- What Is the Critical Path In Project Management?
- What Is the Critical Path Method (CPM)?
- How to Calculate the Critical Path
- When Should You Use Critical Path Analysis?
- Free Critical Path Template for Excel
- What Is the Importance of CPM in Project Management?
- Critical Path Method Example
- Benefits of Using CPM in Project Management
- Disadvantages of the Critical Path Method
- CPM Training Video
- Finding the Critical Path with Project Management Software
- Must-Have Features of Critical Path Software
- How to Find the Critical Path with ProjectManager
- Critical Path Method FAQs
What Is the Critical Path in Project Management?
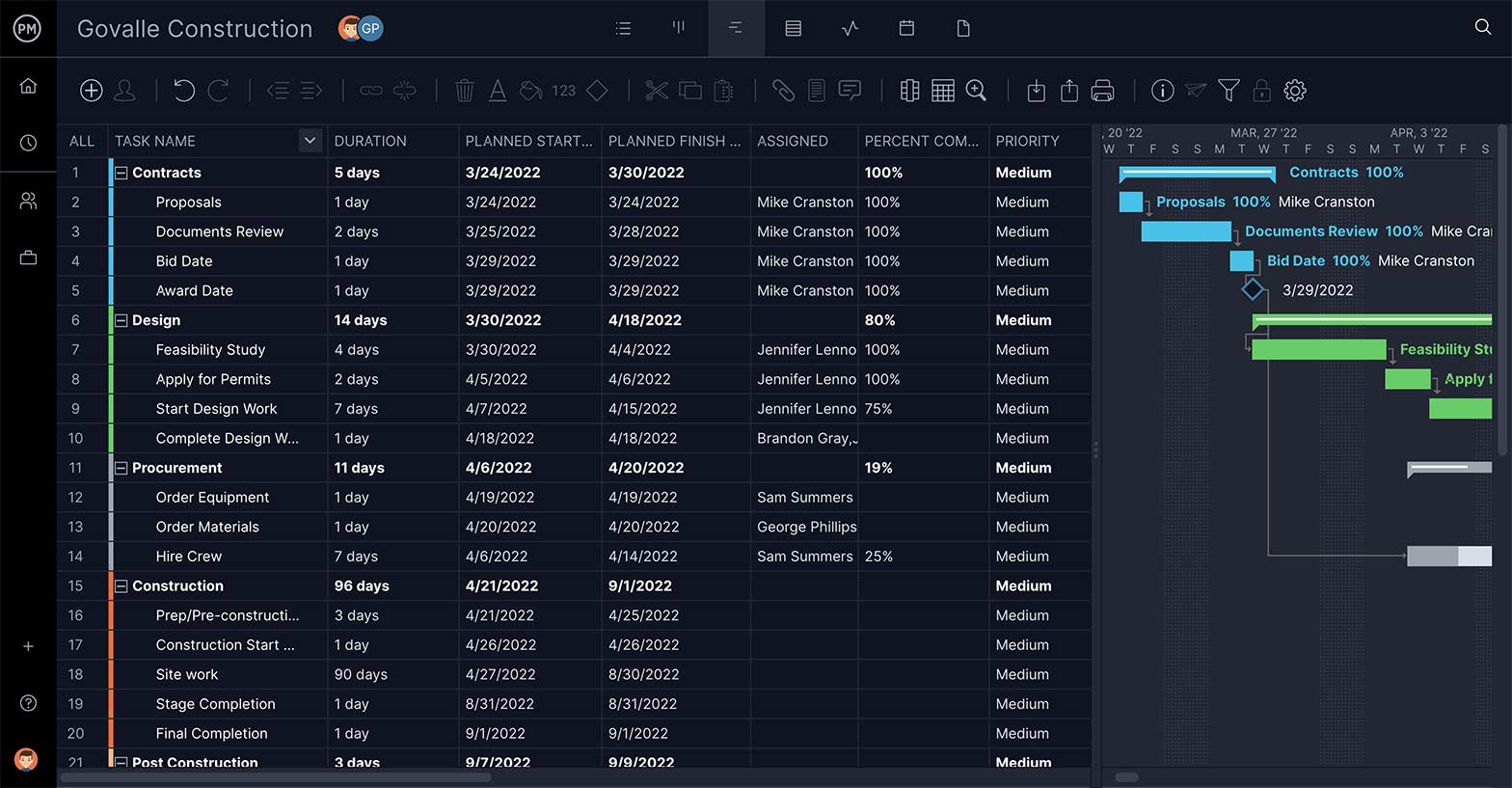
In most projects, there are at least two or more sequences of interrelated or dependent tasks that must be executed in parallel. The critical path of a project is the longest sequence of tasks that must be executed to complete a project.
The tasks on the critical path are called critical activities because if they’re delayed, the whole project completion will be delayed, unlike activities in non-critical task sequences which can be delayed without affecting the overall project timeline.
To find the critical path, project managers use the critical path method (CPM). Finding the critical path of a project is very helpful for project managers because it allows them to:
- Accurately estimate the total project duration.
- Estimate the time that’s necessary to complete each project task.
- Identify critical activities that must be completed on time and require close supervision.
- Find out which project tasks can be delayed without affecting the project schedule by calculating slack for each task.
- Identify task dependencies, resource constraints and project risks.
- Prioritize tasks and create realistic project schedules.
Once done by hand, the critical path can now be calculated automatically with project scheduling software equipped with Gantt charts, which makes the CPM method much easier. ProjectManager is project management software that helps you quickly implement the critical path method. Build a project schedule on our award-winning Gantt chart, then simply filter for the critical path. When it’s time to execute, your team can collaborate with a task list, kanban board or calendar. And you can track everything with dashboards and reports to ensure you stay on track. Get started today absolutely free.
ProjectManager can calculate the critical path for you on our award-winning Gantt charts—learn more.
However, before you learn how to use project management software like ProjectManager to automatically identify the project’s critical path, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the critical path diagram and CPM formulas. This allows you to better understand how to manage the critical path of your projects using project scheduling software.
What Is the Critical Path Method (CPM)?
The critical path method (CPM) is a project management technique that’s used by project managers to create an accurate project schedule. The CPM method, also known as critical path analysis (CPA) or critical path scheduling, consists of using the critical path diagram to visually represent the task sequences of a project. Once these task sequences or paths are defined, their duration is calculated using the critical path algorithm to identify the critical path.
Let’s zoom into each element to better understand how to implement the critical path method in project management.

Get your free
Critical Path Template
Use this free Critical Path Template to manage your projects better.
Get the templateCritical Path Diagram
A critical path diagram is a network diagram that depicts the order in which project tasks must be completed, their duration and when they’re expected to start and finish. This critical path diagram shows two distinct task sequences, but depending on the project, there might be more task sequences that need to be executed in parallel.
When making a project schedule, every project task has a start and finish time, which can be calculated by using the variables of the critical path algorithm, which are the earliest start time (ES), latest start time (LS), earliest finish time (EF), latest finish time (LF) and slack which are depicted in the critical path diagram example below.
