Project management is a complex discipline requiring structured methodologies to ensure success. The Project Management Institute (PMI) has developed the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) as a global standard, providing a comprehensive framework for managing projects effectively. The PMBOK outlines essential concepts, best practices and industry standards that help project managers streamline their processes. Additionally, it serves as the foundation for PMI certifications, ensuring professionals acquire the skills needed to navigate diverse project challenges.
What Is the PMBOK?
The PMBOK is a globally recognized standard that provides best practices and guidelines for managing projects effectively. Developed by PMI, it serves as a reference for project managers by outlining methodologies, processes and terminologies used across industries.
The guide is structured around knowledge areas, process groups and project management processes that ensure consistency and efficiency in project execution. It is widely used for training, certification preparation and establishing a common project management language.
Once knowledge of project management is acquired, the right tools must be applied. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software that has multiple project views that allows project managers and their teams to work how they want across different methodologies and processes.
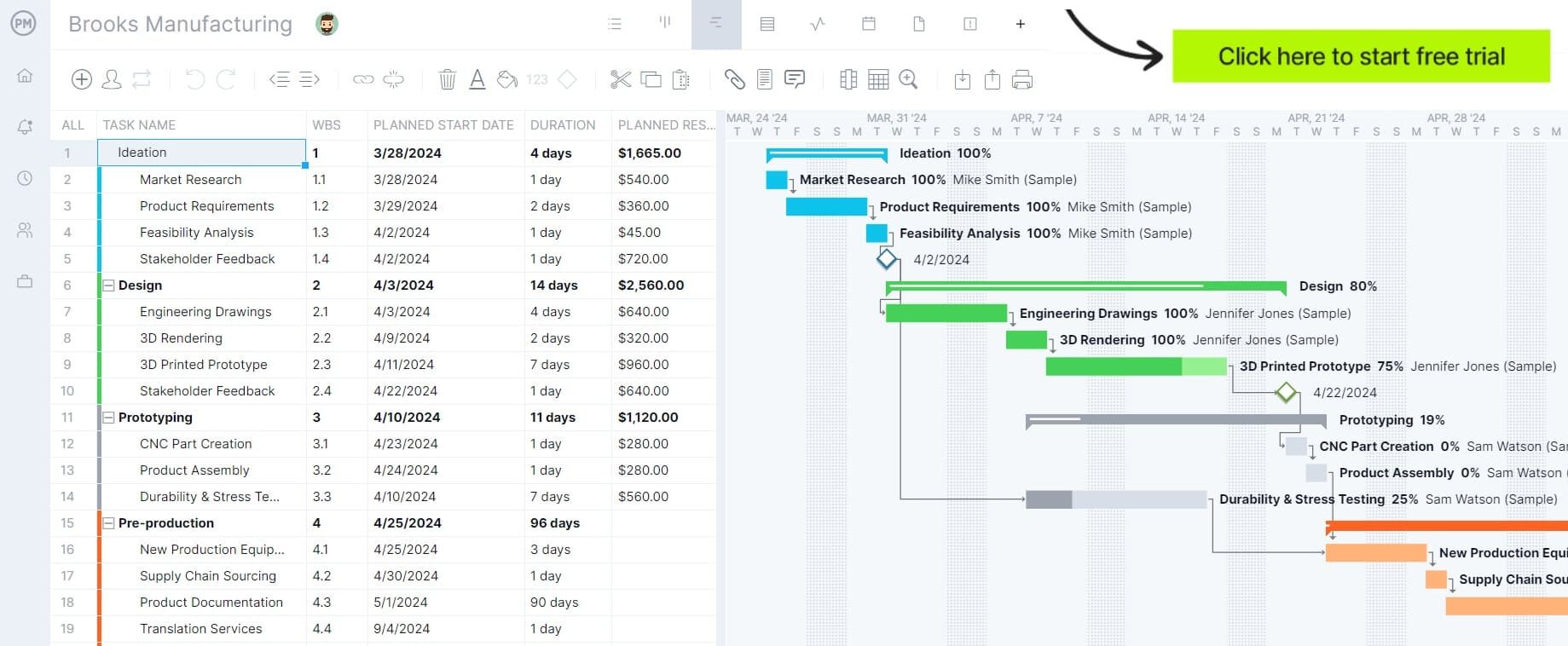
Project managers planning traditional projects as construction can schedule tasks, resources and costs on our robust Gantt charts. They can also link all four types of task dependencies to avoid delays and cost overruns. It’s easy to filter for the critical path to identify essential tasks. Then, set the project cost, scope and schedule baseline to track progress.
