Technology, labor, distribution and consumer demographics have changed in the last few years. As such, business processes must constantly evolve to adapt and bring satisfaction to the customer as efficiently as possible. Organizations are continually looking for a leadership team that’s experienced in business process management (BPM).
It can seem like a tall order to disrupt the status quo at your company. Still, with the implementation of smart business process improvement strategies, you’ll be able to make these changes as fluidly as possible. Let’s look at business process improvement (BPI), define it, explore strategies and then note the business and project management tools that can help implement and analyze progress in your company.
What Is Business Process?
Before we can improve the business process, we must first understand it. Business process is simply a series of tasks that you and your team perform repeatedly to create a product or service for your stakeholder, sponsor or customer. Business process can be modeled as a flowchart, which details the tasks necessary to serve that business goal.
A business process starts with an objective and ends with the achievement of that goal, which provides value for the customer. A business process can often be broken down into smaller processes, allowing for divisions of labor.
In general, the business process is broken down into three types.
- Operational: This includes the core business and creates a value stream, such as orders from customers, opening accounts, manufacturing, etc.
- Management: This includes such processes as corporate governance, budget and employee oversight.
- Supporting: This includes those processes that support other processes such as accounting, recruitment, technical support, etc.
Each of those types also exhibits the six characteristics of a business process:
- It has definite boundaries, inputs and outputs
- It has an ordered list of activities in sequence
- It asks: “Who is the customer?”
- It must add value for the customer
- It is embedded in an organizational process
- It usually spans several functions
Lastly, when working on a business process it helps to have an owner, someone who is responsible for overseeing and improving this process.
What Is Business Process Improvement?
Business process improvement (BPI) is a systematic process for analyzing, redesigning and optimizing business processes. The goal is to achieve greater adaptability and efficiency by reducing bottlenecks and redundancies. When the workflow is improved, it leads to better quality, lower costs and increased customer satisfaction.
To achieve continuous process improvement, teams first need to examine their current processes to find inefficiencies or bottlenecks. This could come from analyzing metrics such as resource utilization rates, cycle times and error rates. From there, BPI helps redesign the process such as automating certain tasks or eliminating unnecessary steps. Finally, organizations need to implement the changes which may include allocating resources, adjusting roles, implementing new technologies, etc.

Get your free
SOP Template
Use this free SOP Template for Word to manage your projects better.
Process Improvement Methodologies
These are systematic approaches to improving processes and increasing quality, efficiency and performance. Each has its strengths and are tailored to fit the organization’s needs or project requirements. Some methodologies include balanced scorecard (BSC), Six Sigma, total quality management (TQM), Kaizen, agile, business process reengineering (BPR), root cause analysis (RCA), value stream mapping (VSM), value chain analysis, and theory of constraints (TOC), to name a few. We’ll learn more about some specific methodologies below.
Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
BSC is a strategic management tool that connects business activities to the vision and strategy of the organization by measuring performance across four different areas; financial, customer, internal processes and learning and growth. It tracks and monitors key performance indicators (KPIs) to help managers make data-driven decisions. It’s a comprehensive view of how improvements can help reach overarching business goals.
Value Stream Mapping
Value stream mapping, as the name suggests, visually maps process steps that are both value-adding and non-value-adding from start to finish. VSM helps with process improvement to pinpoint inefficiencies and waste in production. As a result, businesses can optimize processes and improve productivity. This methodology eliminates waste and can result in customer-focused business operations. It’s commonly used in industries that want to achieve leaner, more agile business models such as manufacturing, construction or healthcare.
Value Chain Analysis
Value chain analysis is a process improvement methodology that looks at all activities within an organization that help create customer value. This could include raw material procurement to final product delivery. Businesses can analyze each activity to identify areas where quality improvements or cost savings can give them a competitive advantage. Value chain analysis often helps make outsourcing and supply chain decisions.