- Earliest start time (ES): This is simply the earliest time that a task can be started in your project. You cannot determine this without first knowing if there are any task dependencies
- Latest start time (LS): This is the very last minute in which you can start a task before it threatens to delay your project timeline
- Earliest finish time (EF): The earliest an activity can be completed, based on its duration and its earliest start time
- Latest finish time (LF): The latest an activity can be completed, based on its duration and its latest start time
- Slack or float: The slack or float of a task, is a term that describes how long you can delay a task before it impacts its task sequence and the project schedule. The tasks on the critical path have zero float because they can’t be delayed
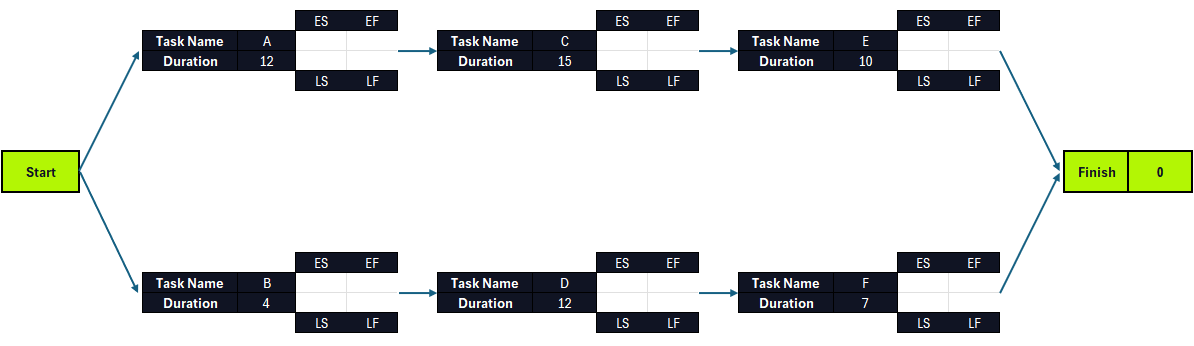
Critical Path Method (CPM) Algorithm
The critical path algorithm has two parts; a forward pass, which allows to find the ES and EF of each project task going from left to right and a backward pass, which is applied from right to left and allows project managers to calculate the LS, LF and slack or float of every task in a project schedule.
Forward Pass Critical Path Formulas
The ES of a project task is equal to the EF of its predecessor, and its EF is calculated by the sum of its ES and its estimated duration, by using the forward pass CPM formula EF = ES + t (where t is the activity duration).
The first step in the forward pass is to calculate the ES for the first task, which has no predecessor. In this case, the ES is zero and the EF is calculated by simply adding the duration of the task and its ES. So the formula for the first task is EF= 0 + t (where t is the activity duration).
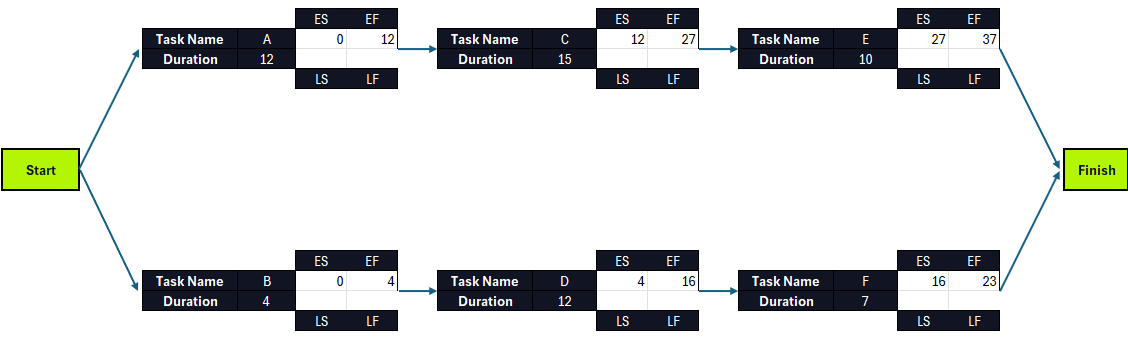
By completing the forward pass calculations, the ES and EF for all project tasks will be calculated. The activity with the largest EF identifies the expected time required to complete the entire project.
This is what a critical path diagram should look like after completing the forward pass. This example shows the largest EF value is 37, which is the estimated project duration.
Backward Pass Critical Path Formulas
The backward pass begins by using the largest EF for the last activity, the value that marks the time required to complete the project, as the LF for the activities is closest to the finish. To find their LS, the duration of those tasks should be subtracted from the LF using the formula: LS = LF – t (t is the activity duration).
The LF for all preceding tasks will be equal to their following task’s LS.
Then the backward pass helps to find the LS for all tasks from right to left, which is calculated by subtracting their estimated duration from the LF value with the formula: LS = LF – t (t is the activity duration).
Then, once the LS and LF values for all tasks are identified, the slack of each project task is calculated by this formula: Slack = LF- EF. This is one of the most important formulas in the critical path algorithm, as the activities with a slack value of zero will determine the project’s critical path.
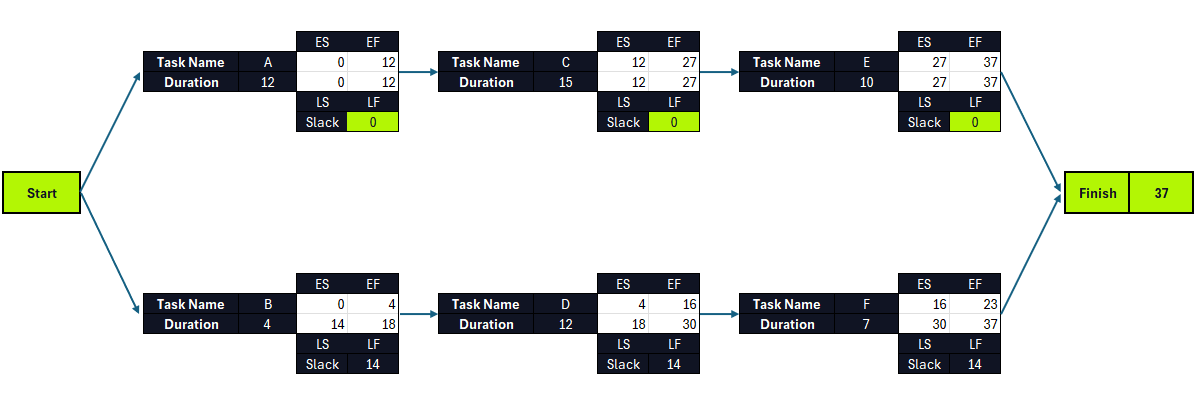
Once this is done, the critical path diagram should be completed, with all ES, EF, LS, LF and slack values, as shown below.
Now that we’ve defined the two key elements of the critical path method, let’s go through a step-by-step guide on how to calculate the critical path of a project.
How to Calculate the Critical Path
Now that you know the key concepts of the critical path method, here’s how to calculate the critical path in seven steps.
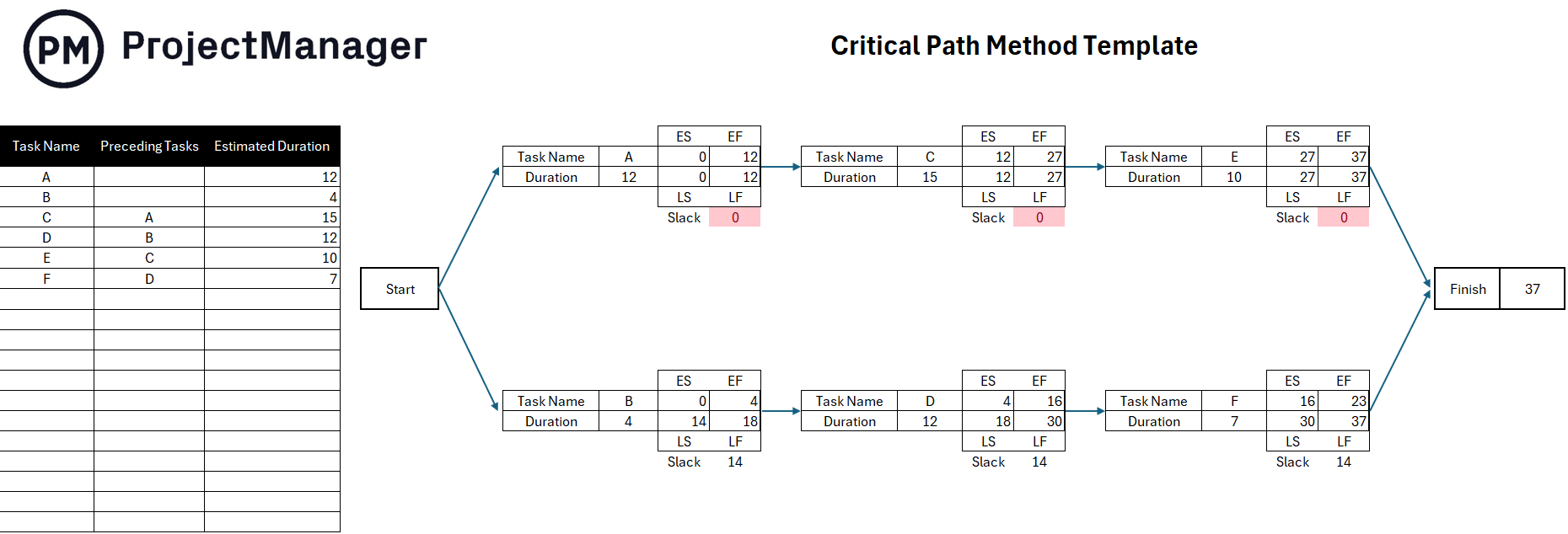
1. List Project Tasks and Estimate their Duration
Use a work breakdown structure to collect all the project activities that lead to the final deliverable and then make a task list that indicates their expected duration, which in this example is measured in days.