If projects are managed in an agile or hybrid environment, kanban boards allow teams to manage their backlog and collaborate on planning sprints. Managers can use the board to spot potential bottlenecks and reallocate resources to clear them before they become a problem. Teams can also use task lists and stakeholders can stay updated with the calendar view. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
Who Should Use the PMBOK?
The PMBOK is essential for project managers seeking to enhance their knowledge and improve project execution. It is a valuable resource for professionals across industries, including construction, IT, healthcare and finance who need a structured approach to project management.
Additionally, organizations that aim to standardize their project management processes benefit from the guide’s framework. It’s also a critical resource for individuals preparing for PMI certifications such as the Project Management Professional (PMP), ensuring they understand industry best practices and methodologies.
What are the Contents of the PMBOK?
The PMBOK is structured into knowledge areas, process groups and project management processes. The knowledge areas cover key disciplines required to manage projects, while the process groups define the stages of a project life cycle. Within each process group, various project management processes describe specific activities, tools and techniques needed for effective project execution. These components provide a structured approach to managing projects, ensuring alignment with industry standards and best practices.
The 10 PMBOK Knowledge Areas
PMBOK knowledge areas categorize different aspects of project management that are essential for success. Each knowledge area encompasses a set of processes that contribute to the overall management of a project. These knowledge areas ensure a holistic approach, addressing integration, scope, schedule, cost, quality, resources, communication, risk, procurement and stakeholders.
1. Integration Management
Integration management focuses on coordinating all project elements to ensure smooth execution. It involves developing a project charter, managing change and ensuring that different components work together effectively. Key processes include project plan development, directing and managing project work, monitoring and controlling project execution and performing integrated change control to align objectives, scope and resources.
2. Scope Management
Scope management ensures that all project requirements are defined and controlled. It includes processes for scope planning, defining deliverables, managing changes and preventing scope creep. Work breakdown structure (WBS) creation, requirements traceability matrix, scope validation, and scope baseline maintenance ensure alignment with project objectives while balancing stakeholder expectations.
3. Schedule Management
Schedule management involves creating and maintaining a project schedule. It includes defining activities, sequencing tasks, estimating durations and developing and controlling the schedule. Critical path method (CPM), schedule compression techniques like crashing and fast-tracking, resource leveling, milestone tracking and earned value management (EVM) ensure schedule adherence while managing dependencies and optimizing task sequencing.
4. Cost Management
Cost management is one of the most critical project management areas in the PMBOK as it allows project management teams to ensure that a project remains within budget. It includes estimating costs, determining budgets and monitoring expenditures to prevent overspending. Cost aggregation, funding limit reconciliation, reserve analysis, lifecycle costing, cost-benefit analysis and earned value analysis (EVA) provide financial oversight, ensuring cost performance index (CPI) and budget adherence throughout the project lifecycle.
5. Quality Management
Quality management focuses on meeting project requirements and customer expectations. It includes quality planning, assurance and control to ensure deliverables meet specified standards. Key elements include quality metrics, Six Sigma methodologies, statistical sampling, cause-and-effect diagrams, process improvement plans, continuous improvement (Kaizen) and cost of quality (CoQ) to prevent defects.
6. Resource Management
Resource management involves acquiring, developing and managing project resources, including team members, equipment and materials, to ensure efficient execution. Resource allocation, capacity planning, skills assessment, RACI matrix, team performance assessments, conflict resolution, virtual teams and resource smoothing strategies optimize workforce utilization while ensuring task accountability and efficiency.
7. Communications Management
Communications management ensures effective information exchange among stakeholders. It includes planning communications, managing stakeholder expectations and ensuring timely project updates. Key aspects include communication models, sender-receiver feedback loops, information distribution, communication channels, status reporting, stakeholder engagement matrix, escalation procedures and collaboration tools for transparency and alignment.
8. Risk Management
Risk management involves identifying, analyzing and responding to project risks. It includes risk planning, mitigation strategies and monitoring to minimize negative impacts. The PMBOK covers this knowledge area in detail, as it includes a variety of risk management tools and techniques such as risk register maintenance, qualitative and quantitative risk analysis, risk response strategies (avoid, transfer, mitigate, accept), contingency planning and periodic risk reviews.
