Capital is money. In finance, capital is money that a company has, such as earnings or credit, which it can spend or invest on assets. Figuring out what to spend its capital on, such as capital spending on long-term assets, is part of capital budgeting.
First, we need to define capital budgeting, what a capital budget is and why it’s important. Then we can go through the capital budgeting techniques and the steps to a capital budgeting process. Finally, we’ll illustrate capital budgeting with some examples.
What Is Capital Budgeting?
Capital budgeting is a process by which investments in large-scale projects are analyzed, evaluated and prioritized. These are investments of significant value, such as the purchase of a new facility, fixed assets or real estate.
The use of capital budgeting offers an objective view that helps managers figure out how to invest capital in order to increase business value but also helps the overall health of the company. It’s used across industries and in small to large businesses.
Capital budgeting is part of the larger financial management of a business, focusing on cash flow implications when making an investment decision. Managers will look at how much capital will be spent for a purchase against how much revenue can be generated by the increased output directly related to the purchase.
Two concepts that underlie capital budgeting are opportunity cost and the time value of money, both of which address the long-term nature of most capital projects. Opportunity costs are the benefits lost because of investment decisions and important to consider when capital budgeting. The time value of money is about the potential rate of return on the investment as well as the reduced purchasing power over time due to inflation.
Whatever capital budgeting decisions one makes, project management software can help track those costs. ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that tracks capital budgets in real time. Managers can toggle over to our live dashboard whenever they want to get a high-level overview of their capital budget. Our dashboard captures real-time data including costs and displays them on easy-to-read graphs and charts. Unlike lightweight alternatives, there’s no time-consuming setup. It’s ready when you are.
What Is a Capital Budget?
A capital budget is how a business makes decisions on its long-term spending. Capital budgets can help a company figure out which improvements are necessary to stay competitive and successful. Also, as noted, a capital budget tries to predict the depreciation and reduced lifetime value of those investments, which can be anything from buying a new office building and equipment to a major upgrade to existing equipment or purchasing intangible assets, such as copyrights or customer lists.
What Is the Importance of Capital Budgeting?
Capital budgeting is important as it provides businesses with a way to evaluate and measure a project’s value against what they have to invest in that project. This way, managers can assess and rank those projects or investments, which is critical as these are large capital investments that can make or break a company.
Therefore, capital budgeting allows decision-makers to analyze potential investments and evaluate which is the best to invest in. These tend to be large investments, as noted, but also projects that can last a year or more, which is another reason why making a reasoned decision is so important. Businesses don’t want to lose money or spend time on a lost leader.
The process of capital budgeting helps managers create a budget for the project’s costs, estimate a timeline for the project’s return on investment and decide if the potential value of that project is worth the capital investment. But even after investing, capital budgeting can be used to measure the project’s progress and how effective the investment is.

Get your free
Project Budget Template
Use this free Project Budget Template to manage your projects better.
Get the Template
Capital Budgeting Techniques
There are several capital budgeting methods that a company can use to help them value and evaluate the capital project. The following capital budgeting techniques can help decision-makers remove projects that don’t meet their minimum performance threshold and provide a comparison to rank one project against the others.
Payback Period
This is a method used to quickly recoup one’s capital investment by comparing the initial cash outflow to the subsequent cast inflows to figure out the point in time at which the project will have paid for itself. It has nothing to do with the value of the project, but the timeframe of the return on investment. Therefore, shorter payback periods are better than longer ones. It’s a simple method, but isn’t a complete model and ignores profitability and terminal values.
Net Present Value
When looking at the net present value of a project, you’re viewing the excess of cash inflows beyond cash outflows, adjusting both streams for the time value of money. This results in a positive or negative monetary value, positive adding value and negative reducing it. The larger positive value is a better investment.
Internal Rate of Return
Use this capital budgeting technique to find the discount rate that’ll bring a project’s net present value to zero. That is, the internal rate of return generates a yield percentage on a project instead of a dollar value. Capital projects that have a higher internal rate of return are usually the better investment.
