Projects are made up of a large number of tasks, and keeping track of those tasks is a primary role of a project manager. Sometimes, the tasks in a project all run smoothly and independently of each other, and there are no complexities. Other times, however, there will be a large chain of dependent tasks that make things more complicated.
What happens if a task needs to be completed today, but the person responsible for it is waiting on another task that hasn’t been completed yet? Delay happens. If you want to avoid delays in your projects, then it’s time to familiarize yourself with float or slack in project management.
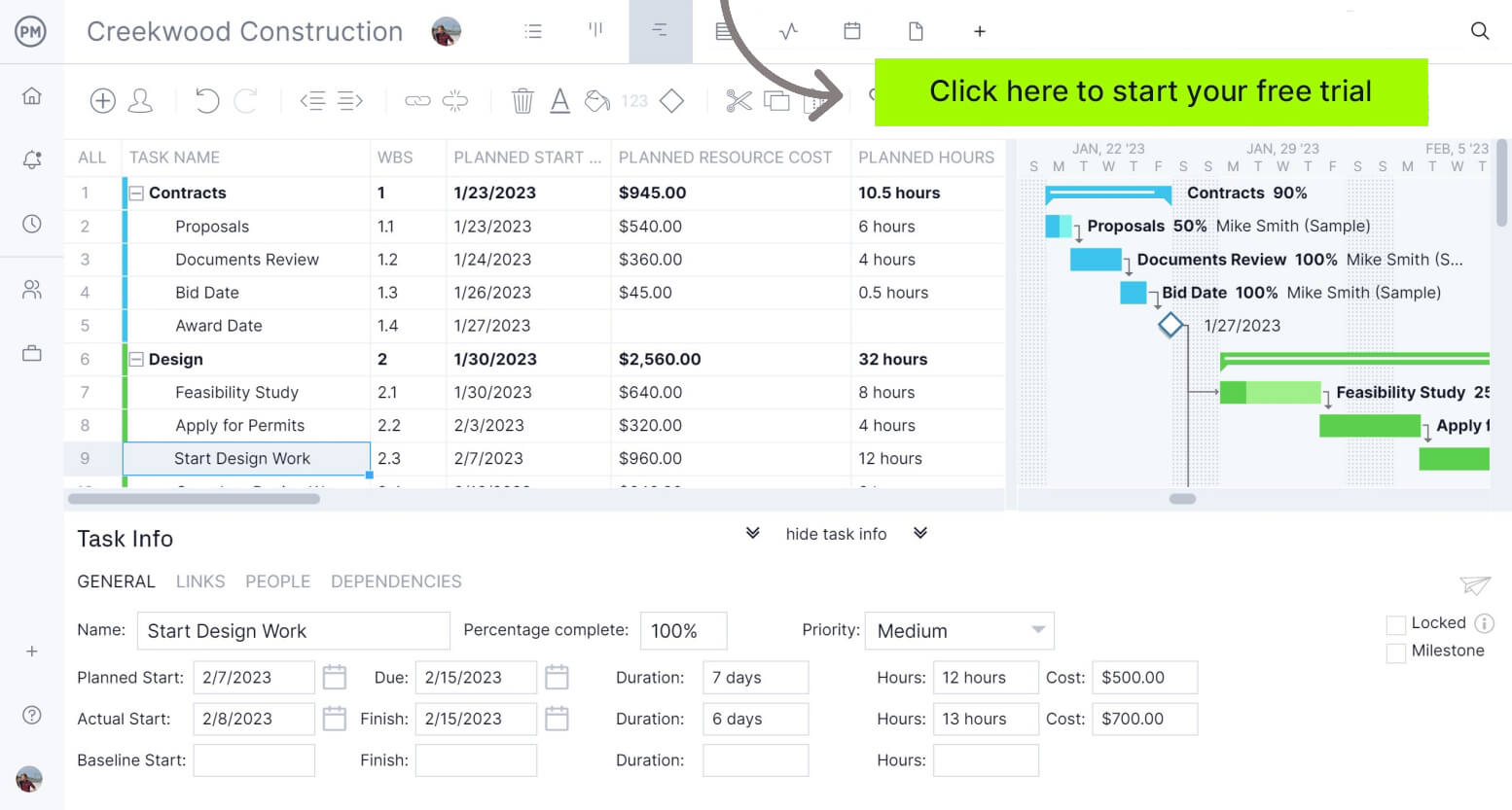
What Is Float or Slack in Project Management?
In project management, float, sometimes also referred to as “slack,” is a number that indicates the amount of time a task can be delayed without impacting subsequent tasks or the project’s overall completion. It’s important to track when you are maintaining your project schedule.
There are two types of float in project management, free float (FF) and total float (TF).
