In the context of product development and project management, requirements are the specifications or characteristics that a product or project deliverable must have to meet government regulations, achieve business goals, or satisfy the expectations of customers, project sponsors, or any other stakeholder group that’s vested in the project.
To satisfy these requirements, there are lots of tasks that must be done in order to deliver a final project. That includes the features, functions and so forth. Tracing those features can ensure that none slip through the cracks, a process that’s best completed by using a requirements traceability matrix.
If you’ve never heard of a requirements traceability matrix and you’re managing a project or developing a product, you’ll need a crash course. We’re going to explain what requirements traceability is, how to make a requirements traceability matrix and explore the different types to help you ensure all of your project requirements are fulfilled.
What Is a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)?
A requirements traceability matrix is the document used to track the requirements as it moves through the product development process. It’s the documentation that confirms that all product requirements have been fulfilled. It lists the requirements, tests, test results and any issues that may have come up over the course of testing that needs to be addressed to bring the project to a successful close.

Get your free
Requirements Traceability Matrix Template
Use this free Requirements Traceability Matrix Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
The requirements traceability matrix is a document that maps user requirements with test cases. The document captures all client requirements and traces those throughout the product development. This document is then delivered at the end of the software development life cycle. The main purpose is to ensure all requirements are accounted for and have been checked with test cases. No functionality should be left unchecked at the end of this process.
Project management software helps you track every step of your product development and make sure you’re fulfilling your requirements along the way. ProjectManager is online software with features that help you track requirements in real time. Kanban boards can be customized for requirements tracing, providing transparency into each step and automation to move to the next status. Task approvals can be set to ensure that quality expectations are met throughout the process. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
When to Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
A requirements traceability matrix can be used anytime there’s a project that’s geared towards the production of a final deliverable that must meet stakeholder requirements.
However, RTMs are mostly used in product and software development, as these industries involve the creation of complex products with lots of requirements, but they can be used for projects in other industries.
As products become more complex, so do requirements, which are overseen by multiple individuals across departments in an organization as they go through the development process, which is why a requirements traceability matrix is a way for product development teams to keep track of these requirements and make sure they’re fulfilled.
Not only that, but each decision made over the course of the project will impact the project’s requirements. For example, in many cases, stakeholders like clients or executives will add new requirements during the product development process, so having a tool to document requirements and understanding their impact is crucial.
What Should Be Included In a Requirements Traceability Matrix?
This crucial document consists of various parts. Below are various components to include in a requirements traceability matrix.
Requirement General Information
The requirements section consists of several details about the requirements themselves. They offer context and essential information that the project team will utilize.
- Requirement ID: A unique identifier for each requirement.
- Requirement Description: A clear and concise description of the requirement.
- Source: The origin of the requirement (e.g., stakeholder, document, regulation).
- Priority: The importance or urgency level of the requirement.
Types of Requirement
This section categorizes the requirements to keep them organized. It also helps with analysis.
- Business Requirements: High-level objectives that outline the product’s value and purpose. Business requirements help address market needs, specify the ideal outcomes and align with strategic goals.
- Functional Requirements: These are specific features or functions that the product needs to perform to meet user needs. It may include workflows, interactions or capabilities.
- Non-Functional Requirements: These include standards linked to the product’s operation as a whole, including its safety, quality or reliability.
- Technical Requirements: These requirements outline the needed systems, technologies or tools to create and support the product. It may include materials, manufacturing processes, integration with existing systems, etc.
- Regulatory Requirements: Regulatory requirements ensure the product complies with legal guidelines, industry standards and safety regulations. They help mitigate risks and protect users.
- Performance Requirements: These criteria measure how effective the product is under certain conditions including capacity, durability and speed. They ensure the product performs optimally.
- Usability Requirements: Conditions that improve the user experience by ensuring the product is not only intuitive but accessible and easy to use. They focus on the simplicity of the design and overall customer satisfaction.
- Maintenance Requirements: These guidelines ensure the product is functional and efficient throughout its life cycle. They include repairability, spare part availability, customer support, etc.
Potential Risks
In the potential risks section of the requirements traceability matrix, list the factors that could impact the fulfillment of a requirement. This could be resource restrictions, market uncertainties or technical challenges. The earlier these risks are identified, the better as it can help mitigate cost overruns, potential delays or failures.
Requirement Status
This is the current progress of a requirement such as draft, in progress, approved or completed. Information from the requirement status helps provide visibility into the development stages and brings light to potential bottlenecks. It also ensures that requirements are delivered within the defined timeline.
Requirement Owner
As the name suggests, the requirement owner is the individual or team who is responsible for ensuring a particular requirement is fulfilled. The requirement owner needs to clarify details, coordinate with other stakeholders and address issues to ensure the implementation is successful.