9. Procurement Management
Procurement management handles the acquisition of goods and services from external vendors. It includes procurement planning, contract negotiation and supplier management. Key components include make-or-buy analysis, request for proposal (RFP) processes, contract types (fixed-price, cost-reimbursable, time and materials), vendor selection criteria, procurement performance audits and dispute-resolution strategies.
10. Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder management ensures that project stakeholders are engaged and their expectations are managed effectively. It includes stakeholder identification, analysis, communication and involvement strategies. Stakeholder engagement assessments, influence-impact grids, power-interest matrices, change management strategies, conflict resolution techniques, proactive stakeholder feedback loops and adaptive engagement models facilitate collaboration and stakeholder satisfaction.
PMBOK Process Groups
PMBOK process groups represent the five stages of a project’s lifecycle. These process groups structure project management activities to ensure organized execution from initiation to completion.
- Initiating: The initiating process group involves defining a project and obtaining necessary approvals. It includes developing a project charter and identifying stakeholders to establish a foundation for success.
- Planning: The planning process group focuses on outlining the project’s scope, objectives, schedule, budget and risks. It involves creating detailed plans to guide project execution and ensure alignment with stakeholder expectations.
- Executing: The executing process group involves carrying out the project plan by managing teams, coordinating resources and ensuring deliverables meet requirements. It focuses on achieving project objectives efficiently.
- Monitoring & Controlling: Monitoring & controlling ensures project performance aligns with the plan. It involves tracking progress, managing changes and mitigating risks to keep the project on course.
- Closing: The closing process group finalizes all project activities, ensuring deliverables meet expectations and documentation is completed. It includes obtaining stakeholder approvals and conducting post-project evaluations.
PMBOK Project Management Tools and Techniques
The PMBOK mentions a variety of project management tools and techniques that can be used to manage the knowledge areas throughout the process groups.
- Earned Value Management: A technique for measuring project performance using cost and schedule variances.
- Project Network Diagrams: Visual representations of project tasks and dependencies that help sequence tasks and estimate the duration of projects.
- Critical Path Method (CPM): CPM is a project scheduling method that identifies the longest sequence of tasks and helps project managers identify critical tasks that can’t be delayed or else they will affect the project’s overall duration.
- Gantt Charts: Bar charts that illustrate a project schedule, show task dependencies and allow to track the percentage of completion of tasks.
- Cost Estimating Techniques: Methods for predicting project costs, including analog and parametric estimating.
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT): PERT is a method for analyzing task durations under uncertainty. It helps accurately estimate the duration of tasks by using three time estimates, a pessimistic, optimistic and most likely scenario.
- Schedule Compression Techniques: These include methods like crashing and fast-tracking to shorten project duration without reducing the project scope.
- Rolling Wave Planning: A progressive elaboration technique for planning in stages. Near-term work is planned in detail while future work is planned at a higher level.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: A decision-making technique comparing the total expected costs of a project or decision to its total expected benefits to determine if it’s worthwhile.
- Work Breakdown Structure: A hierarchical breakdown of project deliverables to be carried out by the project team to accomplish objectives and create the required deliverables.

PMBOK Project Management Documentation
The PMBOK mentions a variety of project management documents that can be used to manage the knowledge areas throughout the process groups.
- Project Charter: A document that formally authorizes a project, outlining objectives, constraints, assumptions and key stakeholders. It defines project scope, high-level deliverables and success criteria and assigns a project manager. It also integrates enterprise environmental factors (EEFs) and organizational process assets (OPAs) to align strategic goals and governance frameworks.
- Team Charter: Outlines the purpose, goals, roles and guidelines of how a project team operates. It helps establish expectations and promotes effective collaboration through a RACI matrix, communication protocols, performance evaluation metrics and collaboration tools.
- Project Management Plan: A comprehensive document that outlines project execution, monitoring, control and closure. It’s the most important document in the PMBOK because it integrates subsidiary plans related to all project management knowledge areas, including scope, schedule, cost, quality, resource, communication, risk, procurement and stakeholder management. These plans ensure alignment with baselines, work performance data, earned value analysis (EVA) and project lifecycle methodologies like agile or waterfall models.
- Business Case: Justifies the need for a project by outlining cost-benefit analysis, feasibility study, return on investment (ROI), net present value (NPV) and payback period. A business case includes problem statements, risk assessments, funding requirements and strategic alignment with organizational objectives.
- Scope Statement: Defines the project scope, deliverables, acceptance criteria, constraints, assumptions and exclusions. It establishes the scope baseline, work breakdown structure (WBS), decomposition methods, requirements traceability matrix, product scope vs. project scope differentiation and control mechanisms to prevent scope creep.
