Manufacturers have a handful of processes they use to make their products. There are five types of manufacturing processes: repetitive, discrete, job shop, continuous process and batch process manufacturing. Let’s take a closer look at the last one, batch production.
First, we’ll define batch production and list examples of industries that use it to manufacture their products. Next, let’s look at the advantages and disadvantages of batch production and compare it to other production methods.
What Is Batch Production?
Batch production is a manufacturing process in which a group of identical products are produced at the same time, rather than one at a time. The manufacturer decides how big the batch will be and how often those batches will be produced.
In batch production, each batch will go through separate stages of the manufacturing process together. That means another batch can’t start a stage unless the previous batch has completed that part of the production cycle. Throughout the batch production process, there are quality checks done at each stage of the production cycle. Machinery is tested between batches to make sure it’s performing as expected. This flexibility is only found in batch production and is unheard of when employing other production processes.
For batch production to run smoothly, project management software can be used to plan, schedule and track all production activities. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software wfith a sheet view that can organize batch production activities, link all four types of task dependencies to avoid costly delays and set a baseline to track planned progress against actual progress in real time to help stay on schedule. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
Batch Production Example
Almost any consumer good can be manufactured using batch production. Items consumers use daily are most commonly created by batch production because they’re needed quickly and are delivered in different forms, designs or styles. Batch production can handle these constraints and produce them faster with better quality control. The following are some examples of batch production.
- Food & Beverage Industry
- Clothing & Apparel
- Furniture & Household Appliances
- Electronic Components
- Automotive Parts
- Pharmaceutical Products
- Chemical Products
- Semi-Finished Goods for Manufacturing
Advantages of Batch Production
We’ve been singing the praises of batch production and for good reason as there are many advantages of using batch production. For one, batch production produces smaller quantities, allowing for more variety of goods to be produced. It also means that the manufacturer can decrease lead times, if necessary.
Batch production is also cost-effective. More products can be manufactured on the same production line, which spreads the manufacturing costs across commodities, lowering costs. That’s because machinery can be continually active, reducing running costs. Maintenance can be scheduled for downtimes, rather than stopping production.
There’s also greater quality control with batch production. That’s because manufacturers can check and test products at each stage of the production process. Faults are found and repaired before they derail product assembly. This, and producing the correct number of goods required, helps reduce waste.
Disadvantages of Batch Production
That doesn’t mean that batch production is without criticism. It’s not the best production planning method for all manufacturers or industries. Here are some reasons why. For example, because there are so many variables required for batch production it can be difficult to automate the system. That will impact attempts to streamline production.
Another issue is the potential for employee downtime. That’s because where there’s a reset or adjustment between stages of production, as well as quality control checks and testing, there can be more time with employees not doing their jobs. This is true also as machinery needs maintenance or cleaning, such as in food production.
Batch production can also be more expensive than mass production. There are more stages in a batch production schedule. Also, initial outlays of batch production equipment and technology can be costly as they need to be specifically designed to perform a range of functions.
Finally, batch production can take longer than other types of production. That’s because the products are being produced in a series of steps. One item cannot move into the next stage until every item in the batch is ready. This extends the manufacturing period and more so if there are alterations to machinery or delays.
How Does Batch Production Compare to Other Production Planning Methods
We’ve already gone in-depth about batch production, but as mentioned earlier, it’s not the only method by which manufacturers can plan production processes. Batch production tends to be done in smaller quantities, which makes it more suitable for products with fluctuating demand. Let’s see how it compares to a few other production approaches.
Batch Production vs. Mass Production
The difference between batch production and mass production is that the former is usually done in small quantities, while the latter is for large-scale manufacturing. Mass production is usually producing a high quantity of the same product. It also focuses on standardization, which makes it hard to customize like batch production. Mass production is continuous and consistent quality is a challenge due to the high-speed, high-volume nature of this production management approach.
Batch Production vs. Flow Production
The key differences between batch and flow production methods is that flow, unlike batch production, schedules involve the production of a continuous flow of goods with minimal interruption. Setup time is also different, as batch production has to be set up between production runs, but flow production has little to no setup time between runs, as its process is continuous and consistent. Flow production has lower inventory levels than batch production and needs less time for quality control measures as its production is more predictable. Flow production usually has short lead times and is more efficient in resource utilization.
Batch Production vs. Continuous Method
The biggest difference between batch production and the continuous method or process production, which is a derivative of flow production, is that the continuous method production is ongoing without a defined start or end. It produces products constantly without interruption, unlike batch production. In batch production, all ingredients can be mixed first and then processed while with the continuous method, ingredients go through the process without interruption, moving from one step to the next without waiting for other ingredients to catch up.
Free Production Management Templates
Batch production, as with other manufacturing processes, can benefit from production management templates. Our site has over 100 project management templates for Excel and Word that can be downloaded for free. These free templates span many industries and cover all aspects of the project life cycle. Here are a few that manufacturers can use to streamline their production process.
Production Schedule Template
Using a production schedule helps to balance the supply and demand for a product. Use our free production schedule template for Excel to track the production of a product over a period of time. This flexible template can also respond to fluctuating demand and set up inventory to avoid stockouts.
Capacity Planning Template
Capacity planning helps managers determine how much production capacity is needed to meet the demand for their products. That is a moving target, as demand changes, which is why our free capacity planning template for Excel is so important. The free template lists all the tasks and estimates their duration, adds the needed resources and hour rates for them and calculates the resource utilization.
Resource Plan Template
Managing resources and making sure that the production has who it needs when it needs them is critical to batch production or any manufacturing process. This free resource plan template for Excel allows managers to list their employees, which department they’re in and their rates. Then there’s a weekly calendar to assign each to the production schedule.