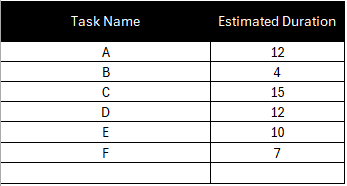
To estimate the duration of each task realistically, you should use data from past projects and other sources of information such as project team members and subject matter experts.
2. Identify Task Dependencies
Determine which tasks depend on the completion of other tasks before they can begin and add a “preceding tasks” column to the task list as shown below. Use your judgment and your team members’ feedback. This will determine how tasks are placed in the critical path diagram, which is why failing to define task dependencies correctly makes the critical path method useless.
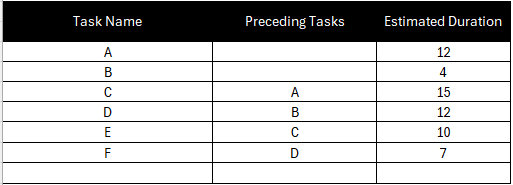
3. Create a Critical Path Diagram
The critical path diagram example below shows the tasks from the list, organized by their dependencies.

4. Use the Critical Path Algorithm Formulas
The next step is to calculate the ES, LS, EF, LF and slack using the critical path formula.
Forward Pass
Let’s start applying the formula to the first two tasks in the critical path diagram, tasks A and B. Because they have no preceding tasks, their ES equals zero. The formula for task A would be EF=0+12 and for task B would be EF=0+4, as we show below.
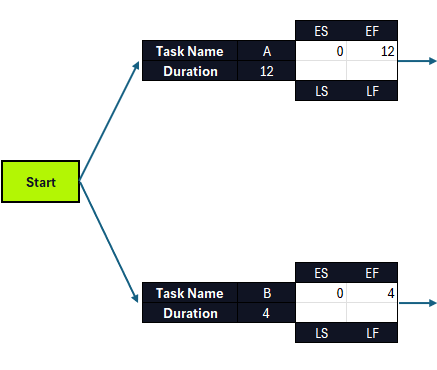
As stated above, the process of calculating the ES and EF for tasks C, D, E and F is slightly different, as their ES value is equal to the EF of their preceding task.
- Task C’s ES is equal to task’s A EF, which is 12
- Task D’s ES is equal to task’s B EF, which is 4
- Task E’s ES is equal to task’s C EF, which is 27
- Task F’s ES is equal to task’s D EF, which is 16
Then, their EF is calculated by adding their ES and duration. As explained above, the largest EF value belongs to task E, which determines the project’s overall duration. In this case, it’s 37 days.
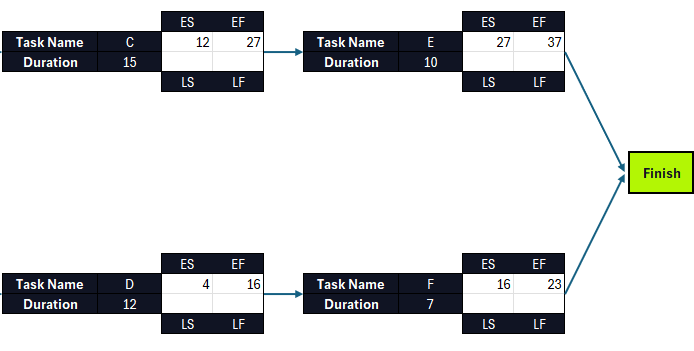
Once the ES and EF of all project tasks have been calculated, it’s time for the backward pass.
Backward Pass
To start the backward pass, we’ll need to assign an LF value to tasks E and F, which will be the largest EF of the critical path diagram, equal to 37 (task E’s EF). Then the next step is to calculate the LS for tasks E and F by subtracting their duration from the LF of 37 with the formula LS= LF – t.
- Task E LS= (37-10)=27
- Task F LS= (37-7)=30
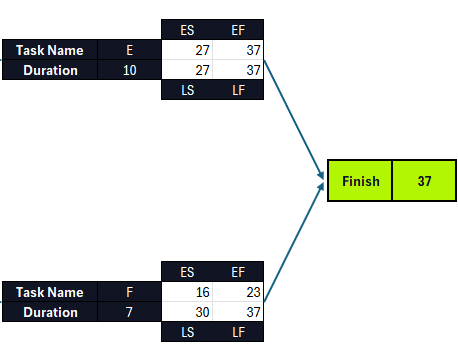
Now, the LF for tasks A, B, C and D will be the LS value of their following task LS and their own LS will be calculated with the formula LS= LF – t.
Once that’s completed, it’s time to calculate the slack for all tasks by using the formula: Slack= LF-EF
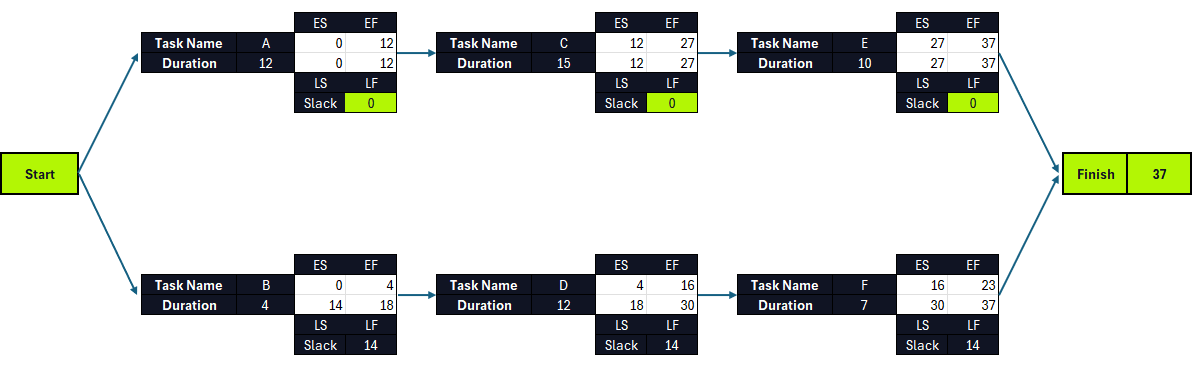
6. Identify the Critical Path
The activities with 0 slack or float make up the critical path, which in this case are tasks A, C and E. All of these critical path activities are dependent tasks except for the first task in your CPM schedule. All project tasks with positive slack are parallel tasks to the critical path activities. In this case, the slack value means they can be delayed for up to 14 days without affecting the timely delivery of this project.
7. Revise During Execution
Continue to update the critical path diagram as you go through the project execution phase.
These critical path analysis steps determine what tasks are critical and which can float, meaning they can be delayed without negatively impacting the project schedule. Now you have the information you need to plan the project execution plan and critical path schedule more accurately and have more of a guarantee you’ll meet your project deadline.
You also need to consider other changes or constraints that might change the project schedule. The more you can account for these unexpected events or risks, the more accurate your critical path schedule will be. If time is added to the project because of these constraints, that’s called a critical path drag, which is how much longer a project will take because of the task and constraint.
