Often the adjective “smart” is just a marketing ploy. Is your smartphone really that intelligent or is it just an example of advanced technology? Not that there’s anything wrong with being technologically advanced. Would you want to give up the advantages of your smartphone? Smart manufacturing is the same thing; it’s a way to produce better with emerging technologies.
Just as a smartphone is a leap forward from the old-fashioned cell phone, so is smart manufacturing to traditional manufacturing. Of course, manufacturing has a long history and has made many advancements over time. Let’s review smart manufacturing and smart factories and explore some examples of smart manufacturing technologies.
What Is Smart Manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing is a term that applies to a wide range of manufacturing that all share the use of computers and other emerging, advanced technologies. The goal is to increase the efficiency of manufacturing processes.
The term smart manufacturing was first used in the mid-2000s as new technologies such as 3D printing or additive manufacturing and artificial intelligence became more prominent. Under the umbrella of smart manufacturing are many types of manufacturing, such as digital manufacturing and cyber manufacturing.
This approach is new and manufacturers globally are still trying to define standards and even what smart manufacturing even means. One thing that smart manufacturing does is improve processes through better connection and communication across manufacturing systems. This streamlines processes and prevents systems from working in isolation but rather more collaboratively.
Smart manufacturing relies on identifying issues in manufacturing systems and finding solutions to add efficiencies to the processes. Project management software can be a tool for achieving these goals. ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that delivers real-time data that enhances control and facilitates smart manufacturing.
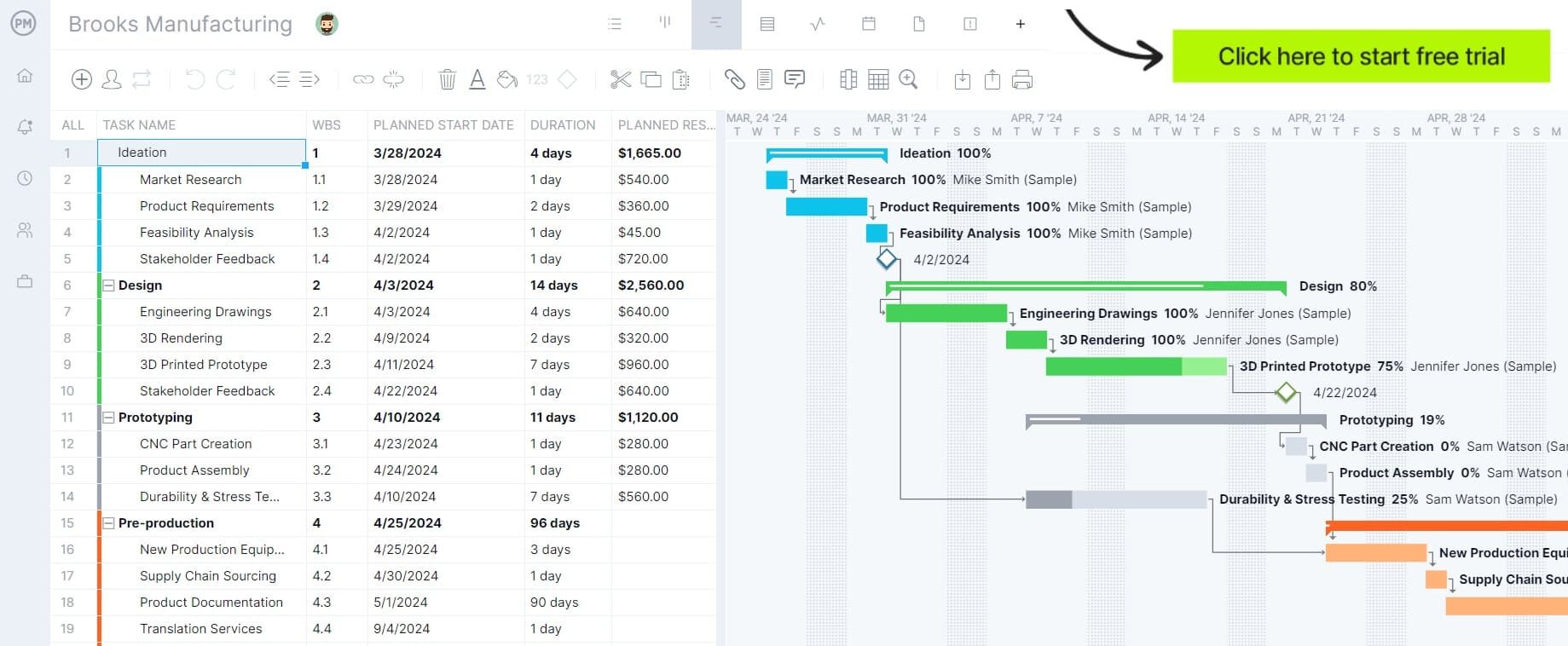
Gantt charts capture live data and allow for dynamic updates to the schedule, reflecting actual production process. Real-time visibility helps track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as resource utilization so managers can make data-driven decisions. Get started with ProjectManager for free.
