If someone asked how much value you get from a day of work, what would you say? Odds are, you’d give one of the customary responses — a fair amount of value, not much value, a lot of value, etc. Unfortunately, these answers aren’t helpful and aren’t valuable to projects.
The schedule performance index was created to eliminate the guesswork and give a specific, quantifiable answer to the question, as well as show where improvements need to be made for maximum efficiency.
What Is the Schedule Performance Index?
Schedule performance index (SPI) is part of a greater project performance measurement method called earned value management (EVM). The SPI itself is a ratio of earned value to planned (or actual) value. Depending on the integer, SPI reflects a project being on schedule, behind schedule or ahead of schedule.
Another way to think about the schedule performance index is how we measure the value of work completed. SPI does this by comparing the progress we planned to make to the actual progress made. In other words, how accurate is our project schedule? Deviations from this project schedule are indicative of a number of things to be aware of.
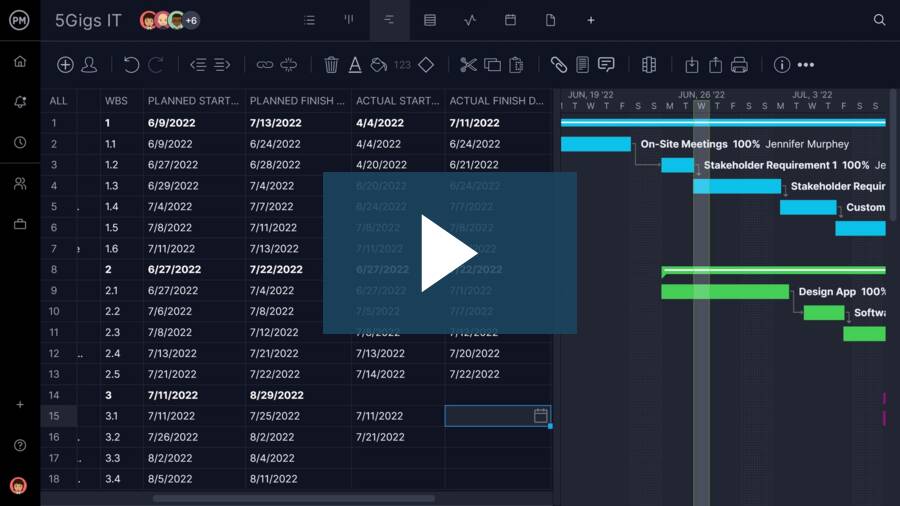
Tracking planned versus actual data is much easier with the help of project management software. ProjectManager, for instance, lets you create schedules with Gantt charts and leverage baselines, planned data, actual data and even critical path calculations. It’s never been easier to keep your schedule on track. Get started today for free.
Schedule Performance Index Key Terms
To understand the schedule performance index and how to calculate it for yourself, you must be familiar with a few key terms. Each of these is an important part of the SPI equation.
- Earned Value Management: Earned Value Management (EVM) is a technique used to measure the performance of a project. Calculating the schedule performance index is part of this process.
- Planned Value: The Planned Value (PV) represents where on the project schedule you planned to be. Another way to think of planned value is as how much you had expected to accomplish by a certain point in time. This usually takes the form of hours worked, or, sometimes, units produced.
- Earned Value: The Earned Value (EV) is the reality; where on the schedule a project is at. Ideally, this number is close to, or the same as, the planned value, meaning everything is on schedule. An SPI calculation confirms this.
- Schedule Variance: Schedule Variance (SV) is another type of calculation in the EVM method, and it’s important to know how it differs from SPI. Schedule variance measures how much a project is diverging from the initial schedule. SPI, on the other hand, measures the ratio of how much work was done to how much work was planned (scheduled).
- Cost Performance Index (CPI): The cost performance index is often confused with the schedule performance index. Cost performance index is the measure of the value of work in comparison to cost. In other words, work is divided by cost. This differs from the schedule performance index, in that CPI measures cost efficiency while SPI measures time efficiency.