When Should You Use Critical Path Analysis?
Critical path analysis is another way of referring to the critical path method. As noted, it’s used by industries with complex projects, such as aerospace, defense, construction and product development.
Therefore, critical path analysis is a crucial first step in developing a project schedule. It’s done early in the life cycle of a project, usually in the planning phase, but it’s not unheard of to have CPM as part of a project proposal before the project has been approved.
By understanding which are the critical tasks in a project you can focus on getting those done in time, resources and costs are an issue. Knowing this in advance of executing a project will help you deliver that project successfully.
Free Critical Path Template for Excel
Need help getting started with a critical path analysis for your project? Download this free critical path template for Excel. All the formulas are embedded and the network diagram is made—all you have to do is input your values.
What Is the Importance of CPM in Project Management?
Projects are made up of tasks that have to adhere to a schedule in order to meet a timeline. It sounds simple, but without mapping the work, your project scope can quickly get out of hand and you’ll find your project off track.
Using the critical path method is important when managing a project because it identifies all the tasks needed to complete the project. It then determines the tasks that must be done on time, those that can be delayed if needed and how much float or slack you have.
When done properly, critical path analysis can help you:
- Identify task dependencies, resource constraints and project risks
- Accurately estimate the duration of each task
- Prioritize tasks based on their float or slack time, which helps with project scheduling and resource allocation
- Identify critical tasks that have no slack and ensure those are completed on time
- Monitor your project progress and measure schedule variance
- Use schedule compression techniques like crash duration or fast-tracking
Critical Path Method Example
Let’s take a look at a critical path example to better understand how the critical path method is used in project management. Although it’s high-level, it can help you visualize the meaning of a CPM schedule.
We’ll use this critical path diagram to explain the elements that make up the critical path analysis process. To keep things simple, we’ve already done the calculations for this example using the CPM formula.
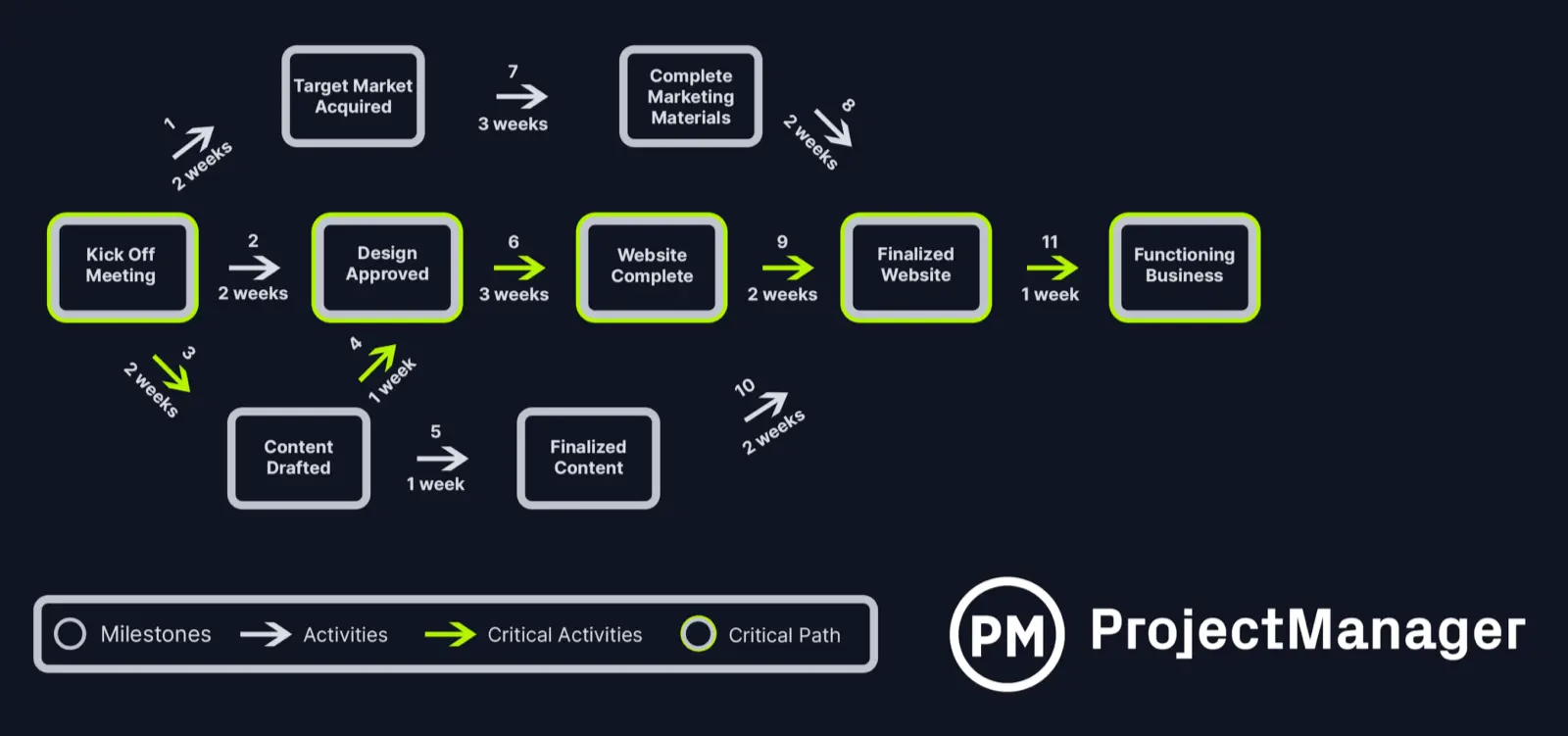
The above critical path method example shows the critical path for getting a website online. All the tasks that are scheduled to build and launch the website are shown in the rectangular nodes.
Some of the tasks are being done at the same time as others. For example, the work on defining a target market is being done as the design is being done and the content for the site is being drafted.
However, not all these tasks are equally important. Some aren’t critical to getting the site live by the deadline. That’s where the critical path comes in. It has identified by the colored arrows all the tasks that must be done to complete the project plan on time.
Benefits of Using CPM in Project Management
There are many reasons to use the critical path method. It’s a great project management tool to help you deliver your project on time and within budget, but we’ve already discussed that at length. Here are some other benefits of using CPM.
Critical Path Analysis Improves Team Communication
It fosters better communication within the project team. Everyone is involved in providing input and that brings the expertise of various project team members together for the better good of the project as a whole. This includes subcontractors, architects, electricians, construction managers, etc.
CPM Helps Prioritize Tasks
Naturally, having determined the critical path is going to help you prioritize your work. You know the tasks that must be done and that gives you wiggle room if there are issues with time or cost. You might not get every activity done, but you’ll get the ones finished that are critical to the project.
CPM & PERT Help Create Accurate Schedules
The critical path method will help you make a more accurate project schedule, especially when you use it in conjunction with PERT charts. You can estimate better and discover areas of risk and prepare to respond to them to avoid costly delays.
CPM & Gantt Charts Help Map Out Project Plans
Another benefit is the visual nature of CPM, especially when mapped on the timeline of a Gantt chart. Having a visual element to communicate the project schedule is always a plus. Not everyone absorbs information in the same way. Visual tools help teams better understand what’s expected of them and when it’s expected.
Disadvantages of the Critical Path Method
While the CPM method is a valuable project management tool, it comes with some downsides. It can be complex and time-consuming to use for complex projects that have numerous tasks and dependencies.
If the critical path needs to be re-evaluated, this process can be lengthy and overwhelming. It also often leads to rigid schedules so it’s harder to adapt to unforeseen circumstances. Sometimes, it results in an overemphasis on the critical path, which can lead to neglecting non-critical tasks.
CPM Training Video
Do you still have questions about the critical path method? In this video, Jennifer Bridges PMP, explains how to find the critical path using a CPM diagram.
Finding the Critical Path with Project Management Software
As stated, the critical path method (CPM) was first invented in the late 1950s. During those times, project scheduling software didn’t exist, and project managers had to calculate the critical path manually.