What Is a Smart Factory?
Smart manufacturing works hand-in-hand with smart factories. A smart factory is an interconnected network of systems and computing that analyzes data, drives automated processes and even learns to make improvements to efficiency and more. Some call these advancements in manufacturing Industry 4.0 or the Fourth Industrial Revolution. This manufacturing revolution is the result of digital transformation and intelligent automation.
Automation and even robotics are nothing new in manufacturing. But a smart factory connects all the siloed systems, such as the people, assets and data management. Smart factories integrate people, machines and big data into a single, digitally connected system, which collects and analyzes that data. It’s constantly learning, interpreting and gaining insights to forecast trends and events. It even recommends workflows and automated processes.
Smart factories have a basic structure of data acquisition, data analysis and intelligent factory automation. This process, involving artificial intelligence, modern database technologies, machine learning, etc., leads to greater productivity and efficiency in manufacturing processes. It also helps manufacturers deliver more sustainable products, higher product quality and, in so doing, improves customer experience.
Get your free
Production Schedule Template
Use this free Production Schedule Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
Examples of Smart Manufacturing Technologies
Smart manufacturing is ever-evolving and continues to develop, but it’s already vast in terms of the technologies that are used to achieve its goals of greater efficiency. The following are some of the smart manufacturing technologies that are being employed by manufacturers in smart factories to improve their production processes.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things enables smart manufacturing to have full visibility of its assets, processes, resources and products. This streamlines business operations, optimizes productivity and improves return on investment (ROI). It does this by connecting equipment, integrating diverse industrial data, securing industrial systems and protecting a manufacturer’s intellectual property.
Big Data Analytics
Big data is simply a larger, more complex data set, often from new data sources. This provides manufacturers with insights into production processes that allow them to employ predictive maintenance and optimize product design and performance. Manufacturers can also use big data to track, trace and analyze their supply chain to streamline it.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The burgeoning field of artificial intelligence is also impacting artificial intelligence in terms of improving production data and prediction and maintenance planning. This helps manufacturers save money maintaining their production lines, but it can also help with more accurate demand forecasting, inventory tracking and even improving safety.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented reality assists manufacturers by simplifying the prototyping process. It helps designers visualize the products they’re developing to see how they’ll perform in a real-world situation. One benefit of this technology is that it reduces the cost of creating physical models. It also helps with quality assurance, which can be done in augmented reality to capture any issues before the product is placed into production.
Machine Learning
Unlike artificial intelligence, which is software designed to mimic human thinking to perform complex tasks, machine learning uses algorithms trained on data that then create models to perform complex tasks. Machine learning in manufacturing will analyze the raw data from factory machines to help conserve energy and predict future consumption, which allows for better planning.
Robotics
Robotics has been used in the production of products for a long time, but even this relatively established practice has benefited from improvements in digital technology. Their use can be divided into three types: material handling, processing operations and assembly and inspection. Robotics automate repetitive, menial tasks, work faster than humans and maintain a higher level of quality on the production line.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has given manufacturers the ability to use data remotely, where in the past it was necessary to have on-premises hardware and software. It works with the Internet of Things to collect machine data and store it for later processing. Sharing capabilities and resources online helps manufacturers both in production and by providing customers with a streamlined process for ordering and delivering products.
Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual model of a physical object. In smart manufacturing, the use of digital twins can increase efficiency and productivity by monitoring and analyzing performance and solving problems quickly. That reduces downtime and maintenance costs. It also helps manufacturers to build better products, find physical issues faster and predict outcomes more accurately.