- Risk Register: A log of identified project risks, mitigation plans, contingency responses, risk categories, probability and impact assessments and qualitative and quantitative risk analysis. It should also include risk triggers, secondary risks, risk response owners, SWOT analysis and risk audits to ensure risk management is proactive.
- Change Log: Tracks changes to project scope, schedule or budget to document change requests, change control board (CCB) decisions, integrated change control processes, impact assessments and root cause analysis. Change logs also focus on corrective and preventive actions, variance analysis, configuration management, change approvals, rejection rationales, lessons learned documentation and baseline adjustments for effective change governance.
- Stakeholder Register: A document listing project stakeholders and their interests, influence, engagement levels, expectations, concerns and preferred communication channels. It should include an influence-impact analysis, stakeholder feedback mechanisms, stakeholder prioritization strategies and adaptive communication approaches to ensure project buy-in and collaboration. The PMBOK covers other similar stakeholder management methods and documentation such as stakeholder maps, analysis and engagement plans.
- Issue Log: A record of project issues including resolutions, priority levels, impact assessments, assigned owners, escalation procedures, resolution timelines, issue dependencies and decision logs. Include any lessons learned from issue resolution, knowledge transfer strategies and integration with project governance frameworks for structured issue management.
Free Project Management Templates
With the PMBOK under one’s belt, project managers and their teams can use these free templates if they’re not ready to upgrade to project management software. We have over 100 free project management templates for Excel and Word that cover every aspect of a project across multiple industries. Here are just a few.
Project Plan Template
Make sure that all the guidelines and procedures of a project are planned with this free project plan template for Word. It covers everything from goals and success criteria to resources, procurement and budget.
Project Budget Template
Speaking about budget, such an important part of the project plan needs its own template. Use this free project budget template for Excel to accurately estimate labor and material costs, and then have the means to track them to stay on budget.