Fortunately, today many project management software alternatives can help with the critical path process. Most of them use Gantt charts to represent CPM diagrams and calculate the critical path, but their feature sets vary greatly. One of the most commonly used project management software to identify the critical path is Microsoft Project. However, it has major drawbacks that make ProjectManager a better choice.
Here are some of the main features that you’ll need as a project manager to properly use the critical path method for your scheduling process.
Must-Have Features of Critical Path Software
Link Tasks and Avoid Bottlenecks
Tasks that are dependent on another need to be a part of your critical path calculation. There are four types: those that are start-start, start-stop, stop-start and stop-stop. By identifying these task dependencies, you can avoid bottlenecks later in the project.
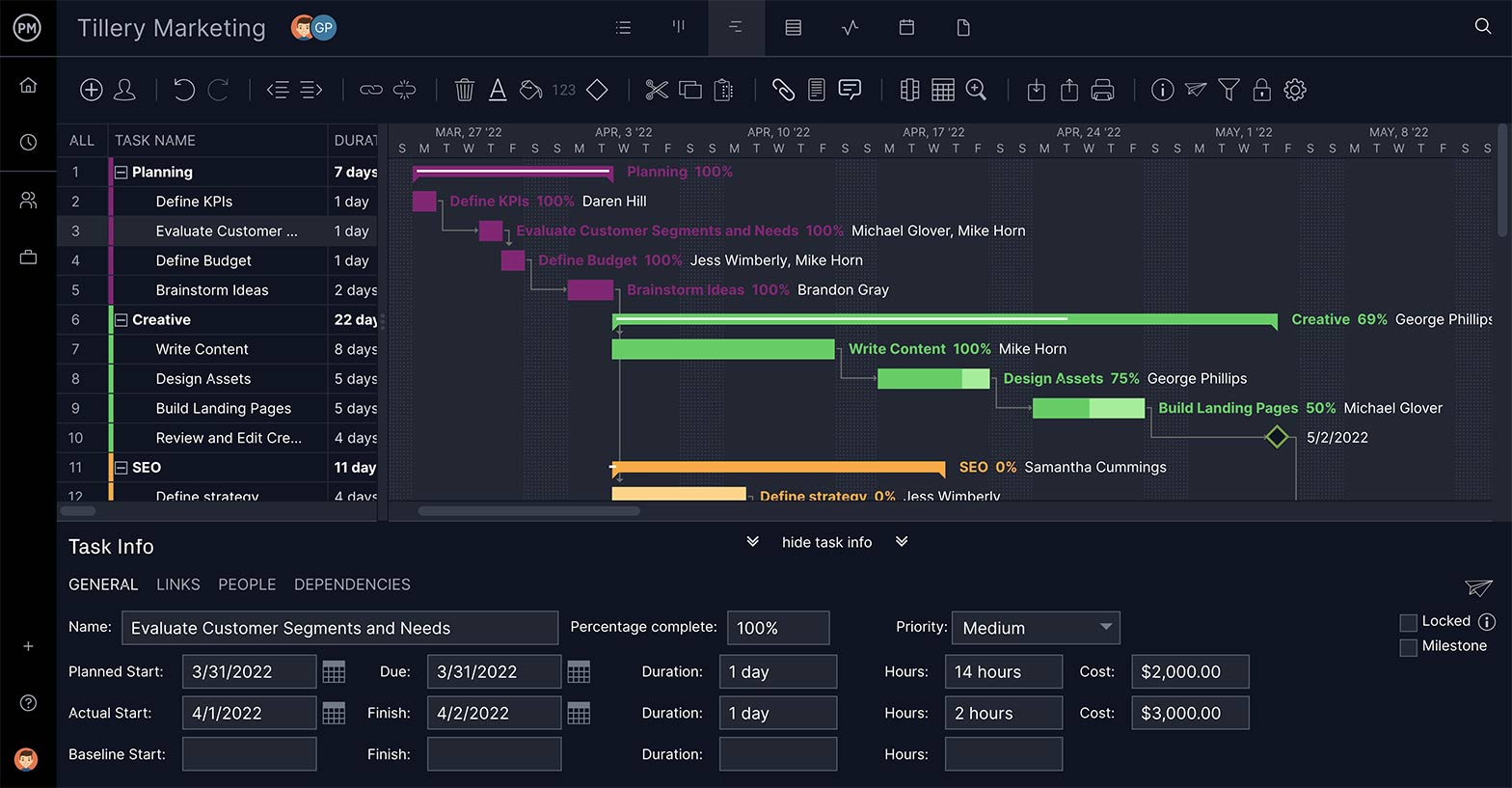
Get a High-Level View of Your Progress
Dashboards are an essential feature for keeping track of critical path activities. They provide a window into the project’s performance and progress by collecting data and displaying it in graphs and charts that show various metrics, such as costs, tasks and more.

Make More Insightful Decisions
Keeping track of a project’s critical path as it’s executed is how you stay on track. But if the information you’re gathering is dated, then you’re always going to be playing catch up. With real-time data from a cloud-based CPM software, you’re always seeing the project as it currently is.
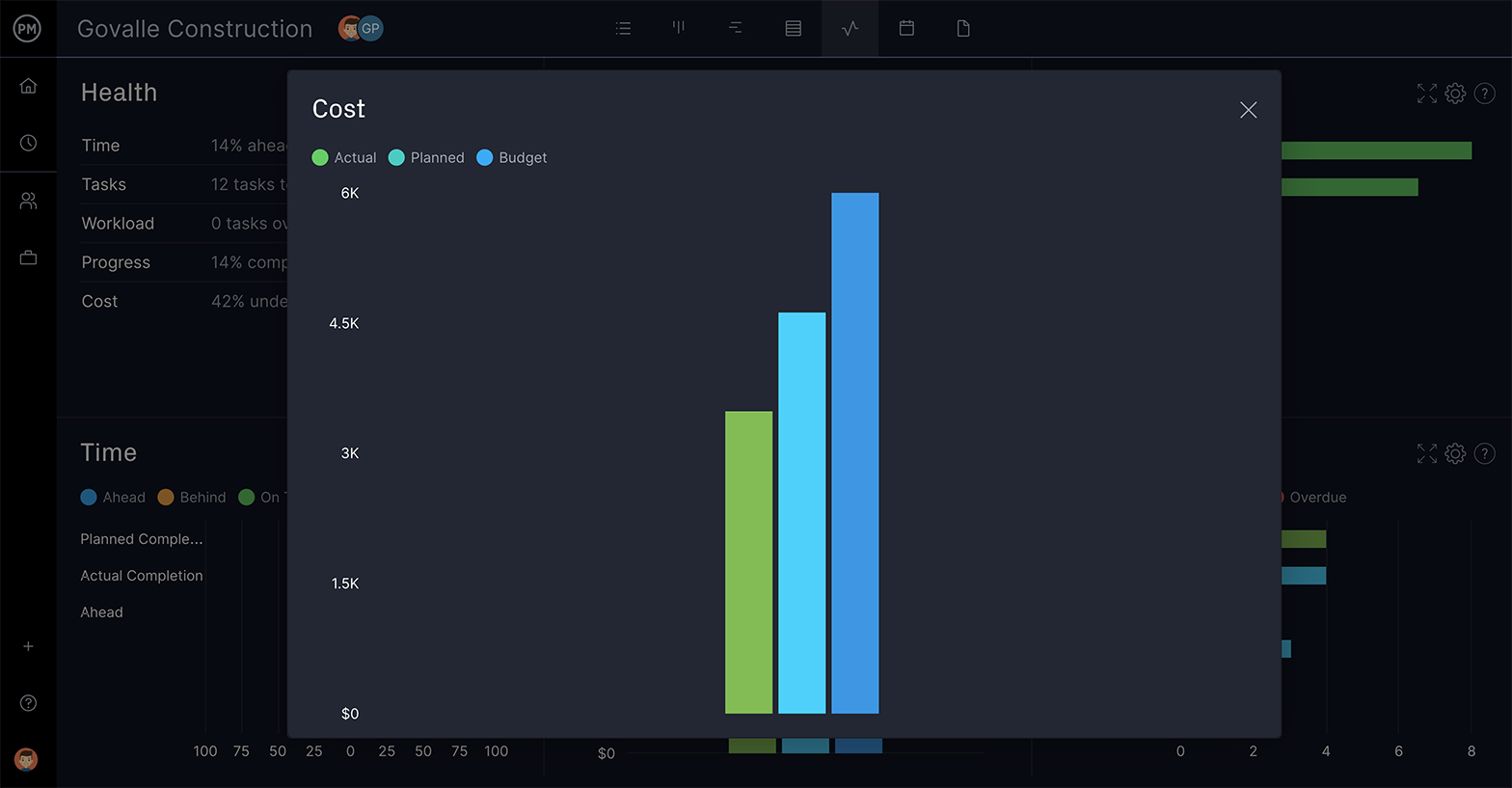
Know Your Project Variance
Schedules are always changing as the project is impacted by internal and external forces. To ensure you’re on target, you need to have project management software that’s collecting data and displaying project variance, so you can compare the actual progress against where you’ve planned to be.
