Projects are all about delivering a product or service. Whether you’re working in project management, manufacturing, supply chains or inventory management, you need to deliver something valuable to your customers. This is why lead time is so important.
There are many stages between the initial idea and the finished product, and knowing your lead time enables you to deliver timely projects. Let’s take a moment to define lead time, determine how to calculate it and see how it works across various industries.
What Is Lead Time in Manufacturing?
Lead time is a manufacturing key performance indicator (KPI) the period between the start of a process and its conclusion. For example, this could be the amount of time it takes to make a product from scratch, the time it takes to process purchase orders or the wait time that spans between the product being shipped and the customer receiving it. Lead time is used in various industries from manufacturing to supply chain management and project management.
The average lead time differs across industries. Though there may be similarities, the lead time changes based on various processes. One thing that all industries have in common is that lead time allows businesses to schedule work and give their clients or end-users a deadline by which they’ll receive the product. Another way that lead times can be helpful is by comparing the results of your preprocessing, processing and postprocessing stages to discover inefficiencies that you can weed out in future projects to work more productively.
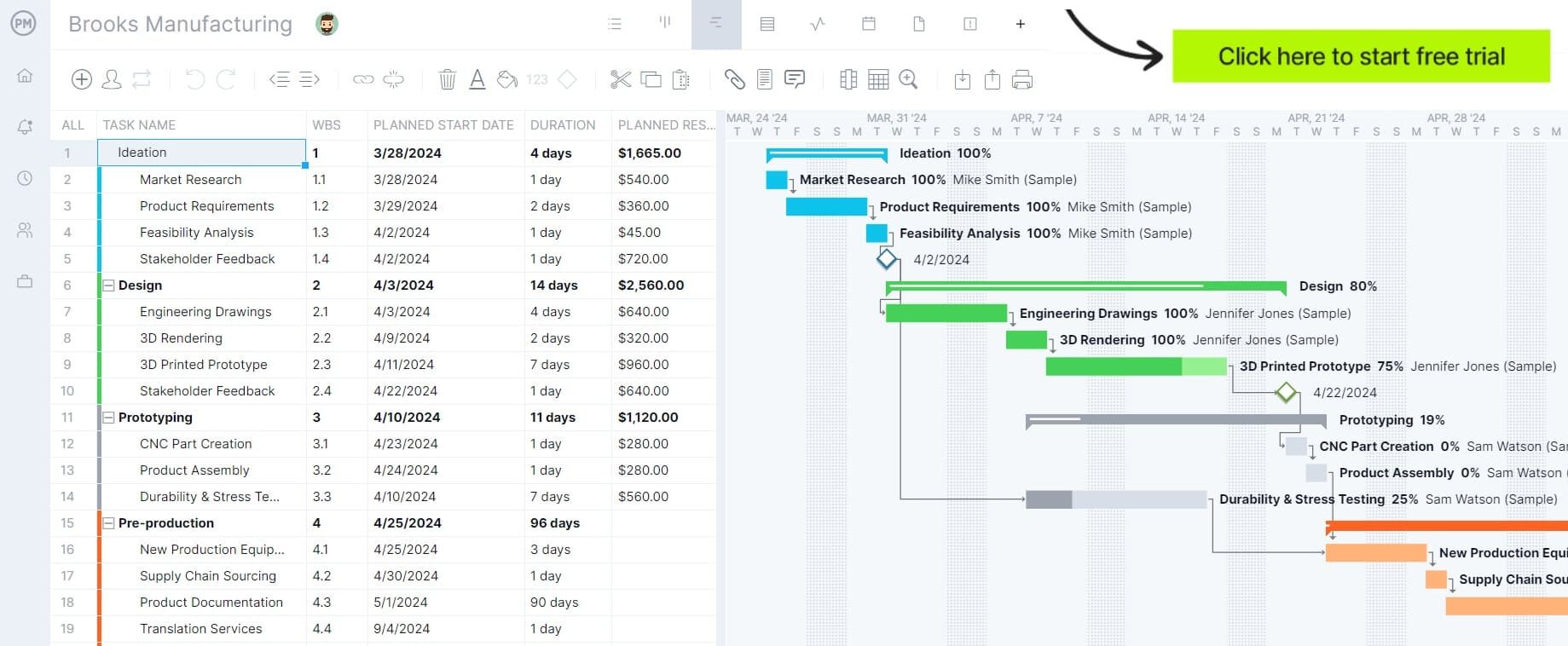
To better manage your lead time, you can rely on project management software. ProjectManager is project management software that helps you track work in real time. One of the multiple project views is the Gantt chart which allows you to plan and track various manufacturing processes and collaborate with your team in real time. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
Components of Lead Time
The components of lead time are not set in stone as they can vary from one industry to the next. Generally, here are the six components of lead time.