Project Dashboard Template
The project dashboard is an essential tool in project management. It provides a high-level overview of the project’s costs, workload and more. Use this free project dashboard template for Excel to track key project metrics and stay on schedule.
How ProjectManager Helps Implement the PMBOK
The PMBOK sets the rules and defines the terms, but it takes more power than an Excel spreadsheet to plan, manage and track a project. These free templates give one a taste of project management, but it’s mostly a tease that doesn’t deliver on the promise of project management software. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software that has multiple project views to plan and execute projects in whatever methodology is being applied. But it goes further to help with resource management and tracking in real time.
Robust Resource Management Keeps Teams Productive
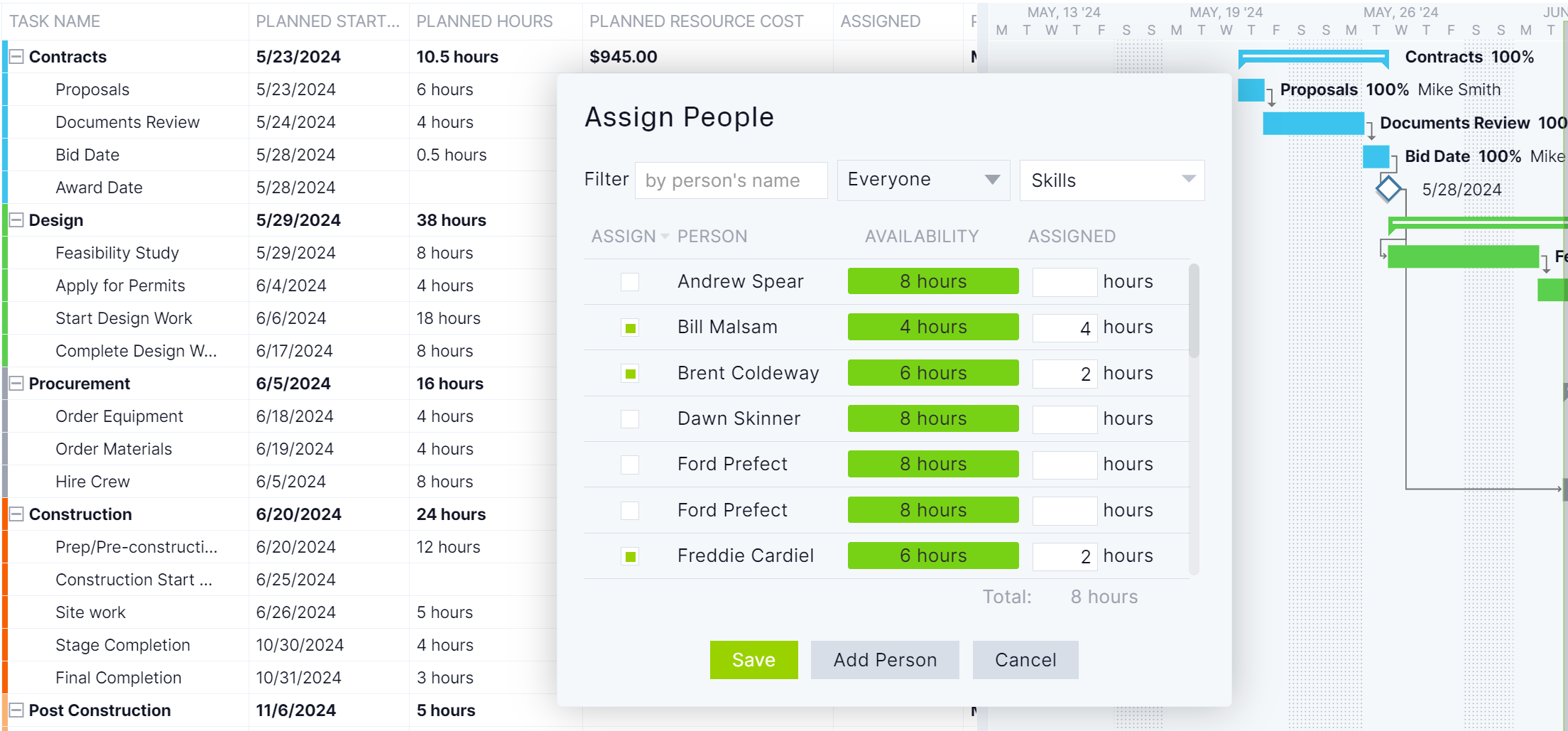
After human and nonhuman resources are scheduled on the Gantt chart, before assigning the team tasks, set the team’s availability. This includes any PTO, vacation, global holidays, pay rates and skill sets. It makes it easier to assign the right person to the right task at the right time. Then, check resource allocation by opening the color-coded workload chart. It shows who’s overallocated or underutilized. The team’s workload can then be balanced to keep everyone working at capacity without risking burnout.
Real-time Project Management Dashboards and Reports
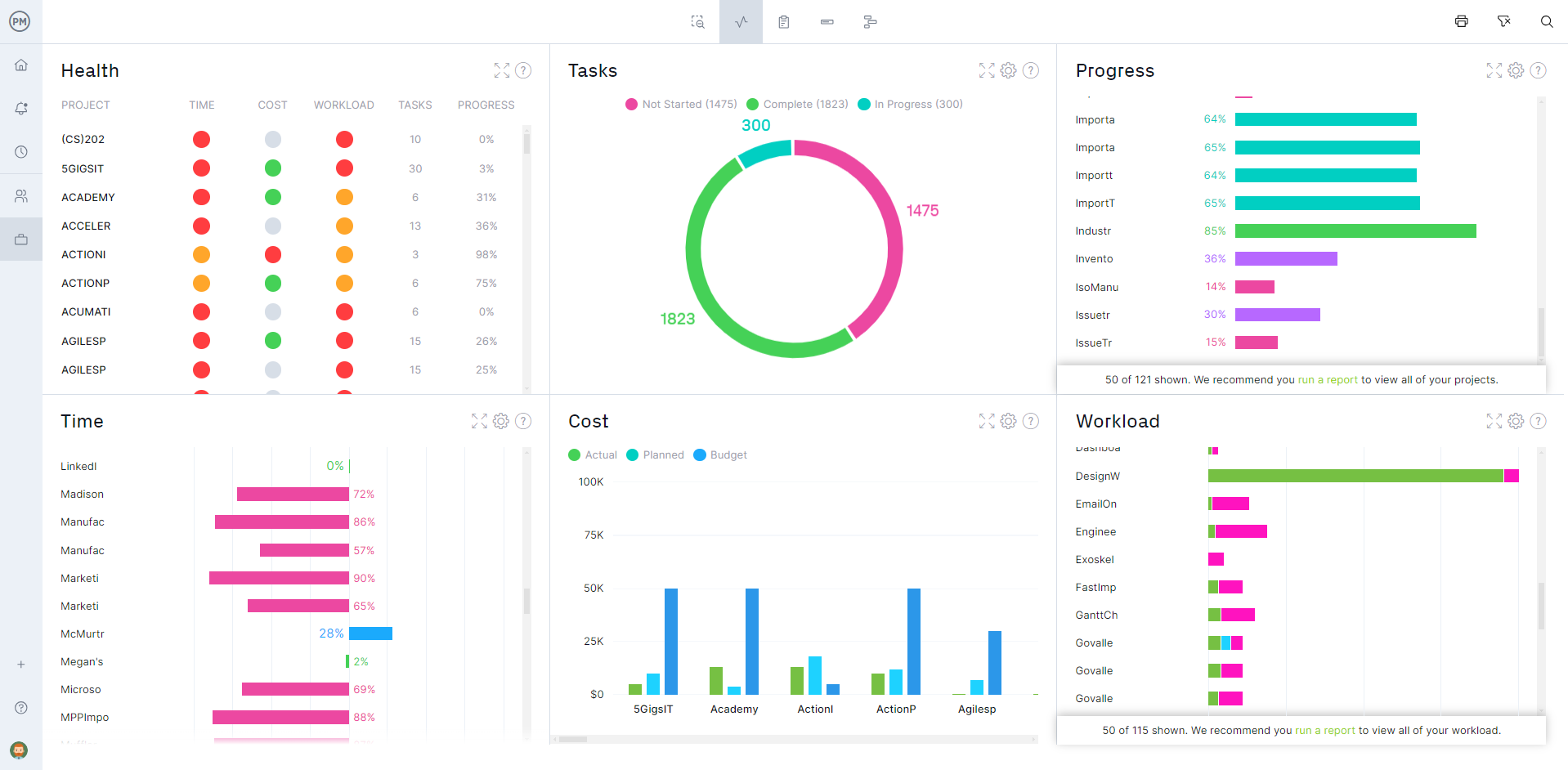
Monitoring and controlling projects is a big part of the PMBOK. That’s covered in our software in multiple ways. For a high-level project overview, toggle to the real-time project or portfolio dashboards that collect live data and display it on easy-to-read graphs and charts that monitor key metrics such as time, cost, workload and more. Customizable reports go deeper into the data and can be filtered to focus on key data points or summarize progress and share with stakeholders. Even our secure timesheets help manage the budget by tracking labor costs.
PMBOK FAQs
These are some of the most frequently asked questions about the PMBOK that can be found online.
Is the PMBOK Free?
No, the PMBOK is not free. However, if you acquire a PMI membership for an annual fee, you may access the PMBOK at no additional cost. This is also true for students or employees from organizations with a PMI partnership. Another way to access the PMBOK at no cost is to find a public library that has a physical or digital copy.