Keep a Record of Your Plan
The critical path helps you plan the project, but once you’ve finalized the schedule, you need to set a baseline. This saves the schedule so you can compare it to your actual progress and know if you’re on time, behind or ahead. Any critical path software should have this feature.
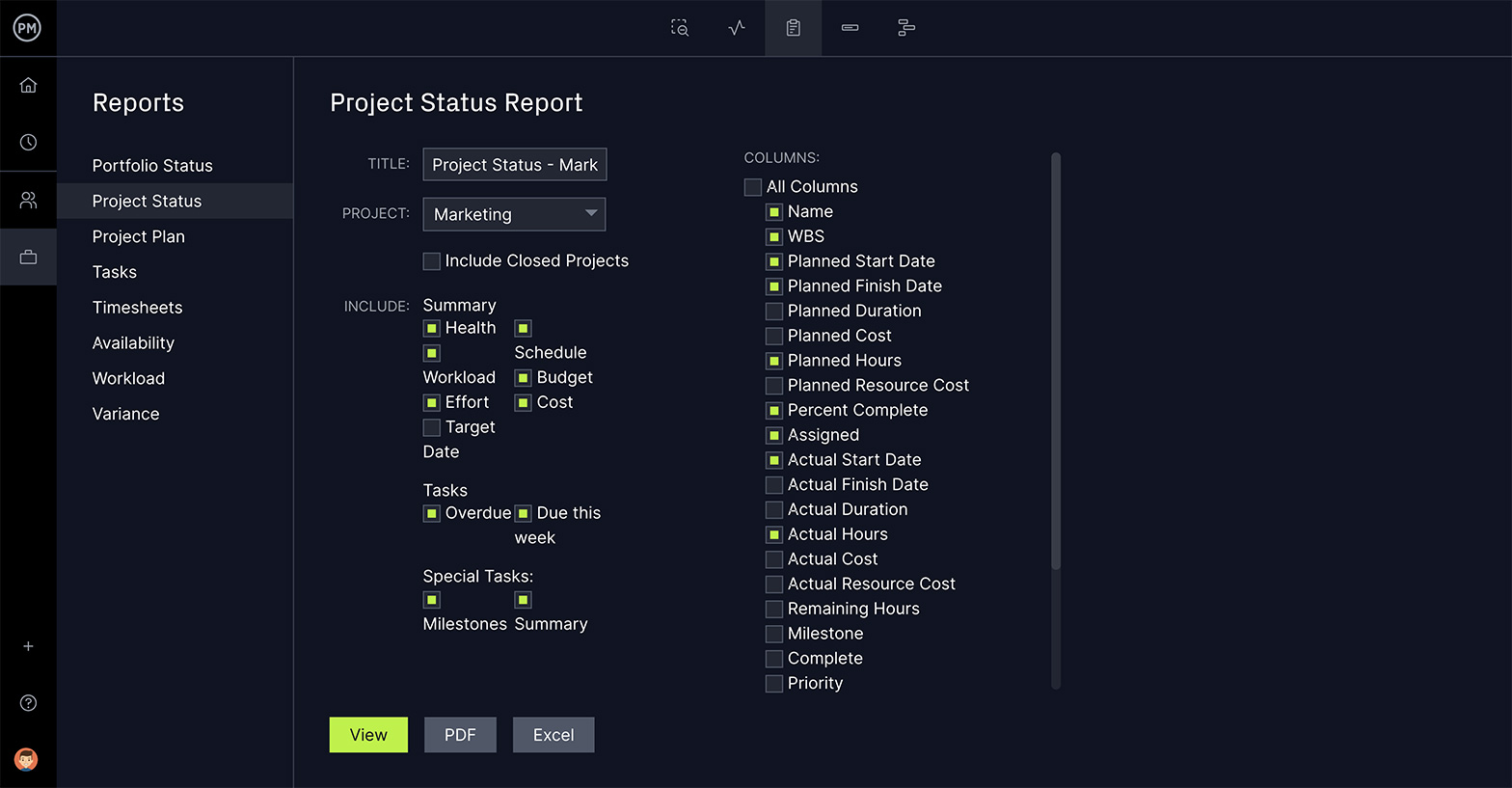
See Deep Data on Performance
Reports serve two purposes. They take you deeper into the project and expose insightful data on project variance, timesheets and more, which helps you stay on track. Filtering the results and sharing the reports is a great communication tool for stakeholder presentations.
How to Find the Critical Path With ProjectManager
Figuring out the critical path by hand takes time, and it must be done throughout the project, which is why using project management software streamlines the process. ProjectManager is award-winning software that automates the critical path method process for you.
Our online Gantt chart filters for critical path, links dependent tasks and is integrated into a full project management software. Sign up for a free 30-day trial of our software and follow along to build a dynamic Gantt chart and automatically calculate your critical path in a few easy steps.
1. Start a Project With a Gantt Chart
Managing a project on Gantt charts allows you to both plan and schedule in one place. Add your tasks and their durations, and they’ll automatically appear on a project timeline, allowing you to see your whole project at once.
In the software, upload your tasks manually or upload a pre-existing spreadsheet. Add task descriptions, deadlines, priority, tabs and assign them to one or more team members. We also provide templates to help you get started.
