You know how it goes—you’re a few months out from a deadline, and your team isn’t anywhere close to finishing the project. You’re quickly running out of budget and time, and you’re starting to stress. Should you tell the stakeholders, or wait a little bit longer?
Well, you’re not alone at least, as this situation happens to more than 45 percent of all large-scale IT projects. For many, this comes both as a detriment to a project’s timeline and to the final product, with 56 percent of projects delivering less value than anticipated. Yikes. How can you stop this from happening? A cost management plan can help.
What Is a Cost Management Plan?
A cost management plan is a method of strategizing the planning and execution of a project’s budget. Of course, this is done in order to complete your project on time and on budget. However, without a proper cost management plan in place, both of those things will falter—costing you and your organization immensely.
What’s more, project success hinges on cost management, as cost is the primary determining factor for the success or failure of the venture overall.
Because a cost management plan is so important, you need to use project management software in order to track your costs. ProjectManager is a cloud-based work and project software that can track your project costs in real time. Build your plan on our award-winning Gantt chart, then track it with a live dashboard that requires no setup. You’ll always know if you’re meeting the cost management plan with ProjectManager, so get started today for free!
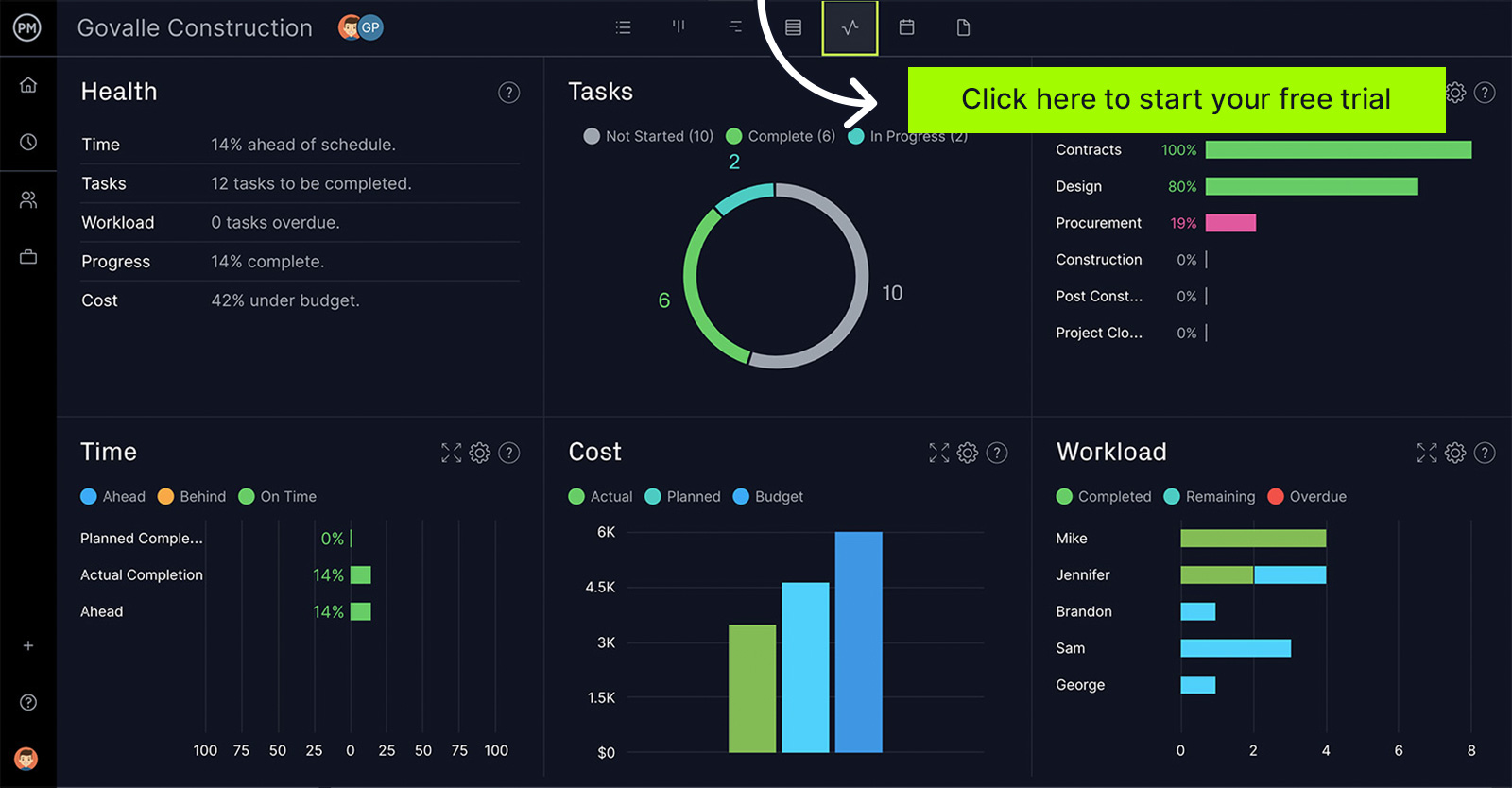
How to Create a Cost Management Plan
Cost management is sometimes also known by its more specific sub-task names, like spend management, cost transparency and cost accounting. It is typically made up of four steps: resource planning, cost estimation, budgeting and cost control. It’s strongly recommended that you use project planning software to assist you in the process of creating a cost management plan, as there will be many tasks, costs and resources to track.