How ProjectManager Helps Manage Batch Production Processes
These free production management templates are helpful, but real efficiency is delivered through project management software. That’s because templates are static documents that have to be manually updated, which takes time and money, plus they’re not collaborative. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software that can do more than any template. Let’s see how it can help with resource management and labor costs.
Manage Resources & Monitor Production Costs
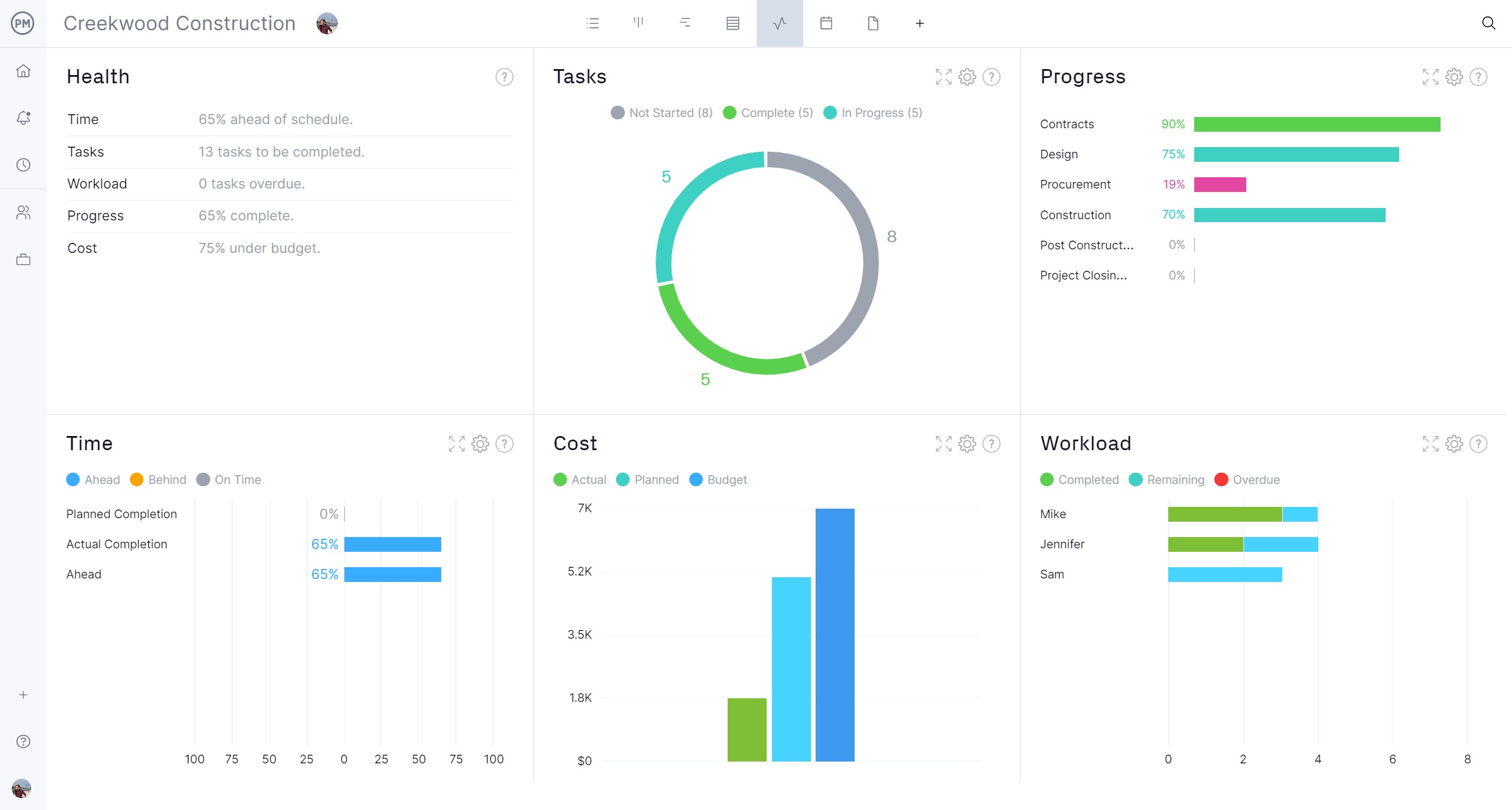
Once the production schedule has been completed and is being executed, managers need to monitor and control what’s happening to ensure that it aligns with their plan. They can toggle to the real-time project dashboard (or portfolio dashboard for viewing multiple projects) and get a high-level overview.
The dashboard automatically collects live data and displays it on easy-to-read graphs and charts that show time, cost, workload and more. For a more detailed look, use customizable reports on status, portfolio, variance and more. Filter the reports to show specific data and share them easily with stakeholders to keep them updated.

Manage Team Work Hours With Workload Charts & Timesheets
Resource management starts when onboarding the production team. Employee availability can be set up at this time, including vacation time, PTO and global holidays, which makes assignments easier and faster. Then go to the color-coded workload chart or the team page to get an overview of the allocation of the team. From there, balance their workload to ensure that everyone is working at capacity and staying productive. To track labor costs, use secure time to see how far each team member is in completing their tasks.

Related Production Management Content
For those who want to explore project management more thoroughly before pulling the trigger on project management software, here are a handful of related articles on everything from making a production flow chart on how to calculate production capacity.
- How to Make a Production Flow Chart for Manufacturing
- Cost of Production: Types of Production Costs
- How to Make a Production Order for Manufacturing
- Production vs. Manufacturing: Key Differences
- How to Calculate Production Capacity: Formula & Examples
- Producción por Lotes: Ventajas y Desventajas
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams whether they’re in the office, on the production line or anywhere else. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay up to date with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who use our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.