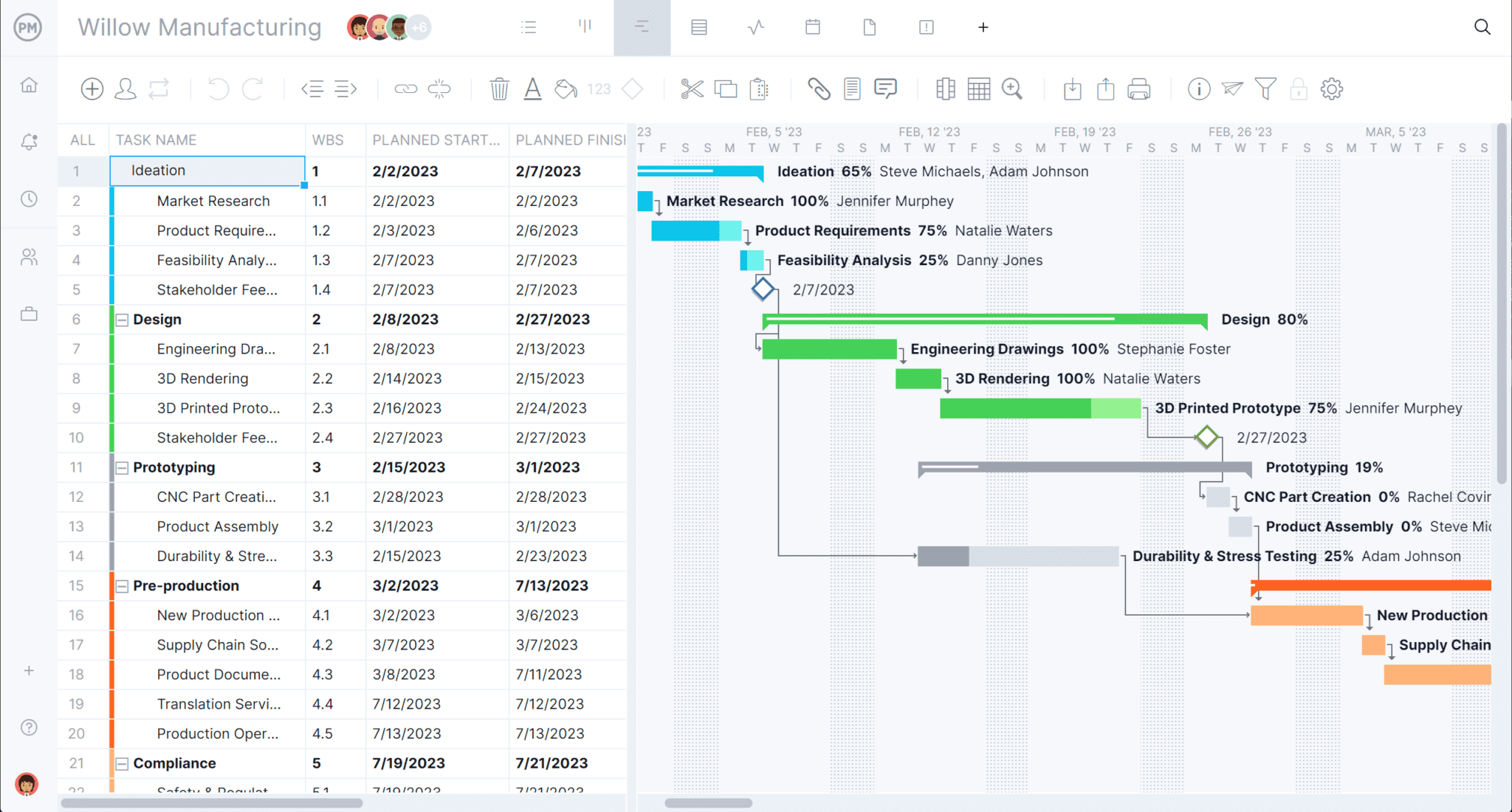
2. Add Task Dependencies
In the software, connect your dependent tasks on the Gantt chart by dragging one onto the other. You’ll see a dotted line indicating that the tasks are linked, and you can then define the type of dependency it is.

3. Set the Project Baseline
Setting the baseline is possible when you’ve finished making your project schedule, complete with deadlines and costs. The baseline captures your data and uses it to compare against your actual progress.
On the Gantt chart, create your baseline for the project by adding the start date to the task and when it’s due to be completed. These planned start and end dates will be compared to your actual project data and show you whether you’re on target.
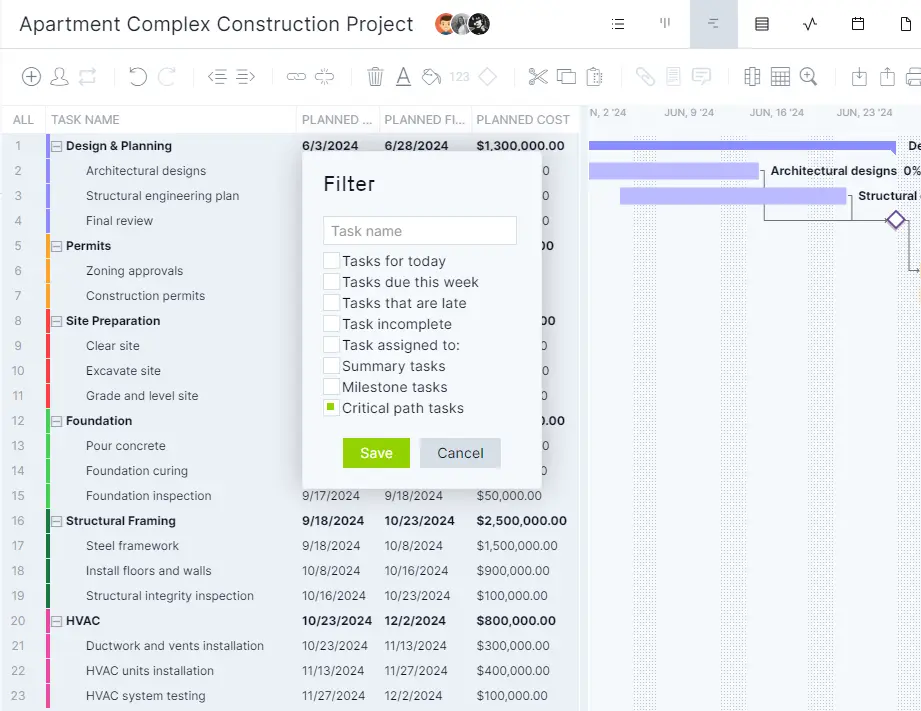
4. See the Critical Path
Easily find the critical path of your project by using our critical path filter. This helps you know what must be done to complete the project and shows if you’re experiencing any slippage.
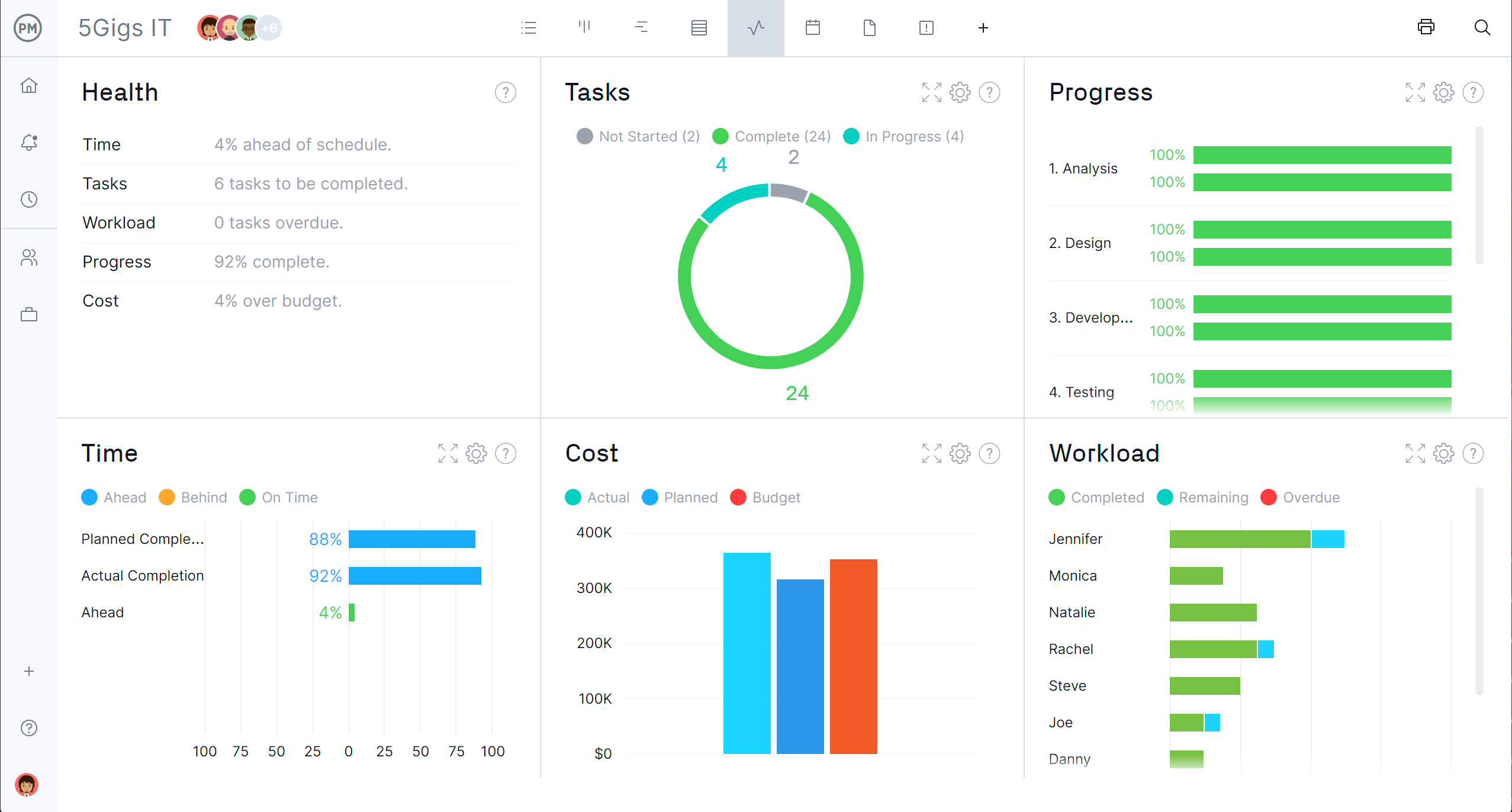
5. See Your Overview With a Dashboard
Now that you’ve got your project planned out, viewing it from a dashboard is the best way to get a high-level view of your progress.
