Manufacturing isn’t free. There are various costs involved in the production of any product. Being able to make accurate estimates of your manufacturing costs is critical to a company’s profitability and competitive advantage. Before work hits the production line, one must know how to calculate manufacturing cost.
First, we need to understand what manufacturing cost is, the different types of manufacturing costs as well as some examples to get context for what we’re talking about. Then we’ll provide formulas to calculate each type of manufacturing cost and the total manufacturing cost. Plus, we’ll explore how software can help.
What Is Manufacturing Cost?
Manufacturing costs are the prices incurred during the manufacturing process. Manufacturing costs are made up of direct materials costs, direct labor costs and manufacturing overhead, which we’ll get to in greater detail shortly. Each of these costs is usually listed as separate line items on an income statement, which is the financial results of the business for a stated period.
Also included is the cost of turning materials into products. The manufacturing cost is a factor in the total delivery cost or the money a manufacturer spends to make and deliver the product. We’ll get to how to calculate the manufacturing cost of production and delivery, but just as important is the ability to track those costs throughout the life cycle of your production to ensure you’re operating within your budget.
Project management software helps manufacturers track production costs. ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that tracks manufacturing costs in real time. Use our kanban board as a tool to track cost estimates versus actual costs, order management and inventory management alongside production. It centralizes production processes to help you build plans and collaborate with your team.

Types of Manufacturing Costs
Determining manufacturing costs is important; it helps manufacturers price their products in such a way that they’re competitive but also ensures high net profits for the company. Knowing the manufacturing cost gives manufacturers the ability to meet goals and make sure their production process is at the right level of productivity.
The first step toward achieving these benefits is to know the different types of manufacturing costs. We’ve already identified manufacturing costs as direct material costs, direct labor costs and manufacturing overhead. Below, we’ve defined each of these manufacturing costs in more detail.
Direct Materials Costs
Direct material costs are the raw materials that will be used to make the finished product. The value of these raw materials increases over the production of the product. Raw materials go through any number of types of operations in the course of manufacturing, such as welding, cutting, etc. When figuring out direct material costs, it’s important to distinguish between direct and indirect. Indirect costs are subsidiary material costs, such as shop supply costs, perishable tools and equipment costs. These are included in manufacturing overhead costs.
Related: 10 Free Manufacturing Excel Templates
Direct Labor Costs
Direct labor costs are those costs related to the workers who are physically involved in producing the finished product. This includes the wages and benefits that the workers earn. These workers are responsible for converting the raw materials into the finished goods.
Manufacturing Overhead
Manufacturing overhead is any costs related to the manufacturing of a product that isn’t direct materials costs or labor costs. These can include indirect labor costs, such as wages for supervisors and the material handling team. These are labor that isn’t directly involved in production. Indirect materials costs are also part of manufacturing overhead, such as the purchase of lubricants, grease and water that aren’t used as raw materials. Then other indirect manufacturing costs can include items such as machine depreciation, land rent, property insurance, electricity, freight and transportation and other expenses that keep the factory operating but aren’t directly related to the manufacturing of the finished product.
Manufacturing Costs Example
To give you an idea as to what manufacturing costs are, it’s often helpful to share an example that illustrates the idea. Let’s imagine Acme Manufacturing, a fictitious company that manufactures dog houses.
The direct materials costs would include the wood to make the house and any glue or nails used to hold it together. Another direct material cost would be paint. The direct labor would be the salaries of the workers who cut the wood, assemble the pieces and then paint the dog house.
Finally, the manufacturing costs will include manufacturing overhead. This will be the cost of rent on the factory, heating, phone and other utilities, the salary of managers, packing and shipping clerks, administrative staff and so forth.
The calculations for all these costs give the manufacturer a clear picture of what it costs to produce each dog house and, therefore, what price the dog house should sell for. This allows the manufacturer to determine their profit margin and also productivity level, for producing more dog houses in the same amount of time could lead to greater profits if there’s a market need.
Get your free
Production Schedule Template
Use this free Production Schedule Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
How to Calculate Direct Materials Costs
We understand what direct material costs are so now it’s time to talk about the formula used to calculate them. Calculate direct materials costs when doing a physical inventory and adding up all the opening and closing direct materials for some time.
Direct Materials Cost = Opening Direct Material Inventory + Direct Material Purchased – Closing Direct Material Inventory
How to Calculate Direct Labor Costs
Direct labor costs are part of a company’s overhead expenses. The formula to calculate this is the pay rate of your direct labor multiplied by the total hours worked. This means each employee whose work can be directly traced back to the creation of the final product.
