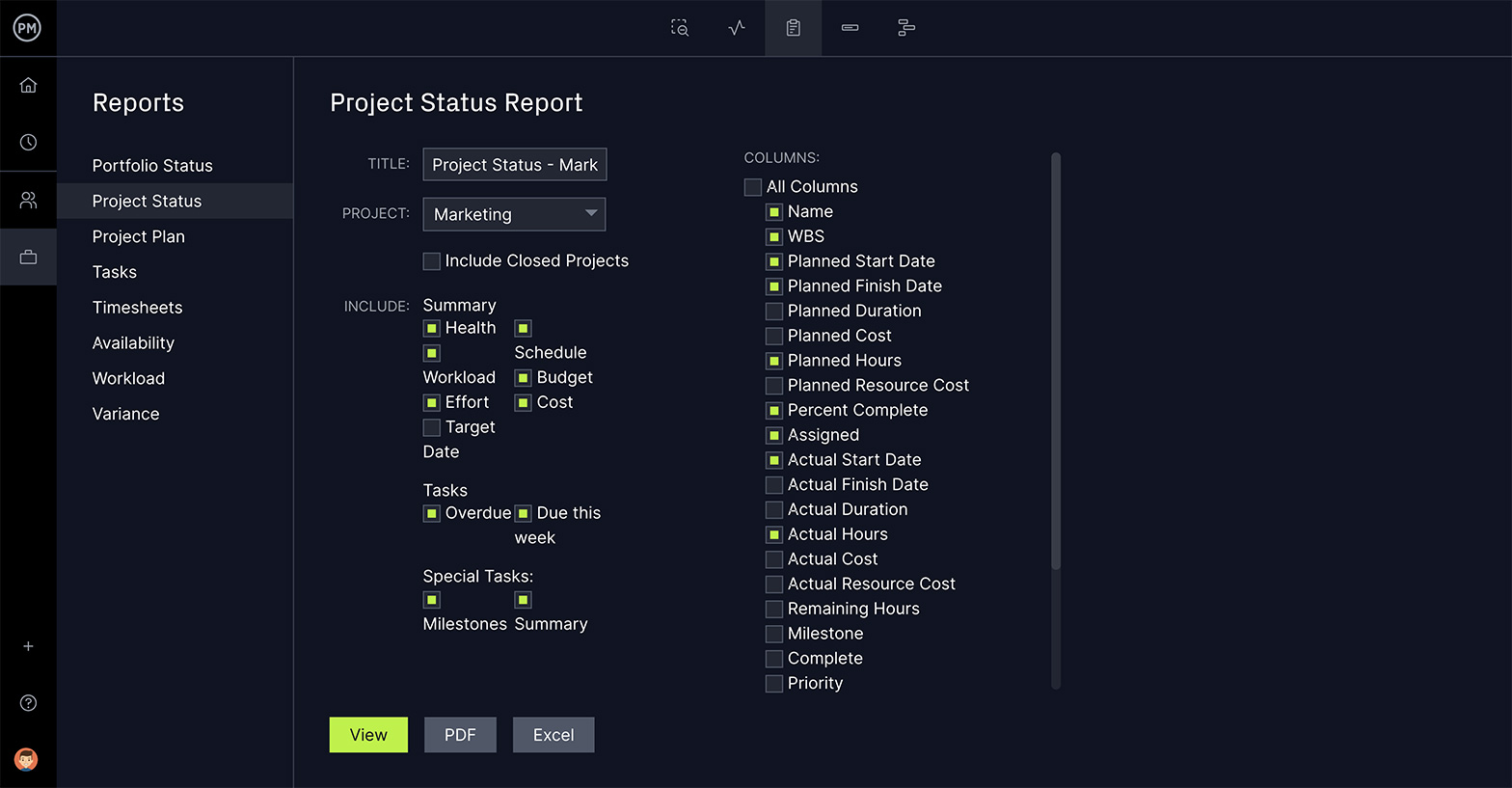
Create Performance Reports in Seconds
ProjectManager is also all you’ll need to create performance reports. You can generate status and portfolio reports, project plans, tasks, timesheets, availability, workload and variance. All our reports are customizable, filtering to see only the data you want, and can be saved as a PDF, Excel or CSV format to help you analyze and share the results with your stakeholders and team.
ProjectManager is award-winning software that plans, monitors and reports on project performance. Resource management tools keep teams working at capacity and with our multiple project views they can work how they want. Keep teams productive and projects on track no matter where or when with ProjectManager. Try ProjectManager today for free!