Acceptance Criteria
Acceptance criteria in a requirements traceability matrix are the measurable conditions that a requirement or deliverable needs to meet before it is considered complete. It ensures the alignment with the project goals, validates the quality and offers a clear basis for approval by stakeholders.
Test Cases
Test cases in a requirements traceability matrix provide detailed scenarios that help validate whether a requirement has been implemented successfully. The result ensures functionality, usability and performance that aligns with specifications.
Requirements Traceability Matrix Example
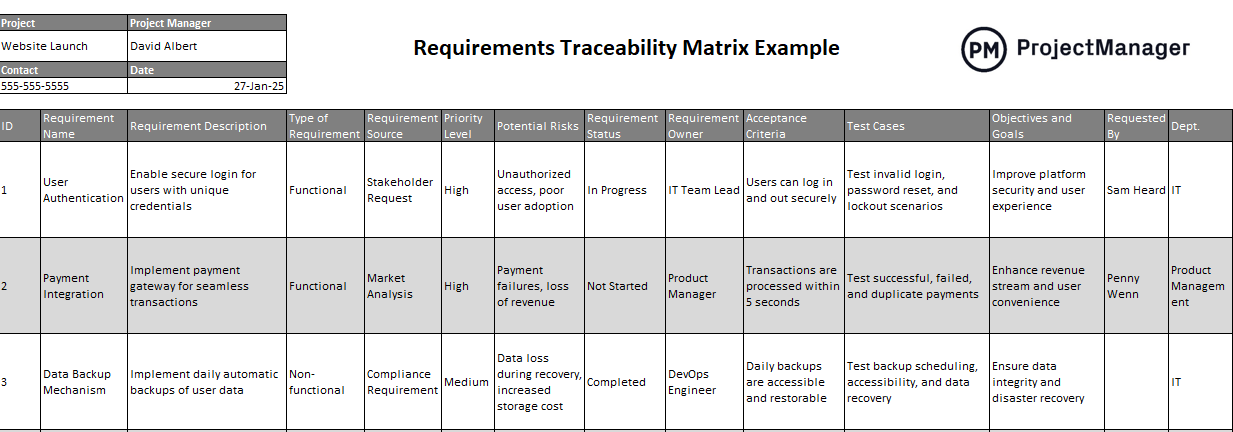
The best way to learn what a requirements traceability matrix works is to take a look at an example. The requirements traceability matrix example below shows three requirements that a software company is carrying out to improve the user experience for its product. As you can see in the image below this RTM shows a description of each requirement, their source, priority level, acceptance criteria, and all of the other elements that were previously outlined in this blog.

Who Makes the Requirements Traceability Matrix?
Multiple stakeholders typically collaborate to gather the requirements for an RTM. Common roles involved in the process include:
- Business analyst: Gathers and documents business objectives and needs.
- Project sponsors and stakeholders: Provide high-level strategic objectives and business goals.
- Product managers: Outline product features using market research, competitive analysis and customer feedback.
- Subject matter experts: Provide specialized knowledge to ensure compliance with industry standards or technical feasibility.
- End users and customers: Offer insights on pain points and desired features.
- Regulatory and compliance teams: Outline mandatory requirements to adhere to industry standards and laws.
- Engineering and development teams: Provide feedback on technical constraints, system capabilities and feasibility.
- Quality assurance teams: Suggest testable criteria to confirm that the requirements can be met.
How to Create a Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM)
Used in software testing and product development, a requirements traceability matrix is an important tool to make sure you fulfill every user requirement. No project should be without one, which is why we’ll take you through a step-by-step guide to making your own requirements traceability matrix.
1. Identify Requirements
The goal of a requirements traceability matrix is to track the user or stakeholder requirements for the project, and it’s easiest to list them on a spreadsheet. But an RTM can be used for a variety of things. For example, you can make sure your requirements have been tested or are compliant. You can also determine which requirements are impacted if something changes. Regardless, the first step is to define the types of requirements that will apply to the project and meet with stakeholders to get a more detailed description of each.
Based on your goal, you’ll start to collect relevant artifacts that include at least the requirements, test cases, test results and issues. After you’ve collected the artifacts, you’ll want to get the most current requirements documents. Each requirement should have a unique ID number that doesn’t change, even if the requirement is reordered. Test cases also need to be defined and given a status. For example, they might be started, done or blocked. If the test fails, then whatever issues led to that failure should be detailed.
3. Create Requirements Traceability Matrix
Now you’re ready to build the RTM. Use a spreadsheet and make four columns. Each column will be for an artifact. The first column outlines the requirements lists, the next has the tests and following that are the test results. You’ll also have a column for issues. This is the bare minimum and you can add more as needed for your project. For instance, a column that numbers each of the requirements would be useful.