Direct labor cost=Pay rate per hour * Total hours
How to Calculate Manufacturing Overhead Costs
As we defined above, manufacturing overhead costs are all the costs not related to direct labor and direct material costs. Unlike the other costs, this is a broad category that includes many different items, such as utilities, equipment, etc. Therefore, first, one must identify these costs, such as the indirect labor and materials costs, add depreciation costs and all other manufacturing overhead costs to get your figure.
Manufacturing overhead = Indirect materials + Indirect labor + Depreciation costs + Utilities + Insurance
Total Manufacturing Cost Formula
To determine the total manufacturing cost for the production of your finished product, add the direct materials cost with the direct labor costs and the manufacturing overhead costs.
Total manufacturing cost = direct materials + direct labor + manufacturing overhead
Manufacturing Costs vs. Production Costs
Understanding the difference between manufacturing costs and production costs can be confusing. Let’s take a moment to explain the difference between the two. Production costs are all the expenses related to a manufacturer conducting its business. Manufacturing costs, as we’ve already discussed, are the expenses that are needed to produce the product.
Both of these figures are used by manufacturers to evaluate the total costs of running their business. For the company to be profitable, the revenue it makes must be more than the total expenses for its manufacturing costs and production costs combined.
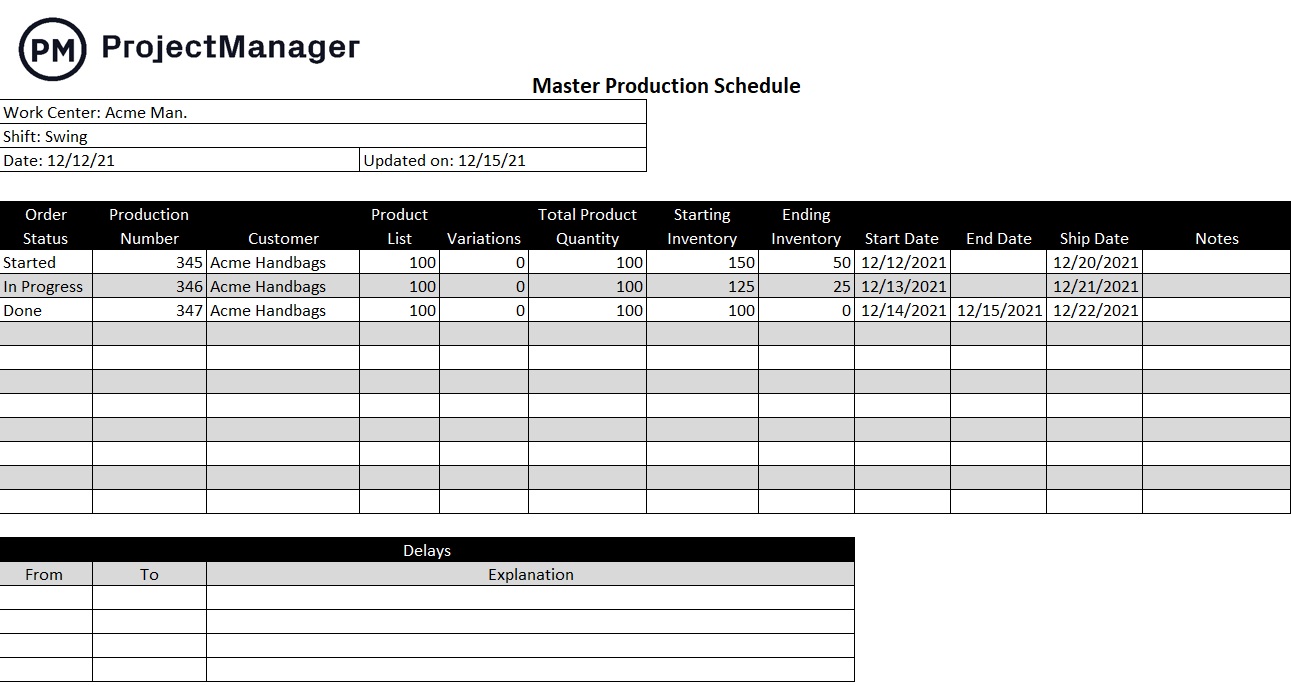
Free Production Schedule Template
As you can see, manufacturing costs and production costs are closely linked. To more efficiently keep tabs on your production schedule to ensure profitability, download our free production template for Excel. Use it to respond to changes in demand and control costs.
Why Manufacturing Cost Is Important
Knowing the costs of production is critical for a manufacturer that wants to stay in business. As noted, you can’t know your profit margins if you don’t know how much it costs to manufacture your product. That means knowing all the costs involved as we’ve already defined.
Knowing the cost of manufacturing a product is more than being able to calculate the price and profits of the item. It helps manufacturers make more insightful decisions in terms of staying competitive and how production manufacturing can be profitable enough money to remain a viable business.