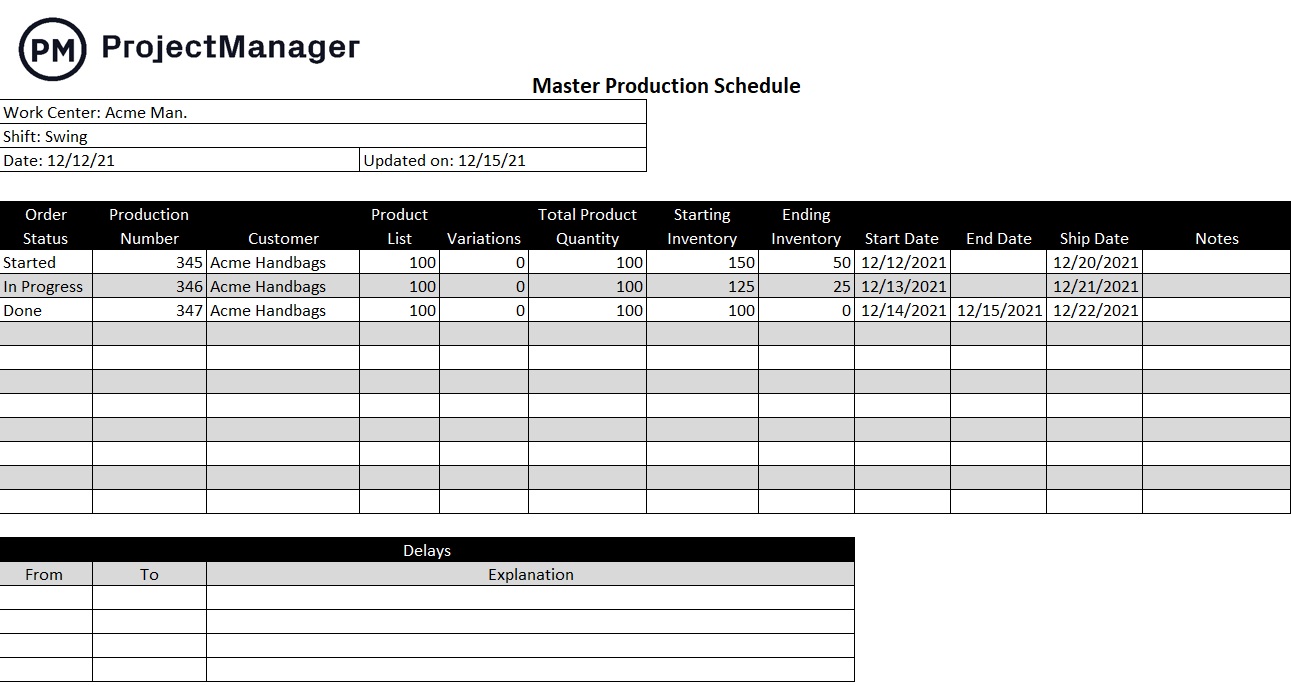
Free Production Schedule Template
Smart manufacturing is all about productivity and efficiency. One way that manufacturers can be more productive is by using templates. Download our free production schedule template for Excel to improve your supply chain management, track targets, manage deliveries and allocate resources.
Benefits of Smart Manufacturing
We’ve already written about some of the benefits of smart manufacturing, but it’s a growing process in manufacturing and deserves a bit more attention to explain its popularity. For one, as we’ve noted, it boosts productivity through better data access across the entire supply chain with real-time data, updated logistics and more.
Because it’s constantly monitoring production in all its aspects, smart manufacturing also creates advanced maintenance. From production to delivery, it monitors and analyzes processes to forecast maintenance and keeps machinery running without undue disruptions of the production line.
Smart manufacturing also helps manufacturers big and small to ideate, manufacture and launch products. They have better working prospects, greater access to insightful data, reduced waste and improvements to process management. All of this allows manufacturers to innovate faster and get those new products to market quickly.
What Industries Use Smart Manufacturing?
Just as manufacturing is used by many industries so, too, is smart manufacturing. You’ll find smart manufacturing being used in industries as diverse as energy and power, automotive, oil and gas and electronics and semiconductor industries. You can find it at the Tesla Gigafactor in Germany, which is a smart factory featuring solar panels for more sustainable production processes and a reduction in operating costs.
The consumer electronics and home appliances manufacturer the Haier group in China also employs a smart factory to encourage the implementation of artificial intelligence in its manufacturing process. The smart factory also improves quality detection, maintenance, machine collaboration, material transportation, energy management and security.
In the U.S., BJC Healthcare uses smart manufacturing and has a smart factory incorporating the Internet of Things in its processes. It uses radio frequency identified (RFID) technology to track medical supplies. For BJC Healthcare, smart manufacturing has reduced costs, increased the efficiency of its operations and improved the overall functioning of its company.
How ProjectManager Helps Manufacturers
Smart manufacturing depends on digital technology. ProjectManager is online project management software that delivers real-time data and a collaborative platform that helps manufacturers make more informed decisions. Our online software means that manufacturing processes across the globe can be controlled from one central hub, planning, managing and tracking all manufacturing processes anywhere and at any time.