Strategic Process Improvement
Another process improvement methodologies is strategic process improvement (SPI). This focuses on aligning process enhancements with the company’s long-term strategic initiatives and goals. SPI revolves around transforming processes that are important to achieving business growth and a competitive advantage. It drives organizational change by focusing on areas such as customer relationship management, financial planning and supply chain management.
Kaizen or Continuous Improvement
Kaizen is a Japanese word that translates to continuous improvement. This method encourages employees on all levels of an organization to contribute small and incremental improvements to processes over time. Everyone feels inspired to be involved in identifying and resolving inefficiencies, from frontline workers to the leadership team. This helps businesses adapt to change, reduce costs and improve quality.
PDCA: Plan, Do, Check, Act
PDCA, or plan, do check and act, is also referred to as the Deming Cycle. Similar to Kaizen, this is a continuous process improvement method that helps with iterative improvements in business processes. First comes “plan” where an improvement opportunity area is identified. Next comes “do,” where the change is implemented, followed by “check” which monitors the results. Finally, “act” consists of implementing the needed adjustments.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that focuses on improving process quality. It achieves this by identifying and removing the causes behind defects to minimize variability. It leverages statistical analysis to measure and control quality. This helps ensure that processes are always meeting high quality standards while keeping operational inefficiencies low. It helps reduce defects and variability to result in noteworthy cost savings and customer satisfaction.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
TQM is another process improvement tool that looks at the organization as a whole. It aims to embed a culture of quality in every process and decision by focusing on factors like continuous improvement, customer satisfaction and employee involvement. TQM shows that quality isn’t solely the responsibility of the quality control team but is embedded in all aspects of the organization.
Process Improvement Steps
By streamlining your business process you’ll have fewer errors and delays, and customer satisfaction will improve. Sounds great right? Well, here are some steps you can take to cut waste, boost efficiency and improve your business process.
1. Identify What Needs to Change
Analyze your business process at a high level and identify what needs changing. You can uncover areas ripe for improvement by conducting a process audit to discover where issues and risks lurk.
2. Analyze Your Pain Points Through Process Mapping
After you’ve figured out which parts of your process need improvement, it’s time to analyze them fully to understand what’s happening and how to realistically make improvements. Ask yourself the tough questions, for example:
- What steps are creating roadblocks?
- What aspects are the most time-consuming?
- Is there an undue increase in cost and resources?
- Is quality impacted?
You can find your answers by using business process mapping to outline everything with a flowchart or a swim lane diagram. These tools visualize all steps in your business process. You want to dive deep into each phase of the process to make sure you’re not leaving out any steps, regardless of how minor they might appear.
This will help to discover the source of the problems occurring in your process. To further your understanding of where the process is breaking down, you’ll want to talk to those people who are directly involved in it. Get their perspective on what’s wrong and what they think can be done to improve the process.
3. Make a Process Improvement Plan
Now you’re going to redesign the inadequate part of your process and apply the improvements you deem necessary to add efficiency. The best way to do this is by making a process improvement plan. This will facilitate working with those people involved in the part you’re focusing on. Include what you learned when mapping the process but continue getting input from them as part of the improvement plan writing process. Be clear about what you want to change, then work on brainstorming or other group activities to collect ideas. At this point don’t stifle any suggestions, regardless of the cost or resources involved. You want to explore first.