How ProjectManager Helps Track Manufacturing Costs
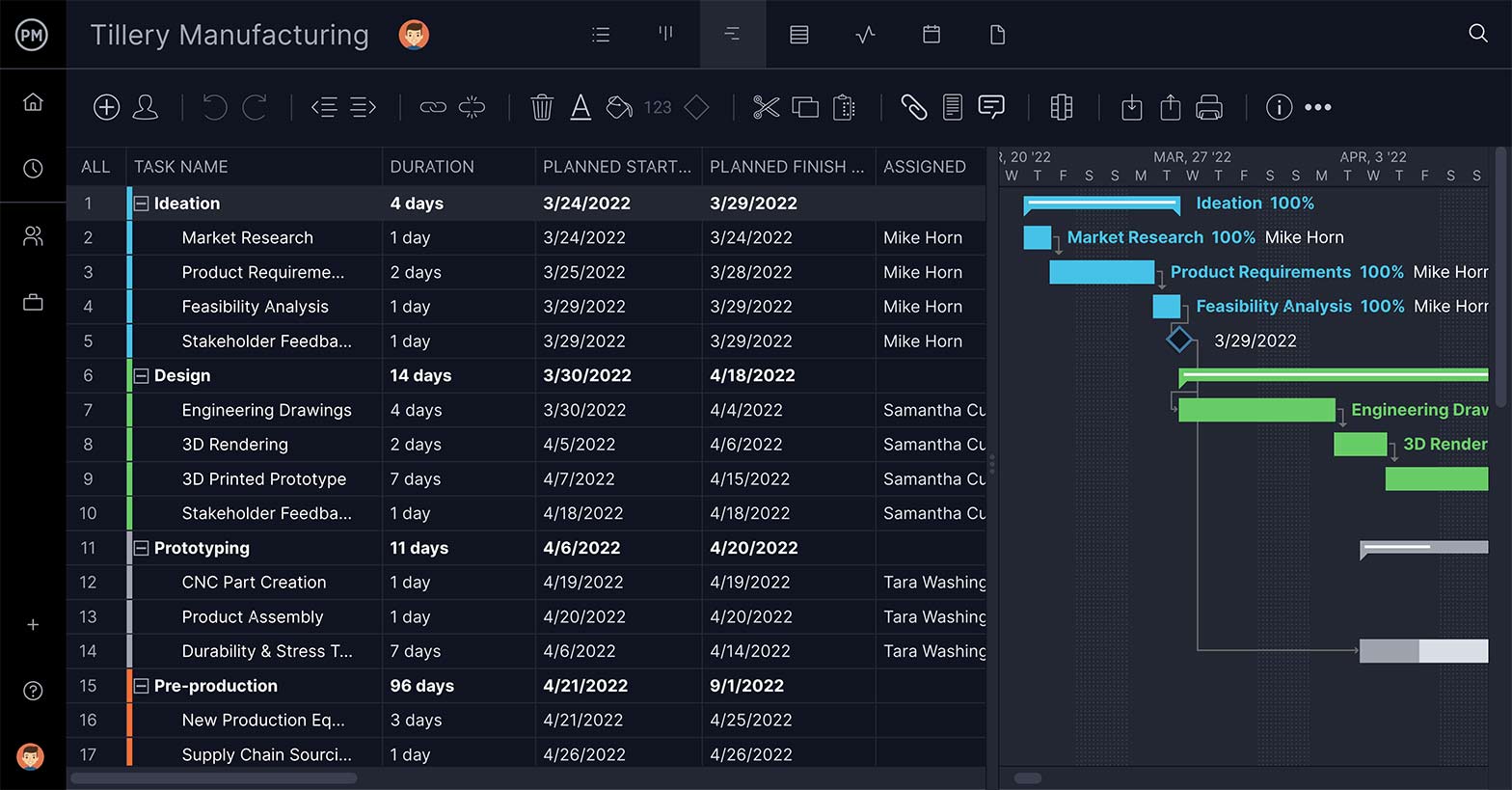
ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that helps manufacturers plan, manage and track their manufacturing costs in real time. Our software has powerful Gantt charts to plan your manufacturing costs and secure timesheets to track labor costs all in real time. That’s on top of our features such as our automated workflows and task approval settings to streamline processes and ensure quality.
Plan and Manage Costs on Robust Gantt Charts
Use our Gantt chart project view to set resources and costs, such as hourly rates for workers and non-human resources, such as equipment, suppliers, etc., for every stage of your production cycle. You can link dependent tasks to avoid costly delays and set milestones to track progress. Once you have manufacturing costs done, set a baseline. This captures your planned costs and allows you to view those planned costs against your actual costs in real time. This data is also shared with other features, such as our dashboards and reports.