Throughput Analysis
This complicated method is also very accurate. Throughput analysis looks at the entire company as a sign profit-generating system, with the throughput being the measured amount of materials going through the system. In this technique, all costs are operating expenses. Therefore, maximizing the throughput maximizes profits.
Profitability Index
The profitability index calculates the cash return per dollar invested in a capital project. This is done by dividing the net present value of all cash inflows by the net present value of all the outflows. If the project has a profitability index of less than one, it’s usually rejected. However, projects with an index greater than one are ranked and prioritized.
Constraint Analysis
Constraint analysis is used to select capital projects based on operation or market limitations. It looks at company processes, such as product manufacturing, to figure out which stages of the process are best for investing. It also identifies bottlenecks that would deter the investment.
Capital Budgeting Process
There are various ways a company will execute the capital budgeting process. Larger companies have a committee dedicated to this process while in smaller companies the work usually falls to the owner or some high-ranking executives and accountants. However you do it, keep in mind your company’s strategic goals and then follow these steps.
1. Gather Project Proposals
First, you’ll want to review the various project proposals and investment opportunities. Look at the expected sales, keep an eye on the external environment for new opportunities, keep your corporate strategy in mind and do a SWOT analysis. Also, ask your employees for suggestions.
2. Determine the Feasibility of the Project
At this point, you’ve found a project and you want to evaluate it. Conducting a feasibility study is a good idea. It’ll establish the feasibility of the project in technical, financial, market and operational ways.
3. Conduct a Cost Benefit Analysis
Capital budgeting is basically a larger cost-benefit analysis, but you’ll want to do one for the specific project you’re considering. It will basically note whether the project is worth the investment. That is, will it return on the investment either through financial or other beneficial ways?
4. Evaluate Project Proposals Using Capital Budgeting Techniques
We’ve talked about many capital budgeting techniques and these powerful tools should be applied at this step to help decision-makers choose the right investment or project.
5. Select the Best Project
Using the methods above, you can rank the projects and choose the one that potentially has the greatest benefits to the organization. Of course, one of the most important of those benefits is which project will prove most profitable.
6. Execute the Project
Once chosen, the project will be implemented. Project management software will help to plan, manage and track the project to ensure that it is delivered on time and within the budget.
7. Track Project Costs, Budget and Performance
When executing the project, managers must monitor the work. They need to keep a close eye on project costs and the budget, the performance of the project and the team executing it as well as the time to ensure that it’s delivered on schedule. Again, project management software has features to do this.
Examples of Capital Budgeting Decisions
We’ve already written about some examples of capital budgeting, but just to make sure we’re clear on the topic, here are a few more. For example, not only investing in equipment, but new technology can be a capital investment. Maintaining existing equipment and technology is also an example of capital budgeting. You can make a capital investment in renovations to existing buildings or expanding the workforce, expanding into new markets and much more.
How ProjectManager Helps With Capital Budgeting
Project management software can help manage the projects that companies invest their capital in. ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that can help these companies better deliver those projects on time and within budget. Our powerful features help plan, manage and track those projects in real time.