4. Copy and Paste
You’ve done the work and now you have to add it to the requirements traceability matrix. Simply add the requirements, test cases, test results (if you have them at this point) and issues to the spreadsheet.
5. Revive the RTM
The requirements traceability matrix is a living document that’ll you’ll often reference for updates. As requirements change, so does the RTM. Some requirements might drop from the project or another test case may be added; all of these changes need to be reflected in the requirements traceability matrix. The requirements ID number, however, should stay the same even if the requirement is reordered or reused.
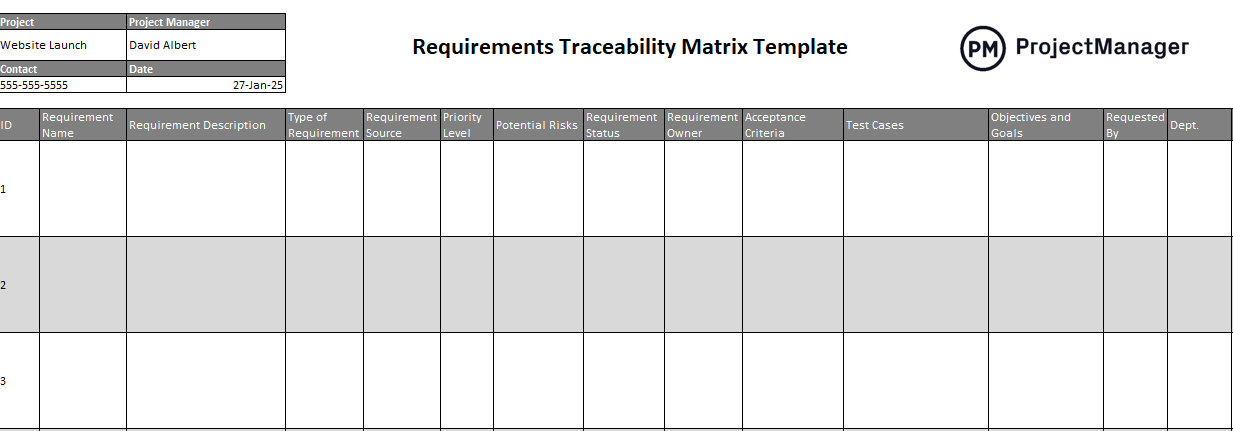
Free Requirements Traceability Matrix Template for Excel
Because you’ll be using the requirements traceability matrix throughout the project, it’s helpful to download our free RTM template for Excel. Once you’ve downloaded the free requirements traceability template for Excel, all you have to do is fill in the blanks to create a document of your requirements, tests and issues.
Benefits of Using a Requirements Traceability Matrix
Requirements traceability comes with many benefits. For one, it ensures that each critical project requirement and the delivery of a viable product has been fulfilled. Tracking these variables over the life cycle of a project can be difficult over the product development life cycle, and having documentation solidifies that you’re not missing any vital points.
Having the visibility of requirements traceability into requirements such as design, development, testing and support, minimizes negative outcomes and maximizes productivity. Other benefits include improving team efficiency, easier compliance with regulations and higher-quality products.
Project management software helps you track every step of your product development and make sure you’re fulfilling your requirements along the way.
Types of Requirements Traceability Matrices
Now that we know what a requirements traceability matrix is and how to create one, let’s look deeper into the topic. There are three different types of requirements traceability matrix: forward traceability, backward traceability and bidirectional traceability. Let’s take a moment to define each.
Forward Traceability
The forward traceability matrix is used to see the requirements of the test cases. This allows for each of the requirements to have a test and also allows one to know that the project’s trajectory is positive.
Backward Traceability
Backward traceability maps the test cases with the requirements. This is done to avoid scope creep and going beyond the initial requirements without cause to do so.
Bidirectional Traceability
As you might guess, a bidirectional traceability matrix is one that combines the forward and the backward traceability in one document. This ensures that every requirement has a related test case.
It’s clear how important a requirements traceability matrix is for project management. If you miss a requirement, you might not deliver what users want. Having a list of those requirements and being able to map them in whatever direction is best for your project ensures that all have been included. But you can also see that they involve a lot of work and manual labor to create, fill in and update.
ProjectManager Helps Track Requirements
ProjectManager is online project management software that allows you to track requirements in real time. Plan, schedule and track requirements all in the same tool. As teams implement and test requirements, everyone gets transparency into the process to ensure that nothing is neglected.