1. Resource Planning
Starting with the resource plan, project managers will typically use a work breakdown structure to show the project and its deliverables in a hierarchy from most important to least. This piece helps project managers to understand where the bulk of the costs will funnel towards, and which components of the project will require the least expenditure.
2. Cost Estimation
The second stage, cost estimation, is a process that’s iterative—meaning that it’s designed to change as the project changes. This stage uses many different estimation techniques that are determined by conceptual goals, historical knowledge, expert judgement, determinative techniques or a component-by-component basis.
Get your free
Project Estimate Template
Use this free Project Estimate Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
Historically-speaking, determinative techniques have been shown to be the most accurate. However, this process only makes sense to use once every last project detail has been mapped out—including the scope and deliverables. For projects that are lacking fine print, less accurate cost estimation techniques will still be valuable during this stage.
3. Budgeting
Now, the cost estimation phase might have felt like you mapped out your budget already, but really you just mapped out the blueprints for your budget. Your project budget will be a little more precise by this measure, and will enable the project to truly succeed.
Budgets are formed and approved after the estimation phase, and are typically released for the project in a series of phases depending on the project’s progress. This will help the project reach its milestones within each budgetary phase, rather than trying to match an overall project budget.
4. Cost Control
Cost control is simple—you’ll measure your project’s dollar value performance against your total cost and timeline. This will help provide a benchmark throughout the project process.
First, your requirements are established well in advance, during the project planning phase. Then, they are used as a method to challenge reasons for changes in cost. This will help to course-correct should a cost increase out of budgetary range and keep the project from ballooning out of control.
Ultimately, your cost management plan will help you to both plan for the project cost, and manage your project cost throughout the course of the project’s life cycle. As your project is underway, your project expenses will be thoroughly documented throughout the project so that your project can stay within budget.
Cost Management Plan Terms and Formulas, Defined
In mapping out your cost management plan, you’ll need to do a lot of different calculations, practice many formulas and triple check your math when you’re done. But that being said, these actions go by many specific names. Let’s define them.
- Work Breakdown Structure: Similar in style to the waterfall method or a simple hierarchical flow chart, this is a product-oriented layout of work, tasks and activities to be done by the team members.
- Cost Baseline: This is created by estimating your costs against the general time period that your project will take place. Your cost baseline is ultimately what you’ll use to compare your performance, usually illustrated on an S-curve.
- Control Threshold: Just as you set your baseline, your cost threshold is the highest or lowest spend your project is allowed to go. Anything above or below that is deemed unacceptable in terms of cost management.
- Level of Precision: This unit of measurement will show how steep your cost estimates will be rounded down or up. Your level of precision will additionally be defined by the scope and total size of your project.
- Earned Value Measurement: The earned value equation helps project managers to better measure the amount of work that has already been performed on said project as accurately as possible.
- Three-Point Estimation: Using this formula, you’ll get three figures. The first would be your best guess (BG) on the amount of work an activity would take if it was performed 100 times. The second would be your pessimistic (P) estimate, which is how long the project would take and how much it would cost if all the negative risks occurred. And your third is your optimistic (O) estimate if all of the positive risks occurred.