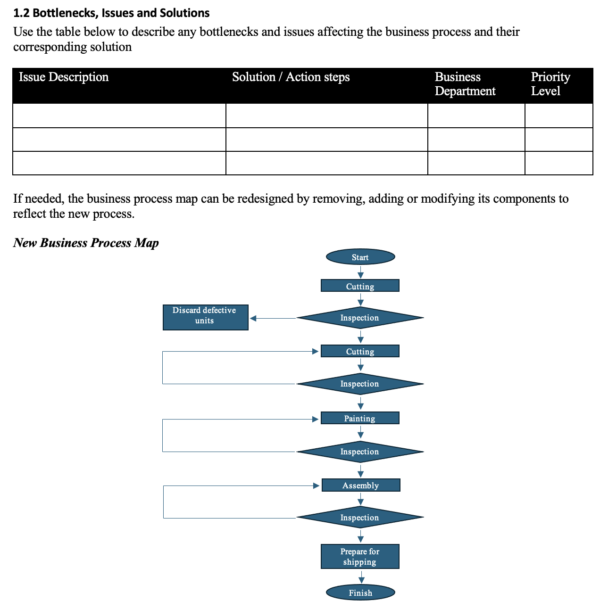
After the exploratory step, you narrow the solutions by considering the ideas within a realistic context. Apply impact and risk analysis. Work to uncover risks and potential failure points to further help you understand the full consequences of the proposal you’re building. Once you and the group have come to a realistic process improvement plan that has been agreed upon, then you’ll want to create a new diagram to document the steps involved.
4. Get Buy-In from Stakeholders
Once you’ve identified and analyzed the issues, you’re going to need to get support from senior management to okay your plans for improvement. These improvements can take time and use resources, so without a commitment from senior management, you won’t have the power to proceed.
5. Estimate Resource Requirements
Now that you have a process improvement plan, you need to determine what resources are needed to implement it. List everything required. Go through the proper channels to approve these resources and communicate clearly why they are necessary to refine and improve the process. A business case might be a good way to justify your request.
6. Make the Change