Plan Projects With Multiple Project Management Tools
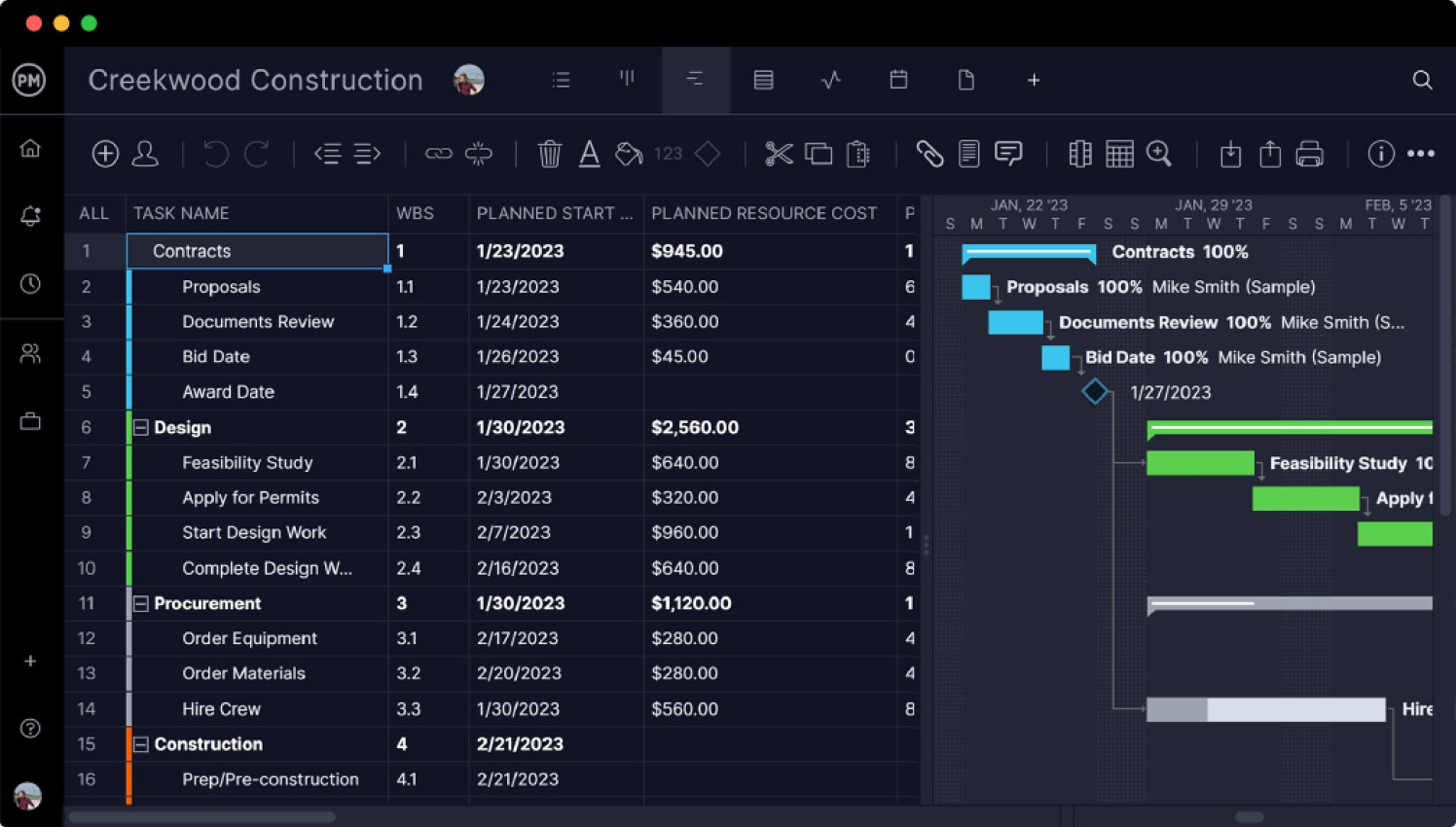
Our multiple project views allow managers to plan and team to execute projects with the tools that they’re most comfortable with. For example, managers can organize tasks, costs and timelines on our robust Gantt charts, which link dependencies, filter for the critical path and then set a baseline to capture that plan and compare it to your actual progress in real time. Meanwhile, the same data is shared on the visual workflow tools of our kanban boards, powerful task lists, sheet and calendar views for teams to execute their tasks and stakeholders to stay updated on progress.

