Some might call a project manager or anyone in an executive position at a company or organization a decision-maker. It’s an umbrella term that encompasses most if not all of what they’re responsible for. One of the many tools that help them make the right decision is a decision tree analysis.
What is a decision tree analysis? We’ll explain the term and how it works and go into the components that make up a decision tree. Then we’ll explain when and why to use it, illustrating this with an example. We’ll even provide a free download of a decision tree template so readers can try it themselves.
What Is a Decision Tree Analysis?
A decision tree analysis is a tool used in project management, strategic planning and other disciplines to help those in a position of authority to evaluate different courses of action based on possible outcomes and their associated risks. This visual tool represents the decisions, uncertainties and potential outcomes that follow in a tree structure with nodes and branches.
Related: 9 Decision Making Tools and Techniques (Free Templates)
This technique helps anyone identify the best path to take in a situation where multiple decisions or outcomes are possible. It helps assess the potential consequences of all those choices so decision-makers are more apt to pick the best one for the company or organization. The only downside is that decision trees can become large and complex if there are too many possible decisions and uncertainties.
Users of decision tree analysis also have to be aware that the accuracy of the analysis depends heavily on the accuracy of the data used. On the other side of the coin, estimating probabilities for chance events can be challenging, especially when data is limited or unknown.
Get your free
Decision Tree Template
Use this free Decision Tree Template to manage your projects better.
Get the Template
That doesn’t mean decision tree analysis should be avoided. It’s incredibly helpful, but only in making the decision. Executing that decision requires project management software. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software that can help manage projects, business processes and workflow.
One way this is accomplished is with multiple project views. Managers can plan and schedule projects on robust Gantt charts, which link all four types of task dependencies to avoid costly delays, filter for the critical path to identify essential tasks and set a baseline to track progress in real time. Those plans can be shared with team members who can execute their assignments on the visual workflow of a kanban board or powerful task lists. Meanwhile, the calendar view provides a monthly overview for stakeholders to stay updated. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
How Does a Decision Tree Analysis Work?
There are several steps to follow when using decision tree analysis. Below, we explain how this process works for project management and strategic planning, among other situations.
- Start by defining the project and identify the key decision or problem that one wants to solve.
- Next, list all the options, alternatives, possible decisions or courses of action that can be taken. A decision branch will represent each of these choices.
- Now, evaluate the uncertainty. For each decision, evaluate possible future events or outcomes, including uncertainties. These are shown as chance nodes.
- At this point, assign a probability to each potential outcome to reflect the likelihood of their occurrence.
- This brings us to the payoff calculation. Estimate the payoff or consequences (e.g., profit, cost saving, project success) of each outcome.
- Finally, calculate the expected value of each decision branch by multiplying the payoff of each outcome by its probability and summing the results. The decision with the highest expected value may be the most favorable.
Components of a Decision Tree
As the name suggests, a decision tree is a tree-like model used for decision analysis. It achieves the same purpose as a decision matrix, but it consists of several key components that work together to visually represent the decision-making process and the potential outcomes based on different choices or events. The main components follow.
- Root Node: The starting point of the decision tree, it represents the initial decision or question to be considered.
- Branches: Represents the different options or alternatives available at each decision or change point. Each branch can lead to another decision node, a chance node or an outcome (leaf node, which we’ll get to shortly).
- Internal Nodes: Also called decision nodes, they represent the points in the tree where decisions are made. They are often represented as squares or rectangles in a decision tree.
- Leaf Nodes: These are the final nodes of the decision tree and represent the outcomes of the decisions made earlier in the tree.
Decision Tree Analysis Symbols
Decision trees, like flow charts and other similar diagrams, use several symbols are commonly used to represent different elements of the decision-making process. These symbols help define and distinguish between decisions, uncertainties and outcomes. Here are the most common symbols used in decision trees.
- Decision node: A square or rectangle represents a decision point where a choice must be made.
- Chance node: A circle represents a point where an uncertain event occurs, with outcomes that are based on chance. The possible outcomes are typically represented by branches with probabilities.