- Free float is the amount of time that a task can be delayed without impacting the subsequent task.
- Total float is the amount of time a task or a project can be delayed without impacting the overall project completion time.
Float is a key piece of the critical path method (CPM), a system used by project managers to efficiently schedule project activities.
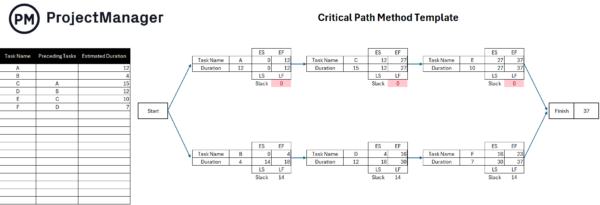
What Is the Critical Path?
The critical path is a sequence of dependent tasks that determines the duration of a project. Tasks on the critical path need to happen for the project to finish, and they need to be done in a specific order. Tasks on the critical path will have a float of zero, meaning there are no delays in the sequence. There is no extra time to spare on these tasks, and if one is delayed, then the project is delayed too.
When a task has a positive float number, it is considered part of the non-critical path, meaning that it has some flexibility to be moved or delayed from its planned start date without impacting the project’s completion.
Get your free
Gantt Chart Template
Use this free Gantt Chart Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
Difference Between Slack and Float in Project Management
To be clear, “slack” and “float” refer to the same concept in project management; the amount of time a task can be delayed without impacting other tasks or the project’s overall completion date. Both represent flexibility within a project schedule.
As we mentioned, there are two types of float; total float (or total slack) and free float. This distinction between “total float” and “free float” is important for precise project scheduling.
How to Calculate Float
There are several different ways to calculate float. The technical calculations that are part of the critical path method will be confusing if you aren’t up to speed on CPM and network diagrams, so we’ll explain how to do these calculations in layman’s terms.
It’s important to note that most project managers don’t even do float calculations by hand because it would be extremely time-consuming, not to mention the project plan is always changing.
Therefore, the best way to get float numbers and other valuable calculations in real-time is to use professional project management software that automatically does the number crunching for you. ProjectManager’s Gantt charts, dashboards and project reports will automatically calculate and provide you with the data you need to track float, slippage, critical paths and more.
However, if you want to do the calculations manually, just follow the steps below.
Total Float Calculation
Total float can apply to the project as a whole, or to an individual task.
A project’s total float is the difference between the finish date of the last task on the critical path and the project completion date. This will tell you how much total time the critical tasks can be delayed before the entire project misses its completion target.
To calculate a task’s total float, simply take the difference between the finish date of the last task on the critical path and the planned finish date of the task you are calculating for.
Free Float Calculation
As you recall, free float is a number that shows how long a particular task can be delayed before it impacts the next sequential task. Therefore, to calculate the free float of a task, simply take the difference between the next task’s planned start date, and the current task’s end date.
An Example of Float in Project Management
So far, we’ve defined what float is, but it will be much easier to understand what it is and why it’s important once we look at an example.
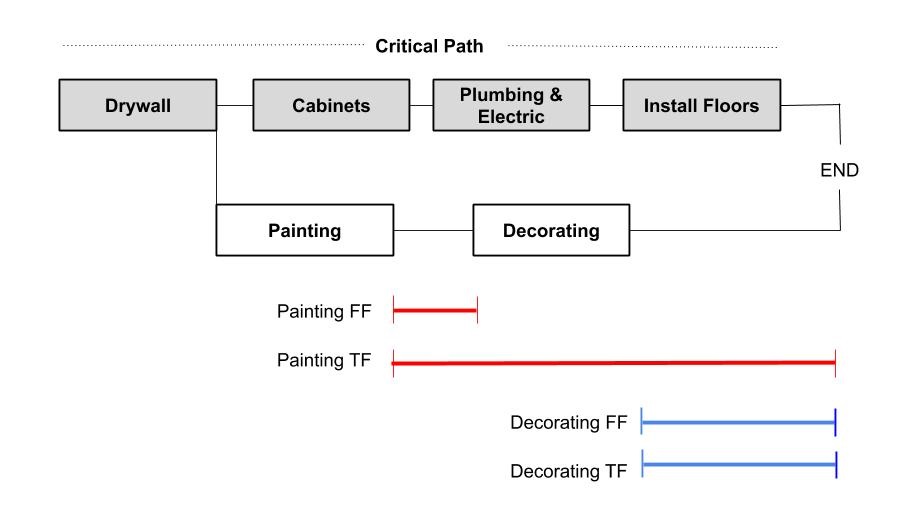
Let’s assume you’re building your new kitchen, and you have 90 days to complete the process because you have a big party planned in three months. To complete the kitchen renovation project, the following things must happen in order:
- Drywall installation
- Cabinet installation
- Plumbing/Electric
- Floor installation
These activities make up the critical path and have zero float.