Implement your redesign. This might mean changing existing systems, teams and processes. Sounds like a project in and of itself? That’s because it is, and you should organize it as one. Plan, allocate time and resources, consider risk and assemble a team to get the work done.

7. Review, Review, Review
Just as you reviewed the existing processes to discover where improvements could be made, you’ll want to review your improvements. Monitor their progress and make sure they’re meeting the milestones you’ve set up. Be ready to adjust your plan accordingly as issues arise.
Stay in communication with your team throughout. Get input from them on how the new process is working. Ask if they’re finding it frustrating on any level. Take this information and tweak your plan to make sure that the process is in fact making improvements and not meaningless change.
ProjectManager Can Help with Business Process Improvement
There can be a lot of preparation, administration and management involved when implementing BPI, so it can be very useful to use project management tools. ProjectManager has features that can help with business process improvements, such as online Gantt charts, kanban boards, workload management software, real-time dashboards and more.
Plan with Gantt Charts
As you work to redesign you process, you’ll want to have a timeline on which to place tasks and deadlines, to make sure you’re scheduling the project as efficiently as you can. That’s where an online Gantt chart comes in. All you need to do is take your task list and import it into ProjectManager and the timeline is populated with those tasks, which can be linked and progress can be tracked.
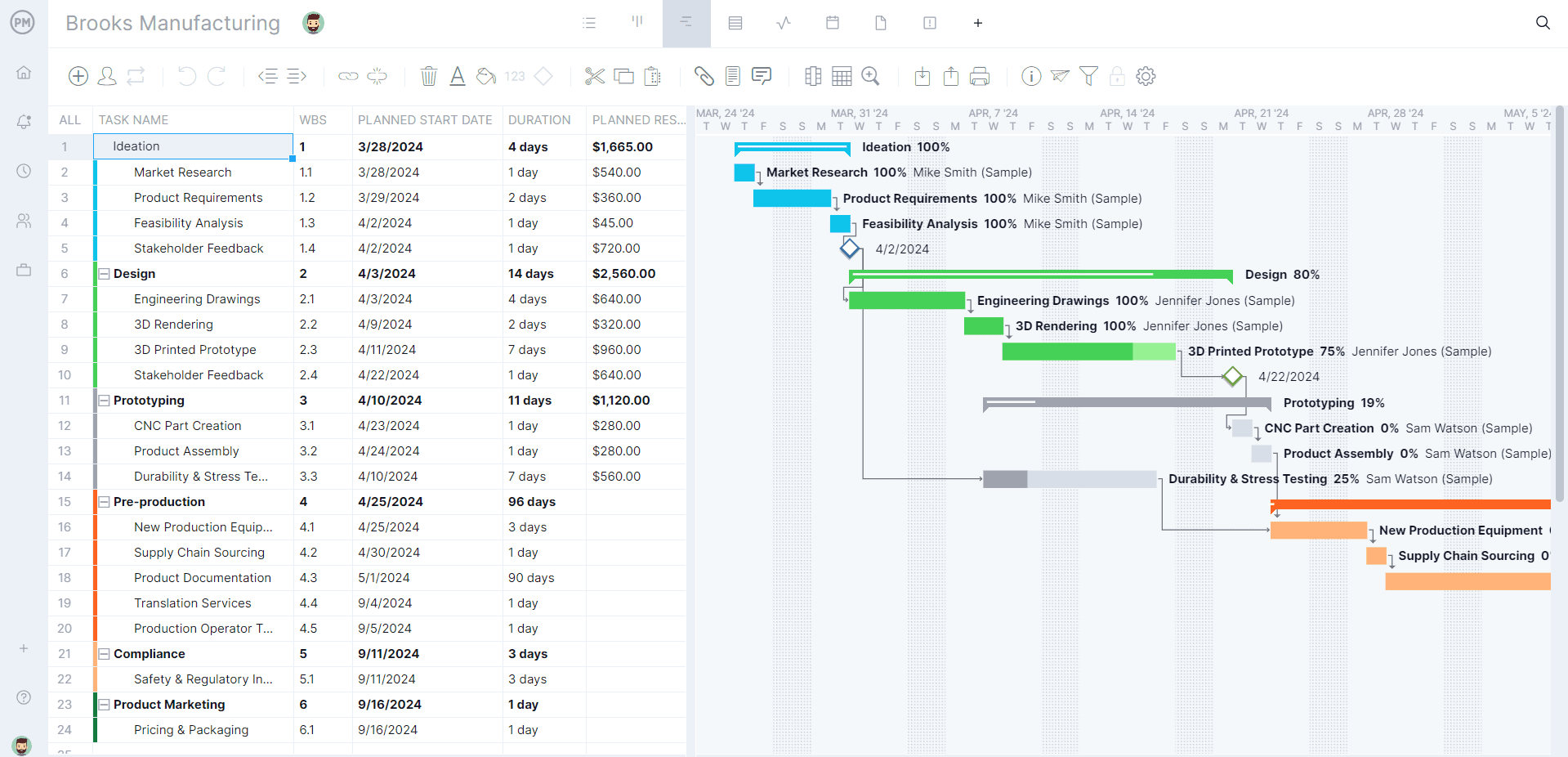
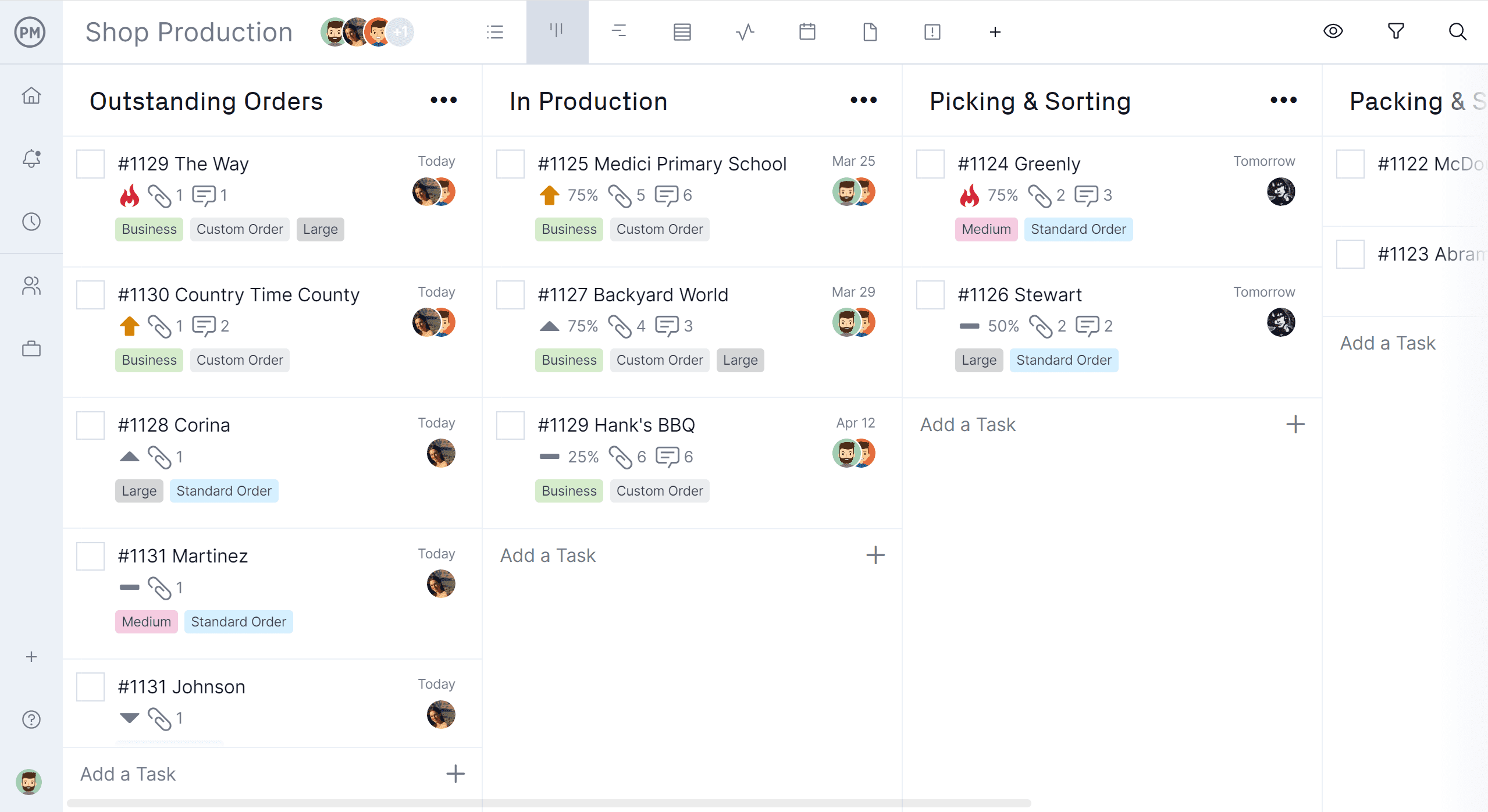
Visualize Workflow with Kanban
ProjectManager’s Kanban is a visual tool to help you see your current process. It’s very flexible and allows you to visualize your work and divide your Kanban board as you see fit. You can break the Kanban board down as far as you want.
This visibility creates clarity, so you can evolve your process as needed to add efficiencies. It helps everyone on the team see the process at a glance, which allows for a more collaborative effort at improving those processes. By visualizing the process, you can quickly see where there are bottlenecks in your process and resolve them.