- Bottom-Up Estimation: This formula involves using the smaller estimates of your project, and then aggregating those into a sum total to determine your overall project cost estimate.
- Analogous Estimation: This estimate is calculated by comparing all past projects’ cost estimates and measuring them against your current project’s time and cost. This is typically done when there are few project details available.
- Parametric Estimation: This estimate is calculated by tying a cost to each task and mapping that cost against the project’s timeline. However many tasks there are will help you find your total cost estimate. This can be done in ProjectManager by using our online Gantt chart. Here, you can assign a cost to each task, and as the project is completed, the total cost is automatically calculated and compared to the budget.
How to Track Results for Your Cost Management Plan
Half of your cost management plan is, well, managing your cost throughout the project lifecycle.
When monitoring your project’s cost, use your benchmarks, as they’ll be the key to decoding whether your project is on track, behind or over budget. Because of this, you’ll want to be able to see your planned progress against your realized progress to ensure you’re still on track. Many people use their project management workflow (whether that’s via the waterfall methodology, a Gantt chart or a kanban tool) to gauge this metric.
Project Cost Estimate Template
As stated above, making an estimate is one of the key steps of the project cost management process so we’ve created a free cost estimate template for Excel to help you complete this important task.
3 Things to Avoid When Making a Cost Management Plan
Knowing what not to do is as important as knowing what not to do when making a cost management plan. A cost management plan is complicated and mistakes can be made. The more aware you are of what those missteps are, the less likely you’ll be of taking them. Here are a few to be on the lookout for.
- Poor Stakeholder Communication: Reports are the main vehicle by which project managers communicate vital cost statistics to the project stakeholders. Stakeholders have a vested interest in the success of the project and therefore are very interested in how it’s progressing.
- Not Using a Work Breakdown Structure: Not mapping every step necessary to reach your project’s final deliverable with a WBS is going to impact your budget, and in so doing, your cost management plan.
- Using Only Spreadsheets: Spreadsheets are powerful and do so much well. But they’re not what you want to manage a cost management plan. It’s easy to make mistakes inputting data, they can quickly become overly complex, and there’s limited reporting and visual capabilities.
Free Templates to Help With Cost Management Planning
It’s more productive to manage your cost management plan with project management software, but if you’re not ready to invest in digital tools, there are templates that can act as a workaround. ProjectManager has dozens of free project management templates, many of which are great for cost management. We selected three of the best cost management planning-related free templates for you to download below.
Project Budget Template
A cost management plan begins with a project budget that forecasts all the costs associated with your project and helps you monitor those costs as you execute the project. Our free project budget template for Excel walks you through the budget process, from capturing labor and materials costs to other line items, such as travel, equipment and fixed items. There’s even a place to track your planned versus actual budget costs.
Project Dashboard Template
Keeping track of your cost management plan as you implement is how you keep to that plan. While real-time software is more accurate and involves less work, you can input data into our free project dashboard template for Excel and see how your costs are with easy-to-read graphs and charts. That way you can catch when costs exceed your planned costs and adjust accordingly to stay within your budget.
Action Plan Template
In order to execute your cost management plan, you’re going to need to have a set of tasks assigned to team members. Our free action plan template for Excel outlines those steps to turn your strategy into reality. You’ll find space to list your tasks and in what phase of the project you’ll execute them, their priority, who’s assigned, duration, start and due dates, resources necessary and even the status of the work being done.
How ProjectManager Helps with Cost Management Plans
Whether your next project is large or small, you’ll need to make sure your cost estimation is as accurate as possible, and easy to manage long-term.
With ProjectManager, you’ll have the power to customize your project reporting to get only the data you need, plus you’ll be able to see actual project progress on team members and their tasks.