Then there are additional tasks like painting and decorating that need to happen, but they have much more flexibility as to when they can be done. These tasks make up the non-critical path.
Painting can be done any time after the drywall is installed, so it has a high float. Decorating can be done any time after the painting is done, so decorating has some float too.
Types of Float in Project Management
In addition to using a hypothetical project scenario to illustrate an example of float, let’s explore how float might appear in different industries.
- Float for IT Projects: IT projects are often complex and have numerous dependencies. If an IT team is rolling out a new employee onboarding system, setting up the database and core system infrastructure is a critical task that can’t be delayed. User training videos aren’t as pressing and there is more flexibility in when they are finalized.
- Float in Manufacturing Projects: If a manufacturer is building a toy car assembly line, a critical task without float is getting the wheels delivered on time. If the wheels are late, the whole line stops. However, a task within this project with float may include painting the car bodies; there are a few days to paint them without delaying the product’s final assembly and shipping.
- Float for Construction Projects: When building a house in a construction project, an example of a task without float is pouring the foundation. If bad weather delays this task, all other tasks will be delayed. A task such as installing the interior trim, on the other hand, has float. If it takes a few extra days, the final inspection and handover won’t be delayed.
- Float for Professional Services Projects: Let’s say a consulting firm is implementing a new customer relationship management (CRM) system for a client. If the data isn’t transferred accurately or on time, the go-live will be delayed. A task such as creating user training documentation has slack as the consultants have a few extra days to complete the manuals without pushing the project deadline.
- Float in Event Planning: If an event planning company is planning a large corporate event, a critical task may be securing the keynote speaker. If the speaker suddenly backs out, the whole schedule will be thrown off. In terms of designing the conference brochures, there are likely a few days of slack or float that allow for unexpected changes.
Why Float Matters for Projects
It might seem that float is just a technical number used in network diagrams, but it is actually a very powerful tool that can help teams learn more about their work and help improve the productivity of projects.
Float Keeps Projects on Track
To start, monitoring a project’s total float (TF) is crucial to ensuring that the overall project is going to be delivered on time. If you notice that a project’s TF is getting close to zero, it’s now crunch time to make sure the final remaining tasks are finished efficiently.
You may even need to add extra resources to help the project team finish the final tasks faster than originally planned. If the project isn’t going to finish on time, then it’s time to have a chat with your client or stakeholders to let them know that they should expect a delay.
Float Improves Prioritization
Free float (FF) is also a helpful number to monitor because it gives you a way to decide which tasks need to be prioritized and which can be pushed back to a later date. If a task has zero float or a low float number, then it should go to the top of the priority list so the project team can knock it out.
Conversely, any tasks with high FF numbers can be pushed to the bottom of the priority list, because there is no rush to get them finished.
Managing Float can Boost Team Morale
Finally, free float can be used to help you keep different project teams happy and efficient. Let’s say that task A is moving towards a very low free float number, meaning it is at risk of delaying task B. In this case, you can give the team working on Task A some extra resources to help them finish their work.
You could also let the team who will be working on task B know that they should prepare for a delay in their work. By monitoring FF, you can catch problems early and make sure that teams don’t get frustrated by sudden delays. If team B knows to expect delays, then they can fill their time by working on something else.
Templates to Help You Manage Project Slack
There are several free project management templates for Excel and Word available on our website. Below are a handful that can improve how teams manage project float.
Critical Path Template
Use this free critical path template for Excel to calculate the critical path of any project. This makes it easy to see which tasks must be completed on time and which have more float.
PERT Chart Template
Download this free PERT chart template for Excel to build a schedule and track its progress to ensure all activities are completed by the deadline. It helps schedule, organize and coordinate project tasks.
Gantt Chart Template
This free Gantt chart template for Excel is the ideal way to visualize the tasks that make up a project schedule. It helps project managers organize which tasks are essential to finish on time and which have more float.
Project Management Tools for Monitoring Work
Calculating float on your tasks and projects can be extremely valuable, but doing the calculations by hand is out of the question for most people. If you would rather have a project management tool do all of the complex calculations for you, then ProjectManager has a suite of PM tools perfect for the job.