- Pre-processing lead time is also called planning time. It speaks to the time it takes to receive a request for replenishment or the development of a project. It takes time to understand the request and create a purchase order if you’re buying something or creating a job.
- Processing lead time occurs after receiving the purchase order and refers to the time it takes to procure or produce the item.
- Post-processing lead time is a mix of the lead times of all the processes that take place after products have been manufactured, including storage, transportation and inspection lead times.
- Waiting time is the period between procuring the necessary resources and the time when item production takes place.
- Storage time refers to inventory or the time your finished product is in the warehouse or factory before it gets delivered.
- Transportation time is the time it takes to move the product from the warehouse or factory to the customer.
- Inspection time is the time it takes for the product to be looked over and approved by the customer after it’s delivered. This might require some back and forth to deal with any issues with the item.
How to Calculate Lead Time
Now that we understand the definition and components of lead time from order to delivery, how do you calculate lead time? This important metric is one of the simplest calculations you’ll find when managing a project, supply chain or manufacturing process.
Accurate lead time calculations help you order the right amount of raw materials for your warehouse, a costly process that can take up valuable real estate if you order too much. On the flip side, you also want to have enough stock on hand to fulfill your orders. That balance of inventory is why calculating lead time is critical.
There are some terms to understand when calculating lead time such as supply delay and reordering delay. Supply delay is how long your supplier takes to fulfill a customer order after it’s placed. A reordering delay is the time between the fulfilled order and the placement of the next order.
Get your free
Kanban Board Template
Use this free Kanban Board Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
Lead Time Formula
There isn’t one way to calculate lead time, but the most common is to subtract the order request date from the order delivery date. This is known as the order lead time formula.
Lead Time (LT) = Order Delivery Date – Order Request Date
However, the order lead time formula only offers a general overview of the duration of a manufacturing process, which leads some project managers to use the manufacturing lead time formula below to get a more detailed view of the steps that occur between the moment a customer places the order and he receives it.
Lead Time = Pre-Processing Time + Processing Time + Post-Processing Time
These lead time components can be further divided into order, manufacturing, production and delivery lead times. We’ll zoom into each of these later on in this guide.
Manufacturing Lead Time Example
To better understand the concept of lead time, let’s look at an example. Take manufacturing, Acme Manufacturing needs to produce 750 widgets to meet its production budget. With its current production rate, it will produce 25 widgets a day. In this case, lead time = works in progress/average production rate. Therefore, the lead time for this example is 30 days. There can be fluctuations in the work-in-progress completion time, but this provides a general idea of Acme Manufacturing’s lead time.
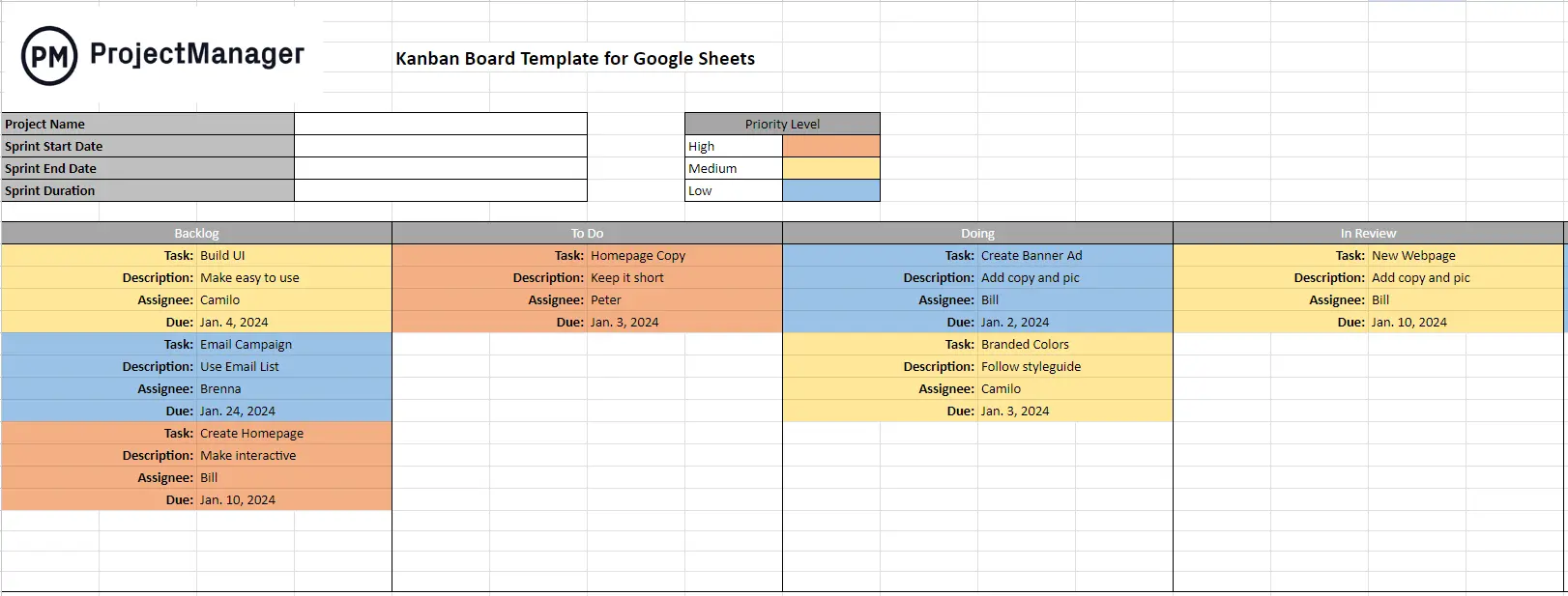