Related: Free Project Schedule Templates
The Schedule Performance Index Formula and How to Calculate SPI
To find the schedule performance index, you must first find the planned value and the earned value. SPI is then calculated by dividing this earned value integer by the planned value integer. Therefore, the schedule performance index is a ratio of earned value to planned value. When you know your earned value and planned value, calculating SPI is as simple as dividing the two.
The SPI Formula
Schedule performance index (SPI) = Earned value (EV) / Planned Value (PV), or SPI = EV/PV
Schedule Performance Index Example
For this example, the project in question is scheduled to last 8 months. During that 8 months, 200,000 units of a product must be made. At the two-month mark, the project managers decide to calculate SPI.
Find Earned Value
First, you must find the earned value (EV). This is as simple as accounting for the number of units created so far. In this example, 40,000 units have been made at the 2-month mark.
EV = 40,000
Find Planned Value
Next, you must find the planned value. Assuming you planned to complete the same number of units each month, that means you would have to create 25,000 units per month. So, after 2 months, you should have made 50,000 units.
PV = 50,000
Calculate SPI
Once you know the earned value and plan, all you need to do to find SPI is divide EV by PV. This quotient will be a number greater than, less than or equal to one. In this example, that will look like this:
40,000 (EV) / 50,000 (PV) = .8
SPI = .8
This .8 (80%) indicates that the project is behind schedule and is only running at a level of 80% efficiency. That means there needs to be a 20% improvement to get back on schedule.
What Does Your SPI Result Mean?
To understand your results, you must know what different SPI numbers symbolize. For example, an SPI above 1 equates to being ahead of schedule, whereas an SPI under 1 means you’re behind schedule. And, if your SPI is equal to 1, your project is exactly on schedule. In summary:
- SPI > 1: Project is ahead of schedule; more work has been completed than expected
- SPI < 1: Project is behind schedule; less work has been done than planned
- SPI = 1: Project is on schedule; earned value and planned value are equal.
Why Is the Schedule Performance Index Important?
Calculating the schedule performance index is how we assess the accuracy of a schedule and how on schedule a project is running. Depending on the schedule performance index, it may be necessary to rethink how the schedule baseline was created or make other adjustments. These adjustments might include creating more padded schedules in the future, redistributing workload, expanding teams and a variety of other actions.
The schedule performance index is especially helpful for calling attention to issues before they worsen. If a project is behind schedule, the SPI will reflect this and indicate changes that need to be made.
Another way to think about a schedule performance index is as a means to see how much work is being completed compared to how far along a project is. When we think about it from this perspective, the schedule performance index is a measure of efficiency.
When Should I Calculate the Schedule Performance Index?
A schedule performance index should be calculated at regular intervals throughout a project. Falling behind schedule is one of the top causes of project failure, and creating an SPI is a simple way to be proactive.
You can decide on these intervals as you’re creating your schedule, as they may be different depending on the type of project and the length of the project. The important thing is that the SPI is calculated regularly.
How ProjectManager Helps You Track Your Schedule
ProjectManager allows you to see your project schedule across multiple views, depending on your preference. Monitor your project on a Gantt chart and a traditional calendar view without jumping between Google Calendar and your project management tool.
Use the online Gantt chart to set baselines to automatically compare things like planned value and earned value. No more struggling with equations and risking mistakes. Our tool does all the calculations for you, in real time, so that you’re always viewing the most current information.
Learn more about the Gantt chart and how our scheduling software works by watching this short video.
And, when you want to check in on the status of tasks, available resources, project budget, overall health and more, use the project dashboard as your command center for everything you need to make smart project decisions.

ProjectManager is an award-winning tool that helps you schedule your project and gives you the tools you need to keep that schedule on track. Stick to your schedule performance index and make your next project a success. Try ProjectManager for free today!