Keep Stakeholders Updated With Customizable Reports
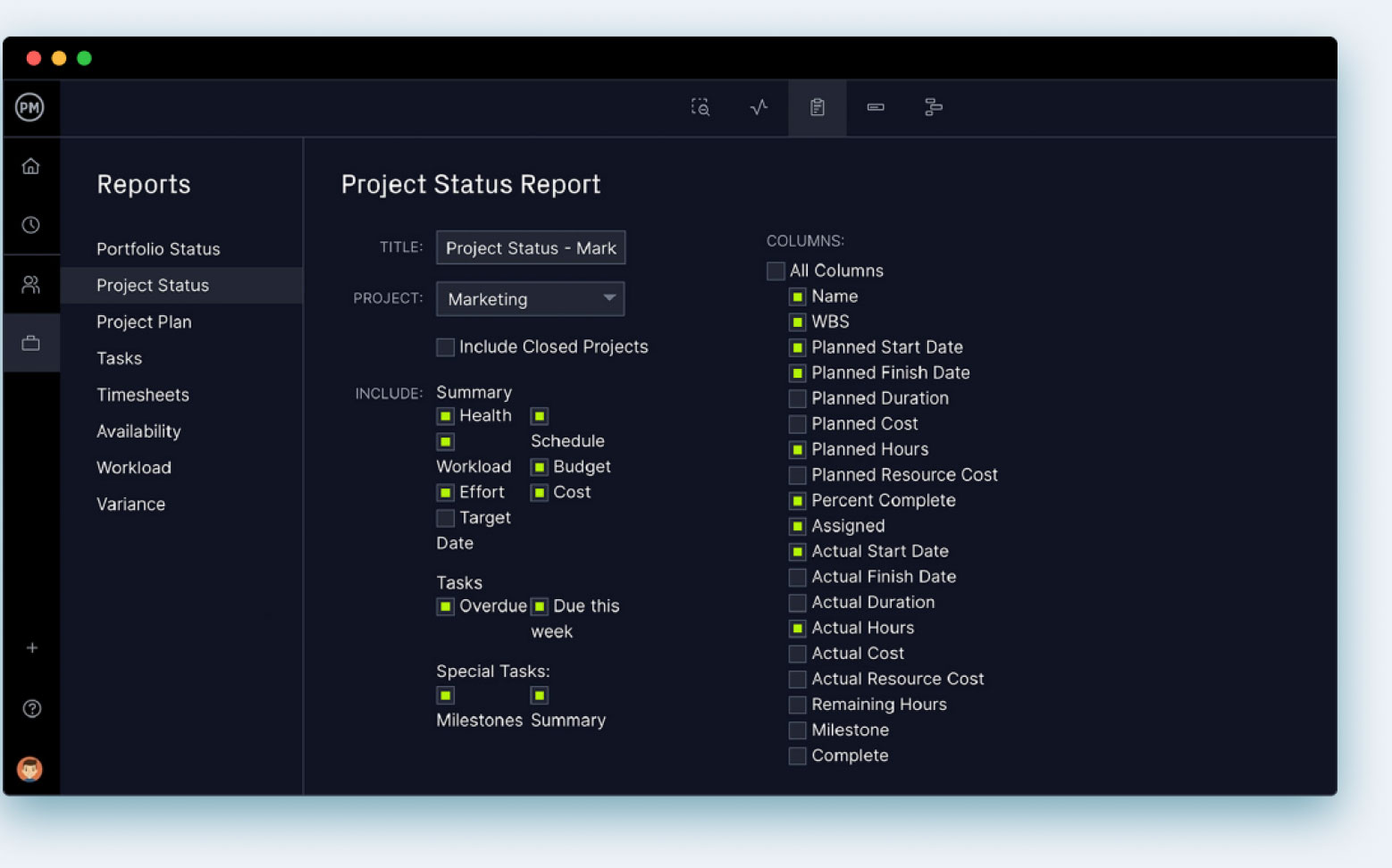
We’ve already explained how the real-time dashboard can provide you with instant access to the progress and performance of your project. But it’s only a high-level overview. If you want to dive deeper into that data, then you’ll use our customizable reports. You can easily generate status reports or portfolio reports to review more than one project at a time. There are also reports on tasks, variance, workload, timesheets and other metrics to help you monitor and manage your project. Plus, all reports can be filtered to show only what you want to see and then shared with stakeholders to keep them updated.
Of course, managing costs is only a small part of what our software can do. Use our online tool to manage project risk, keep teams working more productively with task management features and manage resources to always have what you need when you need it. We’ll help you get that return on your capital investment.
ProjectManager is online project management software that connects teams in the office, out in the field or even at home. They can share files, comment at the task level and much more to foster greater collaboration. Join teams at Avis, Siemens and Nestle who use our software to succeed. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.