- Outcome/end node, also called leaf or terminal node: A triangle, though sometimes represented as a small circle, which is the outcome or result of a decision path.
- Branches: While defined above, these are represented by arrows that show the flow of decisions and outcomes in a decision tree chart.
- Annotations/labels: Text descriptions along branches or nodes to clarify decisions, probabilities or values.
When to Use a Decision Tree Analysis
This versatile tool can be applied in various scenarios, particularly when faced with complex decisions involving multiple alternatives, uncertainties and outcomes. Here’s when it is particularly useful in different contexts such as the following.
- Project Management: Decision tree analysis is especially useful for project managers who must make multiple decisions throughout the life cycle of a project. A few examples include when allocating resources, budgeting and scheduling projects and dealing with the risk inherent in any project.
- Business Strategic Planning & Scenario Planning: Any time a company needs to evaluate several strategic options under uncertain conditions, a decision tree is helpful. Some of these situations might include market expansion, new product development, mergers and acquisitions or diversification.
- Risk Analysis: Risk deals with several uncertain outcomes and, therefore, is perfect for decision tree analysis. It allows for the evaluation of outcomes against the likelihood of specific events and is especially useful for quantifying risks and assessing their potential financial impact.
- Root Cause Analysis: Decision trees can also be used in root cause analysis to map out the possible causes of a particular problem or issue and the likely outcomes of addressing different causes. Some of those causes could be manufacturing defects, system failures and customer complaints.
Decision Tree Analysis Example
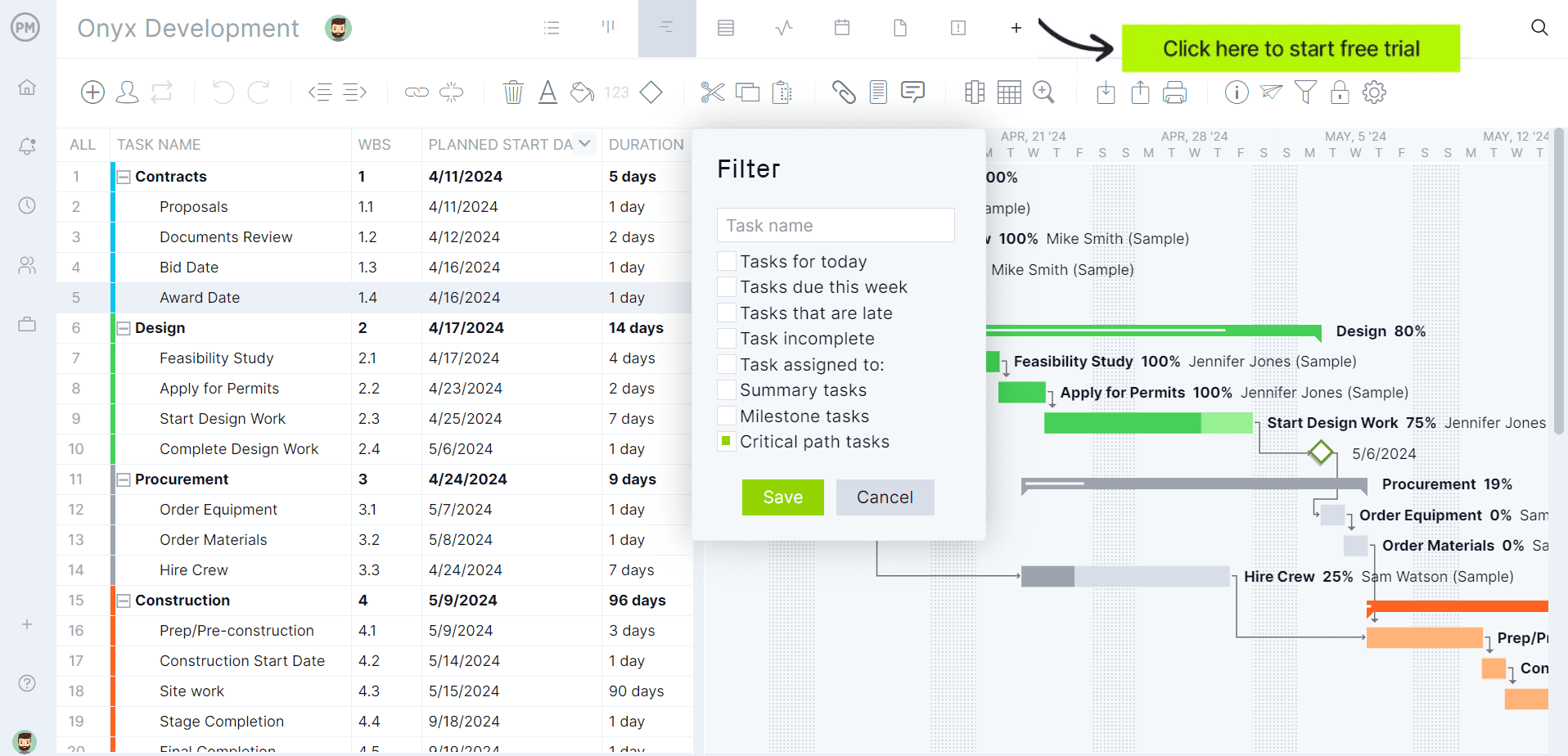
Now that we understand the concept and the parts that make up the visual tool, the next step in understanding the process is going through a decision tree analysis example. The example is shown in the image below.
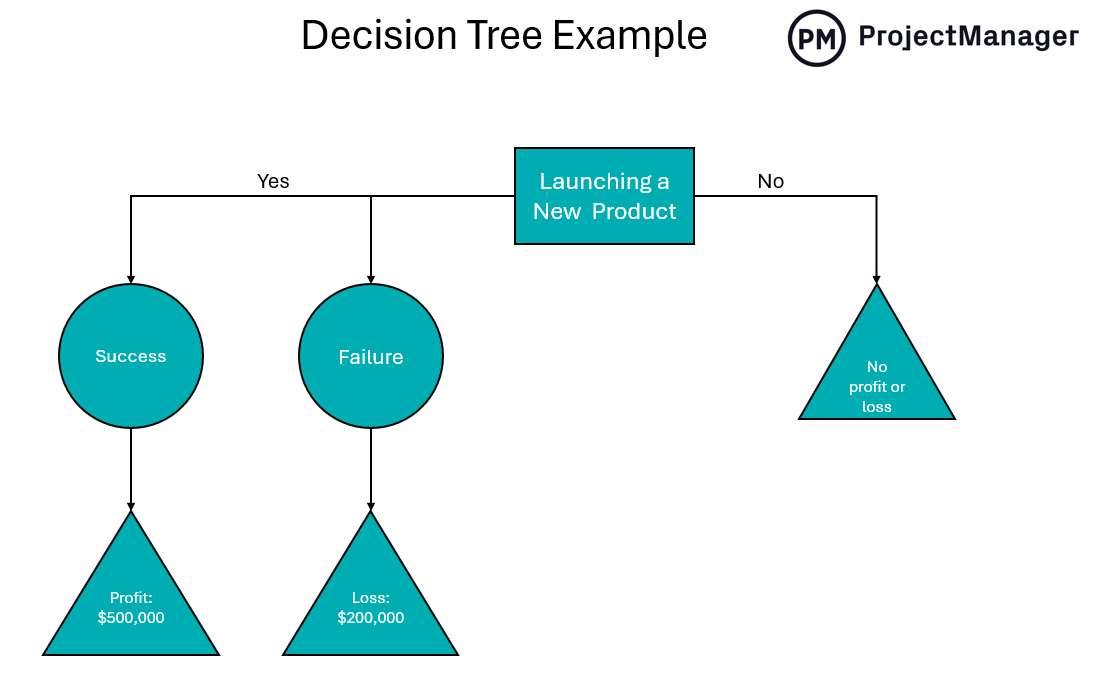
To begin, add the root node or decision that is to be made. In this case, we’re exploring whether or not to launch a product. Therefore, the decision is: should the product be launched or not? This is followed by two branches, one for yes and the other for no.