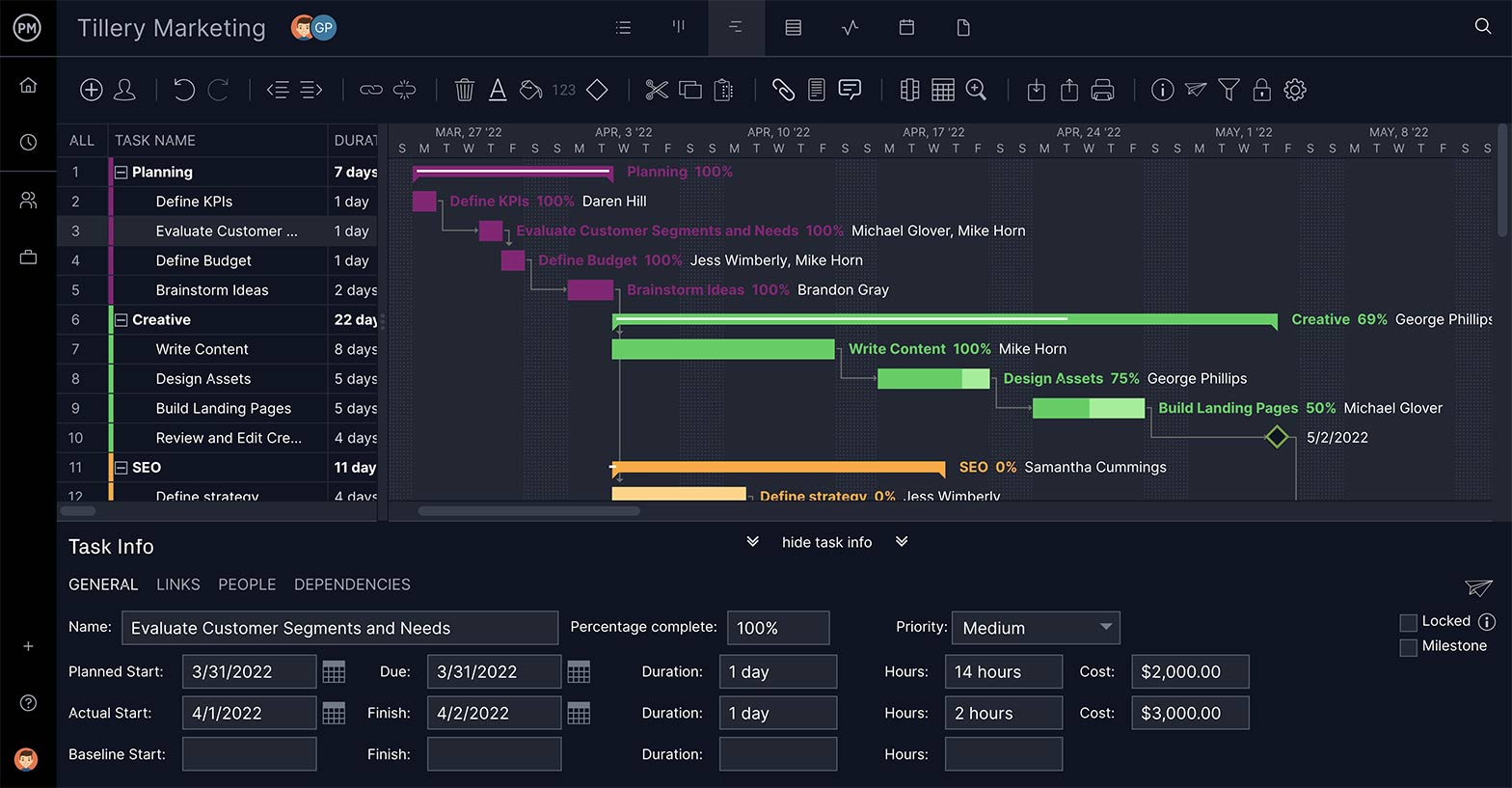
And whether you’re using determinative techniques, historical data, analogous estimation or three-point estimation to gauge your project cost estimates, you’ll have a tool that can plug in your project data and calculate your estimates for you. Additionally, with our real-time dashboards and project reporting features, you’ll be able to get a visual on the estimated benchmarks of your project, so you can see if you’re ahead or behind schedule with the click of a button.
Estimating your costs and getting an accurate reading before project kickoff is one of the most important components to ensure project success. That’s why ProjectManager is dedicated to giving teams the software they need to plan cost estimates, employ a management plan and collaborate effectively no matter where they’re located. Sign up for a free 30-day trial of ProjectManager today.