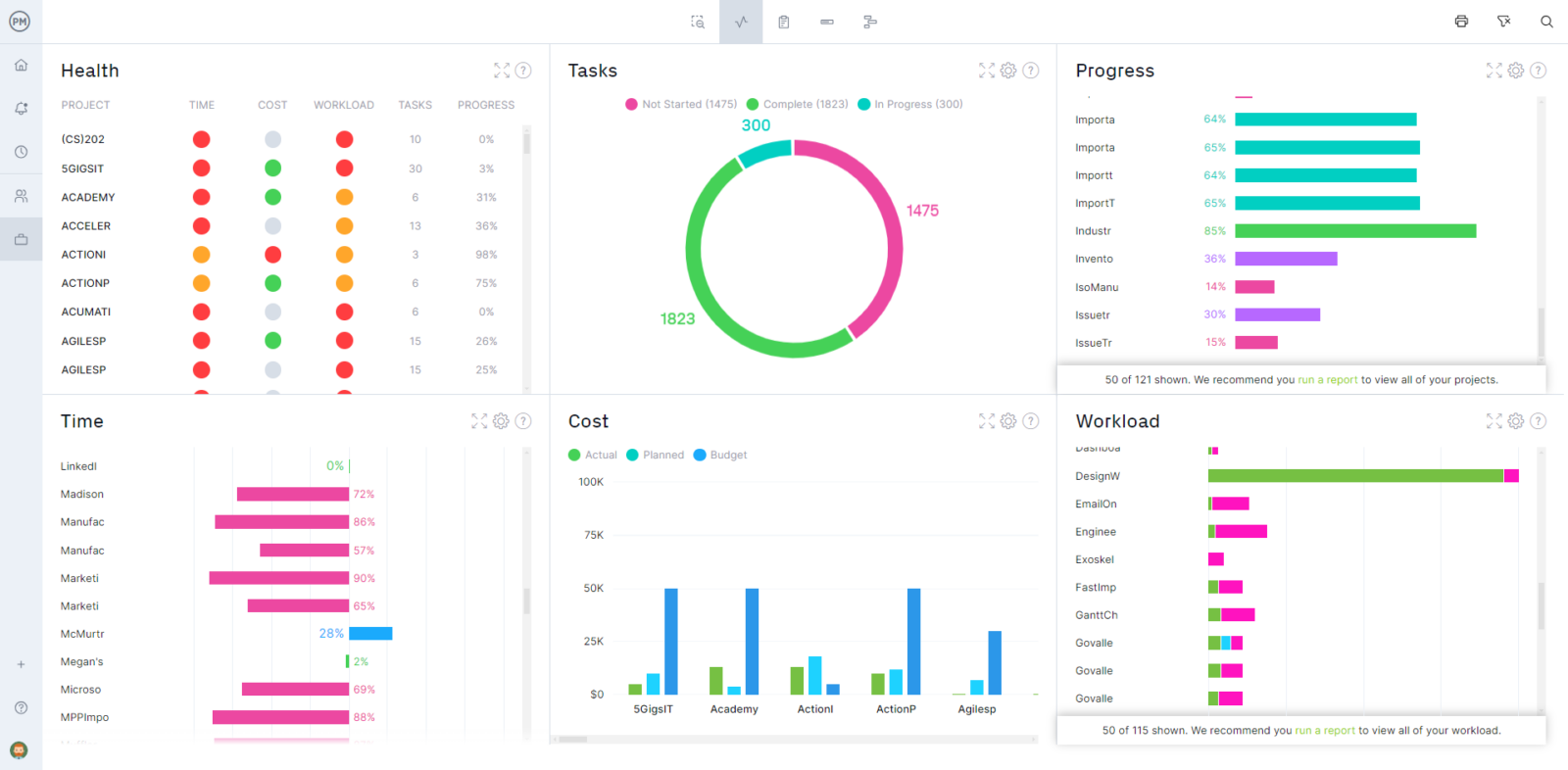
Get Overview With Real-Time Dashboard
Whenever you need a high-level view of the requirements and testing, you can look at our real-time dashboard. It automatically collects live data and crunches the numbers to show you six metrics in easy-to-read graphs and charts. Monitor your team’s workload, tasks and time while also checking on costs and more. Best of all, there’s no setup required.

Dive Deeper Into Data With Customizable Reports
When you need more detail than the dashboard can deliver use our one-click reports. You can generate reports on status or portfolio status if you’re managing more than one project. But there are also reports on time, cost, variance and more. All can be filtered to report on only the data you want to see to help you make more insightful decisions. They can easily be shared to keep stakeholders updated.
Our software helps you plan, schedule and track work in real time. Stay on top of changes with notifications and even comment and share files across departments. Everyone is always working on the same page which helps productivity. Add to that features for task and resource management and you have an all-around project management software.
ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that helps you work more productively and track that work to stay on schedule. Connect teams, departments and even outside vendors to facilitate communication and keep everyone working better together. Join teams at NASA, Siemens and Nestle who use our tool to deliver success. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.