If yes, add a chance node or outcome to analyze whether the project will be successful. Branch one will be successful with a lead node or outcome being a profit of $500,000. Branch two follows if the product launch is a failure, which leads to the leaf node of a loss of $200,000.
The other choice, of course, is not to launch the product. The outcome of this is simple. The result is the status quo. In other words, there’s no profit or loss. Now, with this information, leaders can make a more informed decision about the product launch.
Decision Tree Template
Rather than drawing the decision tree freehand or investing in a program that can do it digitally, readers have the option of downloading this free decision tree template for PowerPoint. It has a page with all the decision tree symbols already made.
There’s also a sample decision tree that users can edit to reflect the process of the decision they’re trying to make. Finally, there’s a page that collects other free related project management templates to download, though we’ll also share some later in this post.
Benefits of Using a Decision Tree Analysis
We touched on the disadvantages of using the decision tree analysis but neglected to explain the many advantages of using one. Here are a handful of reasons why using this visual tool is so beneficial.
- Provides a clear, visual representation of choices, outcomes and paths, making them easy to interpret and communicate
- Organizes complex problems into manageable segments, ensuring no critical factor is overlooked
- Assigning probabilities and values allows for expected value calculations, supporting scenario planning decisions
- Can handle a mix of qualitative and quantitative data, adapting to various decision contexts
- Facilitates what-if analysis, helping to evaluate the impact of different choices under varying conditions
Free Related Templates
As promised, below are a few free project management templates out of the over 100 that can be downloaded immediately from our site to address every aspect of managing a project across any number of industries.