Where Can I Buy the PMBOK?
The most common methods to purchase the PMBOK are to buy it directly from the PMI website or through online vendors like eBay, Amazon, Google Play or Apple Books. On the other hand, some buyers might prefer brick-and-mortar bookstores such as Barnes & Noble, books-a-million or local independent bookstores.
How Much Does the PMBOK Cost?
The price of the PMBOK varies depending on the seller, the format (paperback, spiral-bound or eBook), the condition (new or used) and other variables that might cause prices to fluctuate. The prices for the seventh edition of the PMBOK listed below are current as of the publishing date of this blog.
- PMI: Access to the PMBOK through a subscription of PMIstandards+ for $8 per month
- Amazon: Paperback $57.45 – $77.94, spiral-bound $93.44 or Kindle version $74.05
- Google Play: Ebook $99, free limited sample
- Apple Books: Ebook $99.99
- eBay: New and used copies available from $35 to $79
- Barnes & Noble: New $65.95, used $47.31
What Is the Latest Edition of the PMBOK?
The latest edition of the PMBOK is the seventh edition, published by the PMI in August 2021. This edition introduces significant changes, including a shift from the traditional process-based approach to a principle-based approach, structured around eight project performance domains and 12 key project management principles.
The previous edition, the sixth edition, was published in September 2017. The PMI typically updates the PMBOK every four to five years to reflect evolving practices in project management. As of February 2025, there is no official announcement regarding the release of an eighth edition.
PMBOK Related Content
For those interested in learning more about project management, below are links to some of the more recent posts we’ve published on our blog that cover the basics.
- Project Management Basics: Definitions, Methods and Tools
- Project Management Skills: Soft, Hard & Technical Skills
- Best Project Management Certifications
- Project Management Tools & Techniques
- Best Project Management Charts for Project Planning
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that allows project management teams to implement PMBOK concepts. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who use our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