Kanban Board Template
Kanban boards are a task management tool that can be used to calculate the lead time of any type of workflow. They consist of two main elements, kanban columns and cards. Columns reflect stages of a process, while kanban cards hold information about tasks such as a description, their start and end dates, priority level, subtasks, and more. These cards are moved throughout the columns to show the stage of completion of tasks. For example, kanban boards can be used to manage the process of manufacturing a product and calculate the lead time of production activities.
This free kanban board template for Excel can be easily customized by editing the cells that make up the kanban boards and kanban cards. By default, it will allow you to track the start and end dates of tasks, but you can add as many task details as necessary by adding extra rows to the kanban cards. Simply follow the steps on our template page to get started.
Lead Time vs. Cycle Time
Cycle time and lead time are both metrics used to evaluate the efficiency and responsiveness of processes. However, they have different scopes and focuses. Cycle time is the time it takes to complete a task from the point at which it starts to the point at which it’s finished. Cycle time focuses on the active work process, such as coding, reviewing and deployment.
As noted above, lead time is the time it takes to deliver a product or service to a customer, from the point the customer requests the point at which they receive the product or service. Therefore, lead time includes the entire workflow, including any wait times or delays.
Types of Lead Time in Manufacturing
The term lead time refers to slightly different things in manufacturing besides measuring the time it takes to produce a product. The concept of lead time also applies to other manufacturing processes such as managing inventories, operational projects, order fulfillment or shipping and delivery.
Production Lead Time
Production lead time is a specific type of lead time in manufacturing, which measures how long it takes to process, prepare materials, manufacture and deliver your order. To calculate this metric, you’d add preprocessing, processing and post-processing data to get your lead time.
Manufacturing lead time is made up of material lead time, which is the time it takes to deliver materials to the manufacturer. In production management, lead time is how long it takes from the point of getting materials to producing a finished product. Customer lead time is the period of moving the finished products from the manufacturer to the customer.
Lead Time in Inventory Management
Lead time in inventory management is how long it takes to restock between the time of the order to when it’s received. This impacts how much inventory a company needs to warehouse to maintain the production cycle they’ve decided upon. Finding this lead time in inventory management requires adding the supply delay with the reordering delay. It’s always ideal to always have enough supply on demand to feed the manufacturing process and keep the production flowing.
This is slightly different than in manufacturing, however, because it doesn’t include processing inventory or raw materials into the final product. In manufacturing, you must also consider the delivery of the product to the customer or retailer.
When dealing with inventory management, you’ll include the supply delay and the reordering delay. To calculate lead time in this instance, add the supply delay to the reordering delay.