Streamline Processes With Automated Workflows
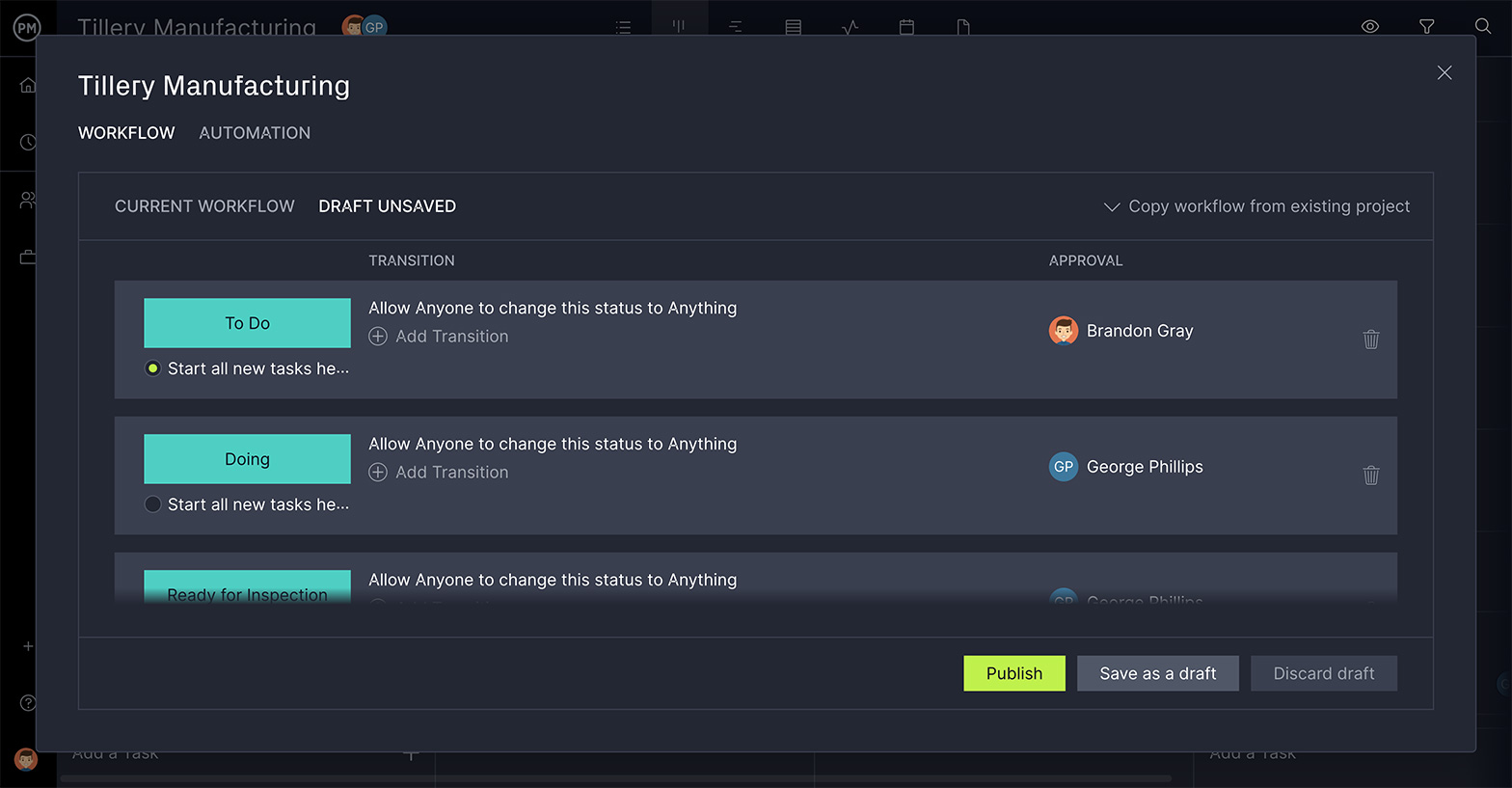
Our automated workflow feature requires no experience with coding. It works with simple “when” and “then” language that defines triggers and actions. Users can set as many triggers as they need, such as status, priority, progress and more. These then will set off an action to change the status of the work, assign a user, add tags and more. This removes the human element and creates greater production efficiency. There are also task approvals to ensure that only an authorized user can move the production forward to make sure that only quality is delivered.

Gain Valuable Insights With Customizable Reports
Smart manufacturing works by collecting and analyzing data to reduce waste and improve productivity. The real-time dashboard is a great tool for a high-level view of production, but when you need more detail just toggle over to the reporting feature of our software. There you can quickly generate status reports or portfolio reports if you’re managing more than one production line. There are also reports on variance, workload and more to give you a full picture of the project in real time. All reports can be filtered to show only the data you want to see and then can be shared in a variety of formats to update stakeholders.
Our software not only helps you automate production, and capture and analyze data but also gives you risk management features to identify and mitigate issues in your production line. There are resources management tools to balance workload and keep your workforce productive and task management features to help everyone work at capacity.
ProjectManager is online project management software that connects teams and empowers them to collaborate. They can share files, comment at the task level and work together whether on the factory floor or in an office. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.