From the dashboard view, track if your project is proceeding as planned. Our dashboard monitors several project metrics, such as variance, tasks and more, automatically calculating your data to display it in easy-to-read charts and graphs.
6. Report on Progress
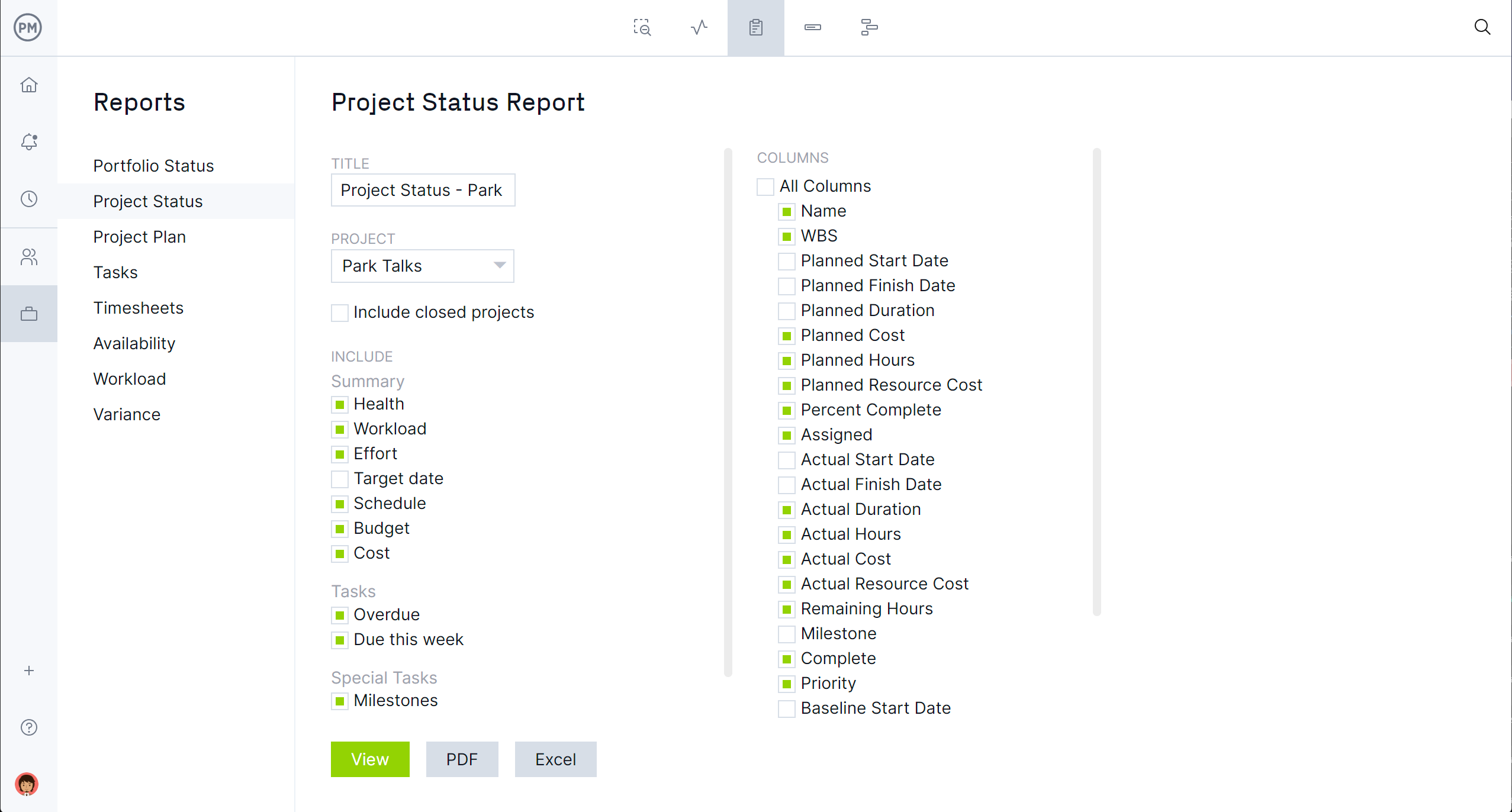
Reporting is crucial to pull data from your project and get and share insights into how it’s doing. Reports come in many varieties, which together provide a snapshot of the whole project’s performance.
Easily generate reports on the critical path, task progress, project status, costs and more in the software. We do the calculations for you, and you can filter the results to show just what you want to see. Our reporting feature is done automatically with one click.
Critical Path Method FAQs
The critical path method is dynamic and can come with many questions. We’ve highlighted only a couple of frequently asked questions below.
Who Invented the Critical Path Method?
The critical path method was developed in the late 1950s by Morgan R. Walker and James E. Kelley. The origins of the critical path method are closely related to the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT), a similar method that is commonly used in conjunction with CPM in project management.
What Is the Difference Between CPM and PERT?
The critical path method (CPM) and program evaluation and review technique (PERT) are both project scheduling techniques. But they aren’t interchangeable.
We’ve been talking about CPM, but before we compare it to PERT let’s define the term. PERT is used to get accurate time estimates for complicated projects.
It uses an algorithm to calculate the estimated duration for unpredictable activities by using an optimistic, pessimistic and most likely time estimates. It focuses on events and milestones on a PERT chart with nodes in the wireframe when developing projects.
Can PERT and CPM be Used Together?
While these are two different techniques, PERT and CPM can be used together for project planning and scheduling. The difference between them lies in that PERT is about time planning and time management, while CPM is about time and budgeting. PERT delivers a project quickly and CPM gets the project done on budget and on time.
Now that we know what’s the critical path of a project, we can learn about the critical path method (CPM), an important project management technique that’s based on this concept.
ProjectManager is an online tool that gets real-time data to determine how accurate your planned schedule is to the actual one, so you can adjust immediately if necessary. See how it can help your project by taking this free 30-day trial.
Critical Path Method Resources
Software
Templates
Articles
- How to Make a CPM Network Diagram Step-by-Step
- Top 10 Project Management Methodologies: An Overview
- 3 Free Tools for Making Network Diagrams
- Project Scheduling Guide
- The Ultimate Guide to Gantt Charts
- What Is a Work Breakdown Structure?
- PERT and CPM: Their Differences and How to Use Them Together
- Método de Ruta Crítica en la Gestión de Proyectos
- Méthode du chemin critique en gestion de projet
- Kritischer-Pfad-Methode im Projektmanagement (mit Vorlage)
- Método do caminho crítico: um guia rápido
External Articles
Start your free 30-day trial
Deliver faster, collaborate better, innovate more effectively — without the high prices and months-long implementation and extensive training required by other products.
Start free trial