Lead Time (LT) = Supply Delay (SD) + Reordering Delay (RD)
Lead Time in Supply Chain Management
Similar to manufacturing, the supply chain lead time is the length of time it takes from generating a purchase order to delivering that item. And as in manufacturing, each part of that supply chain lead time has its own lead time:
- Material lead time is the time it takes for raw materials to be delivered to the factory.
- Production lead time is how long it takes the factory to get an order through production and deliver the finished goods.
- Customer lead time is the time when a customer makes an order to when they receive that order.
Adding these lead times together gives you the total lead time. However, when it comes to satisfaction, the most important lead time is how long it takes to reach the customer. As customers have come to expect fast delivery times, if you can shorten customer lead time, you can increase sales.
Order Lead Time
Order lead time is how long it takes to process an order. This applies to many of the industries listed above. More specifically, it’s the minimum amount of time between the purchase order and delivery of the product.
To figure out the order lead time, you need to know the following:
- Actual order lead time (A-OLT) is how long it takes from getting the order to fulfilling it.
- Requested order lead time (R-OLT) is the time between the order and when the customer wants delivery.
- Quote order lead time (Q-OLT) is the time between the order entry date and delivery date as it is represented on the contract.
- Confirmed order lead time (C-OLT) is the date on which the delivery has been confirmed.
Delivery Lead Time
Delivery lead time is the amount of time it takes for a product to travel from a supplier to a customer. It’s a key metric in supply chain management. Delivery lead time is calculated by adding up production time, processing time and transportation time.
Lead Time in Project Management
Lead time in project management occurs when one activity begins as another is being executed. It’s also called working in parallel. Lead time can also refer to task dependencies, such as finish-to-start relationships, where one task must be complete before the next can begin. This is different than lag time in project management, which is the amount of time that must pass before another task can begin. Lag is also part of task dependencies and it can occur in all four task dependencies: finish-to-start, start-to-start, finish-to-finish and start-to-finish.
However, both lead and lag time are used when creating a project schedule. It helps project managers sequence their activities and tasks to meet the project deadline. An easy way to remember these terms is that lag is holding up time and lead is hurrying up time.
How to Reduce Lead Time
There are several ways to reduce lead time. Here are some of them.
Map Business Processes and Optimize Workflows
Mapping business processes and optimizing workflows can help reduce lead time by identifying bottlenecks and redundancies as well as streamlining execution techniques. Using a workflow diagram can help visualize the processes and help identify strengths and weaknesses in it.
Balance Your Team’s Workload
Balancing the team’s workload keeps them working at capacity, which leads to greater productivity. Besides making sure resources are distributed evenly, managers can prioritize tasks, delegate work and communicate more effectively.
Increase Resource Capacity
There are several ways to reduce lead time by increasing resource capacity. Demand forecasting uses historical data to determine the demand for a product or service, which helps deliver it when a customer needs it. Collaborating with suppliers lets them know when to expect reorders based on sales data, which allows them to speed up the fulfillment process. Automating tasks and optimizing production scheduling can also reduce lead time.
How ProjectManager Helps With Lead Time Reduction
Regardless of which industry you work in, ProjectManager is an ideal tool to track your lead time and overcome inefficiencies. Our software delivers real-time data that helps you find issues that can delay your production and fix them fast to stay productive.
Monitor Progress and Performance on Real-Time Dashboards
Our real-time dashboards automatically capture and calculate live data before displaying it on colorful graphs that track time, costs and four other metrics. You get a high-level view of your production to catch anomalies and resolve them before they can cause problems. There’s no setup as with inferior software products and it’s ready to use when you are.

Dive Deeper Into Data With Robust Reporting Features
The more data, the better. With a keystroke, you can dive into project status, portfolio status, workload, costs, tasks and so much more. Every report can be filtered to help you zero in on what you’re looking for. The reports are also easy to share as a PDF attachment or even print out to keep stakeholders updated on progress.
You’ve seen how our Gantt chart helps you plan, while dashboards and reports feed you the data you need to stay on schedule and within your budget. There are also resource management features that help balance your workload and keep your teams working at capacity to meet your lead time every time.
ProjectManager is award-winning software that connects hybrid teams and helps everyone work together and productively. Organize tasks, teams and projects with a collaborative platform that connects everyone in real time. Join teams at NASA, Siemens and Nestle who use our software. Get started with ProjectManager today for free!