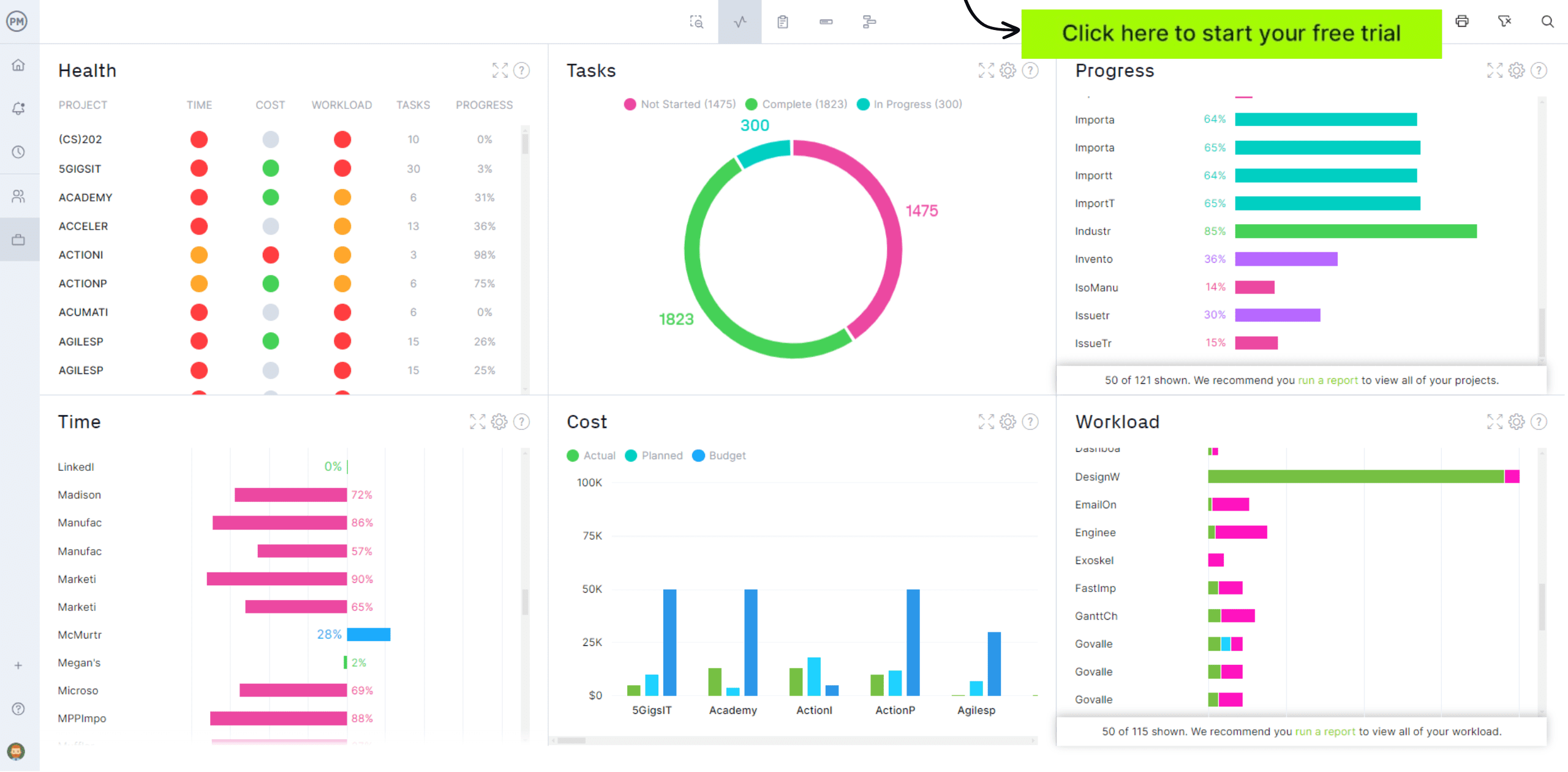
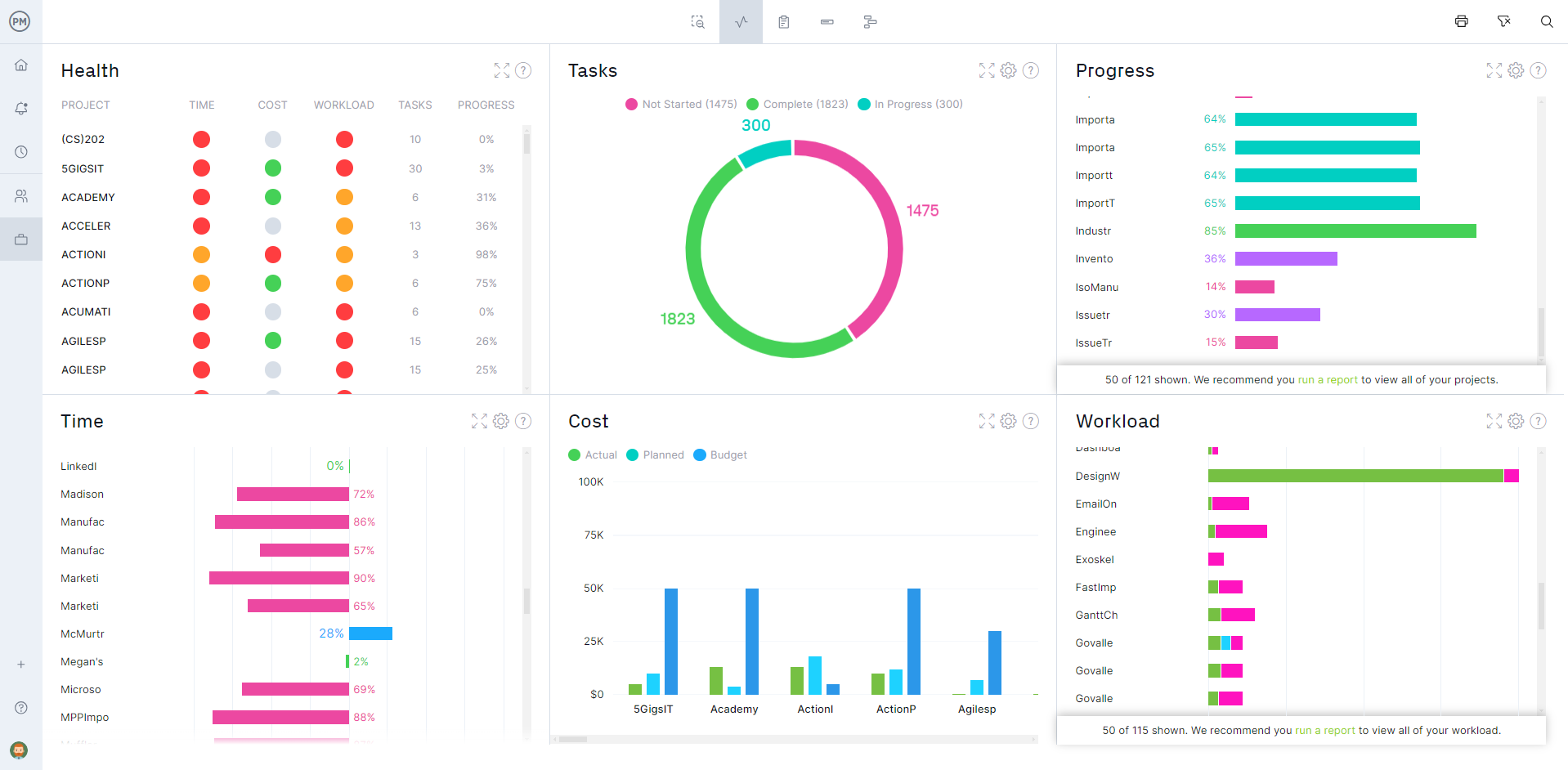
Track with Dashboards
Because ProjectManager is a cloud-based project management software it captures the progress of your work in real time. The real-time dashboard, therefore, gives you one screen in which you can see all the data you collect on the progress, cost, workload, etc., related to the process. From this overview, the issues that are preventing you from improving productivity often come quickly into focus.
Business process improvement is key to keeping your project productive and aligned with the overall organizational strategy of your business. Fortunately, ProjectManager has the tools you’ll need to plan, implement, monitor and share those improvements. Try it yourself with this free 30-day trial.