Decision Matrix Template
Another helpful tool to help one decide on the best course of action is this free decision matrix template for Excel. It helps one evaluate and prioritize a list of options to identify, analyze and rate sets of information.
Fishbone Diagram Template
Use this free fishbone diagram template for Word to help with root cause analysis. Also called a cause-and-effect diagram, it’s used to help find why there are imperfections, variations, defects or failures in a process or project.
Scenario Planning Matrix Template
Scenario planning is a strategy used to consider possible future events. Download this free scenario planning matrix template for Excel to analyze four scenarios in terms of their impact and uncertainty.
ProjectManager Helps Manage Projects, Business Processes and Workflows
We’ve already shown how ProjectManager’s multiple project views can turn a decision into a practical plan. But there is so much more to our software than that. In terms of decision tree analysis, we have risk management features that can identify risk and their impact and likelihood of occurrence, then track them until they’re resolved.
There are also automated workflows that can streamline repetitive tasks and keep teams focused on work that requires more of their attention. Task approval settings ensure quality assurance, too. But that’s only the start of how our software manages projects, business processes and workflows.
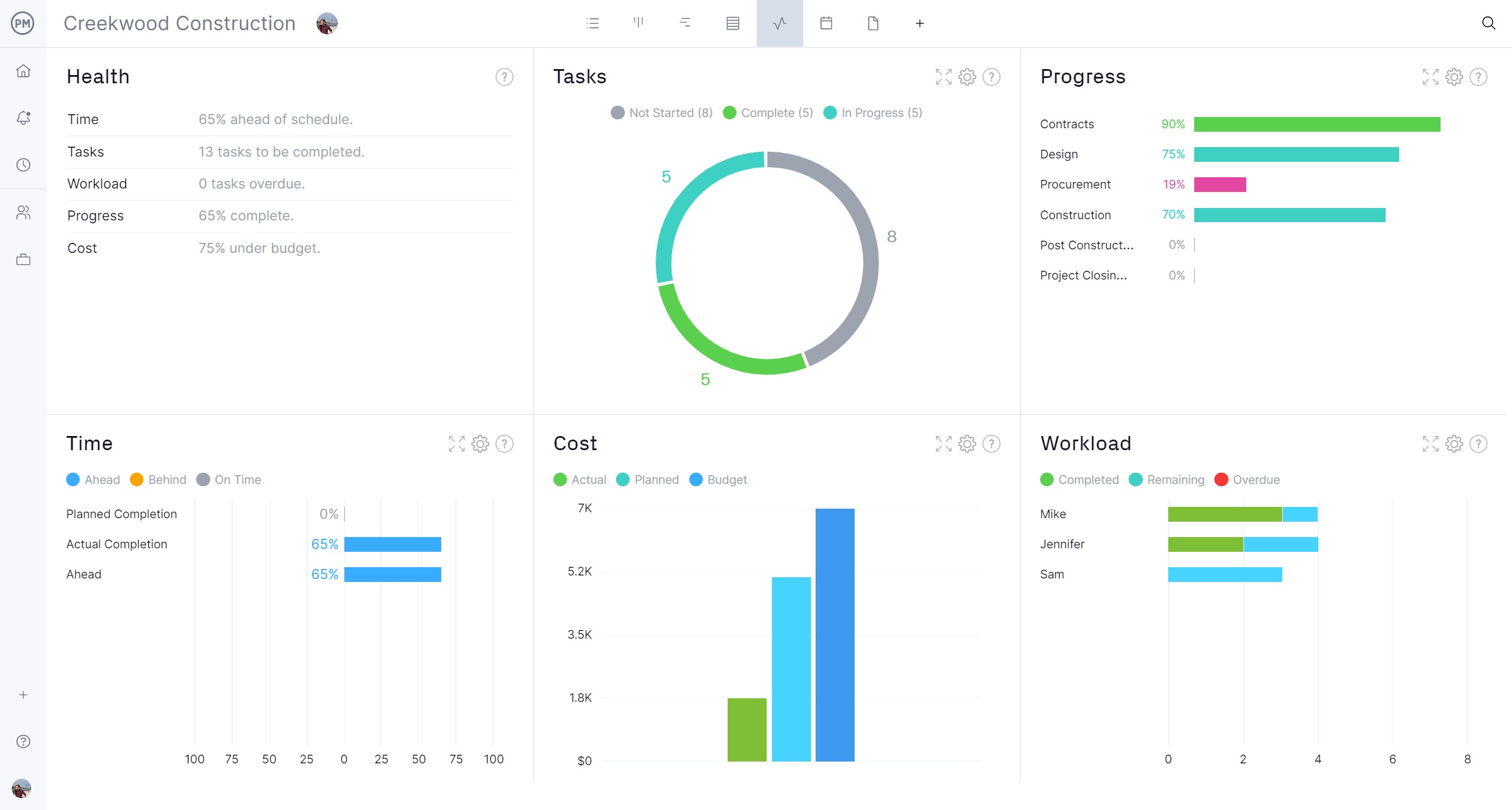
Real-Time Dashboards and Reports
Making plans is only the beginning. Those plans must be monitored as there are always internal and external forces at play working to push them off schedule and lead to cost overruns. For a high-level overview, toggle over to the real-time project dashboard or portfolio dashboard for those managing multiple projects. Each automatically collects live data and displays it on easy-to-read graphs and charts that show time, cost, workload and more. Customizable reports go deeper into the data and can be filtered to offer a more cursory view to share with stakeholders and keep them updated.