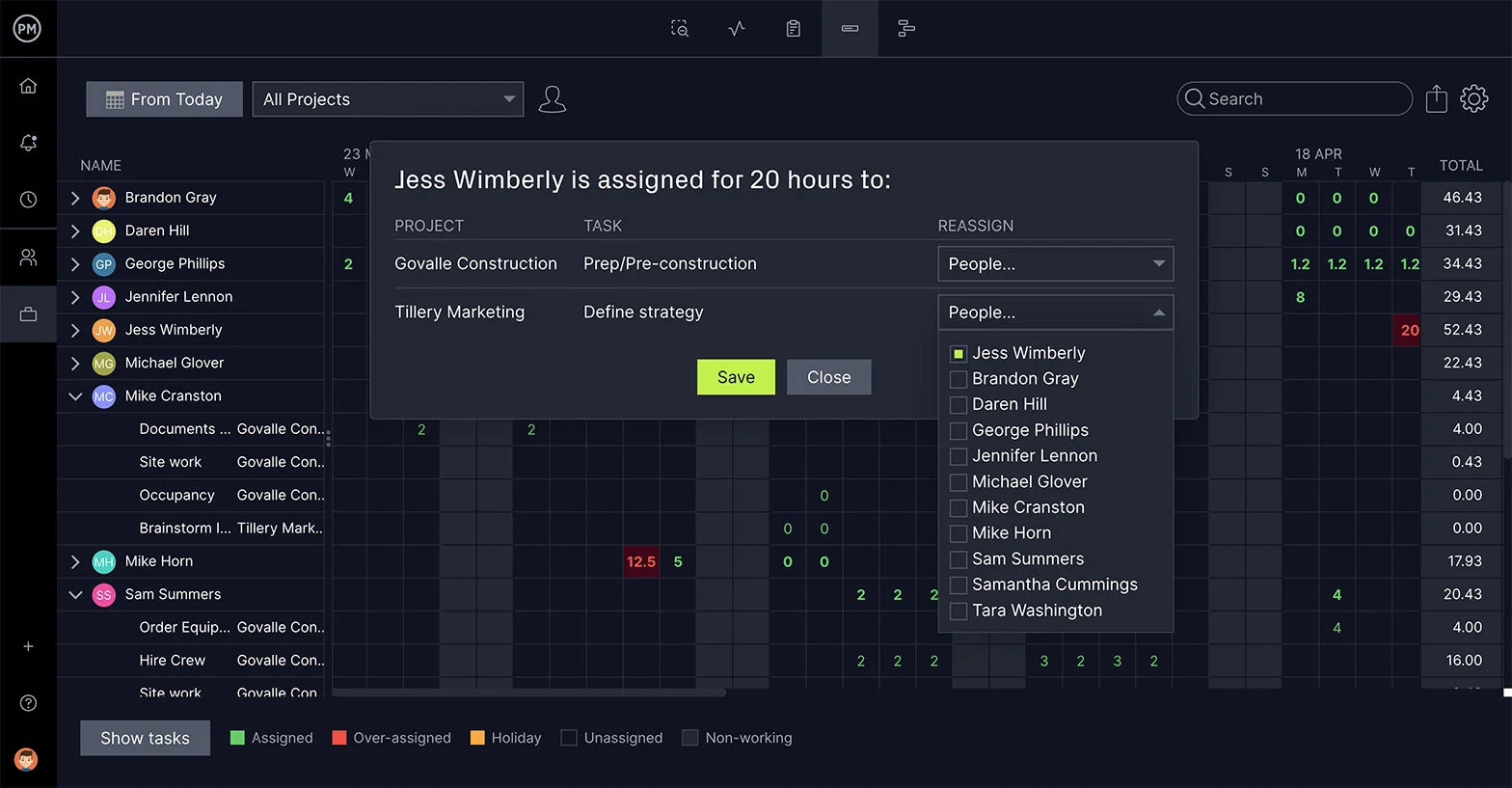
 Use Timesheets to Monitor Labor Costs
Use Timesheets to Monitor Labor Costs
Timesheets can help manufacturers streamline their payroll with a secure process that includes locking timesheets once submitted to managers, who can review and route them to payroll. But they also serve as a means of monitoring labor costs to make sure you’re not overspending your budget. Managers can view timesheets to monitor labor costs and get further information by generating a timesheet report.
Real-time dashboards give managers a high-level view of their costs and for a deeper dive into the data they can use our customizable reporting tools. It’s quick and easy to generate a status report or portfolio report, track more than one production, and then filter the report to show only the data you want to see. Reports can also be shared in a variety of formats with stakeholders to keep them updated
ProjectManager is online project management software that connects teams whether they’re in the office or on the assembly line. Our software facilitates collaboration and allows the project team to share files, comment at the task level and more. You can use risk management, task management and resource management features to control production and keep to your manufacturing schedule. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.