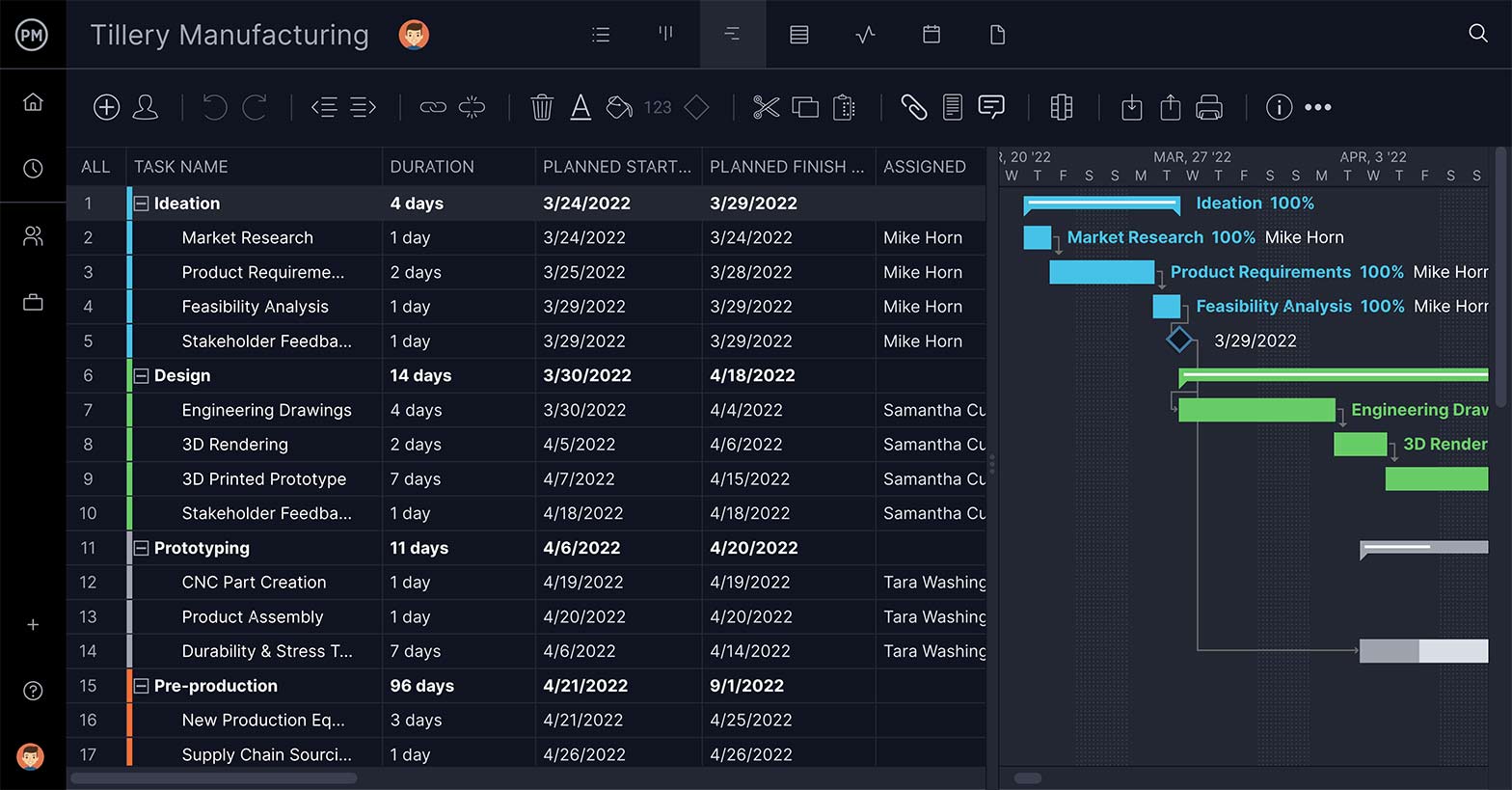
Gantt Charts For Critical Path
ProjectManager’s Gantt chart is one of the most powerful tools on the market for scheduling work. Here, you can add tasks, create project milestones and automatically calculate the critical path of your project. Save hours of drawing network diagrams and making calculations, and instead let the Gantt chart software do all of the work for you.
Real-Time Project Dashboards
ProjectManager’s real-time project dashboard is a helpful way to stay on top of your projects at all times. Once you’ve assigned tasks to your team, the project dashboard will begin to collect data automatically. When team members update their progress on tasks, the data is reflected in the dashboard’s charts.
All of the calculations are done automatically, so you can see progress in real-time. On the dashboard you will see the project’s planned vs. actual progress as a percentage—this is our own way of showing you the total project float.

You can also, at-a-glance, see how many tasks are done and how many are still needing to be executed. The dashboard is the central command center for any project, giving you the information you need to keep all of your projects on track.
Take a free 30-day trial of ProjectManager today to see how easy it is to calculate float and plan, monitor and report on your projects. ProjectManager offers powerful PM tools, but it’s easy to get you and your team up and running quickly with no training required. The software stores all of your work in the cloud, so your team can stay synced no matter where they are. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