 Robust Resource Allocation and Cost Tracking Features
Robust Resource Allocation and Cost Tracking Features
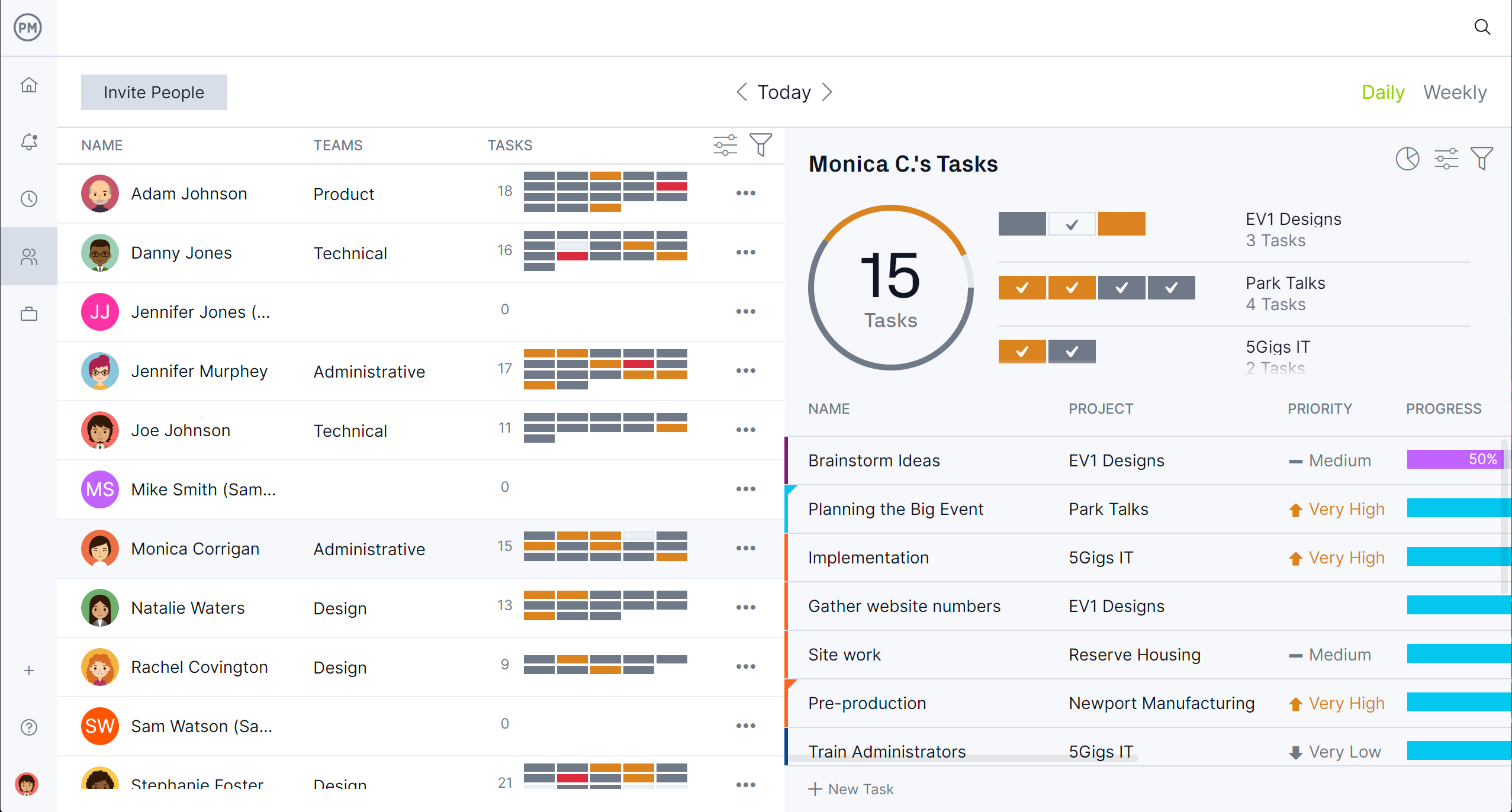
Resources are how project plans become reality. Human and non-human resources and their costs can be scheduled on Gantt charts and team availability, including PTO, vacation, global holidays and skill sets, can be set when onboarding, which helps make assigning simpler. Then managers can use the color-coded workload page to balance workload and keep everyone working at capacity without threatening burnout. The team page provides an overview of the daily and weekly tasks of everyone across projects. It can be filtered by priority, progress and more to ensure resources are properly allocated.

Related Decision-Making Content
As one might expect, there are many more ways to help project managers and their like make decisions beyond decision tree analysis. Here are some more recent blogs posted on the topic, for those interested in learning more.
- 9 Decision Making Tools and Techniques (Free Templates)
- What Is a Decision Matrix? (Example & Template Included)
- Decision Matrix Template for Excel (Free Download)
- DACI: A Decision Making Framework
- How to Use a Project Decision Log for Optimal Results
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams whether they’re in the field or the office. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who use our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.