Production management has to control a variety of functions to deliver projects on time without overspending. There’s the workforce responsible for the production itself, but also the equipment used, any raw materials needed, workflows and much more.
Managing all aspects of production requires good management. Production management is the process of optimizing the production of goods. It focuses on quality, capacity, resources and time. We’ll go into more detail, explaining the benefits of production management and how production scheduling software can create greater efficiencies.
What Is Production Management?
Production management is the process that oversees turning production inputs, such as raw materials, equipment parts and components, into production outputs, which are whatever products or goods a company produces.
The scope of production management consists of various areas that include production planning, budgeting, scheduling and control. Production managers must oversee these areas to ensure products are manufactured on time and within budget.
Therefore, production management is concerned with every aspect of production. This means it works with the management of all materials necessary for production, including inventory or warehousing of those materials, to the design of the product or goods, utilization of equipment inventory, monitoring performance and more. The overall goal is to achieve the objectives of the company’s production strategy.
ProjectManager is award-winning product management software that has robust features that can be used to build a product roadmap that plans your work, resource costs and more. Use the Gantt chart to schedule and track various production processes, build a plan and collaborate with your team in real time. Use it to spot bottlenecks, share documents and ensure quality. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
The Importance of Production Management
When it all comes together, production management will help your production line run smoothly, without interruption or delay. This is done by putting time and effort into production planning, production scheduling, production control and equipment maintenance. Part of these four disciplines, of course, is managing the workforce, methods, materials and costs. Let’s take a closer look at these four parts of production management.
Scope of Production Management
As stated above, production management is a process or discipline that consists of four key areas: production planning, budgeting, scheduling and control, which define the scope of production management.
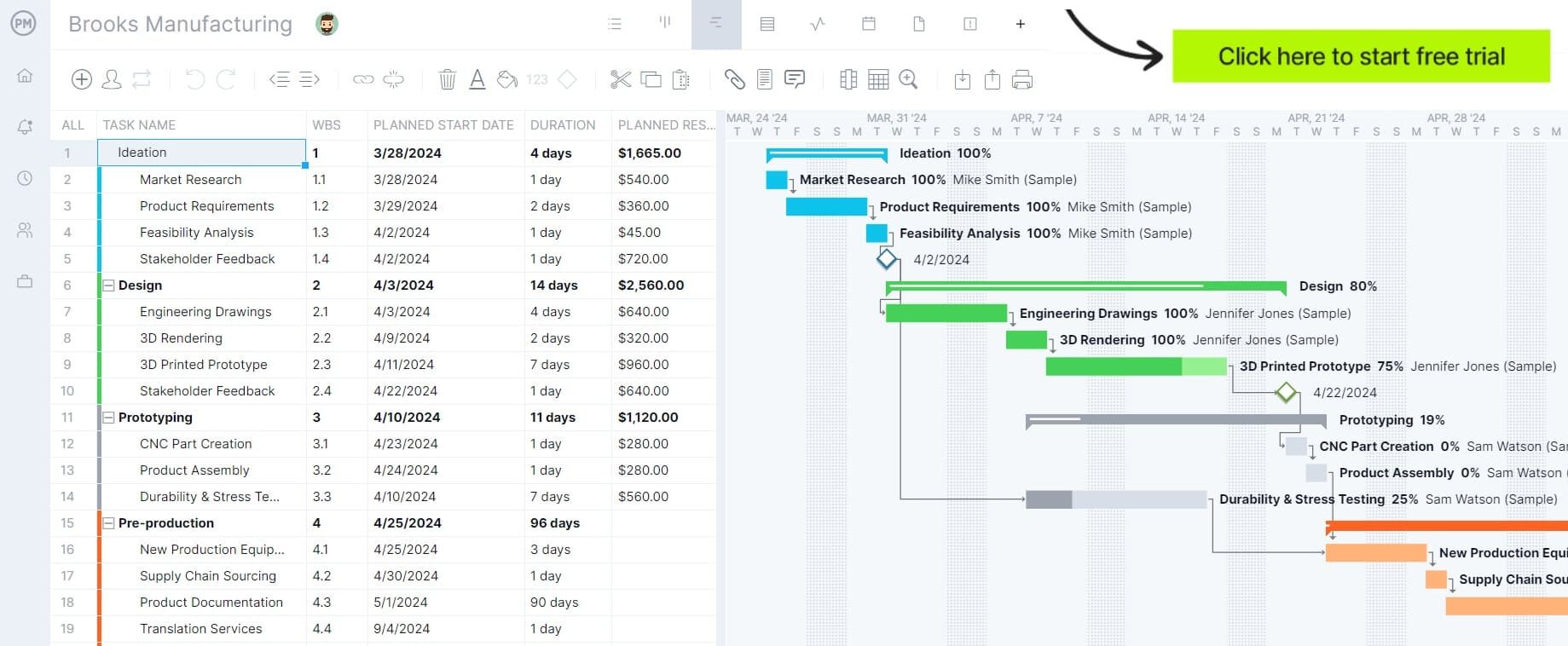
Production Planning
Production planning is figuring out the design of a product and how you’ll execute that design. It’s about organizing tasks, resources, costs and schedules to deliver your product or goods as efficiently as possible. Through an efficient production process, products are delivered to customers on time, lead time is reduced and capacity is balanced with demand.
To control all these elements and have them work together to deliver your product on time, you need to manage human resources, the supply chain and much more. Project management software can help you organize all parts of your production so they work together like a well-oiled machine.
Get your free
Capacity Planning Template
Use this free Capacity Planning Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
Production Budgeting
A production budget is an important production management document that allows organizations to estimate the quantity of product they’ll need to produce to meet the forecasted customer demand, minimize their operating costs and maintain their desired stock, production and work-in-progress inventory levels.
Production Scheduling
Production scheduling is the planning and streamlining of processes for creating and delivering projects to market. It takes into account supply chain management, labor, logistics, costs and the timeframe for production. The master production schedule helps manufacturers determine costs, helps them allocate the financial resources needed for each stage of production, ensures the timely delivery of a quality product to customers as well as takes into account the logistics and time required to ship final products to distributors and retail stores.
Production Control
An integral part of manufacturing and supply chain management is production control, which monitors production to keep production running smoothly. It’s used with inventory control and quality control as part of the larger operations management. Production control requires managers to predict, plan and schedule work keeping in mind human resources, materials and cost to meet quality and quantity expectations.
Production Optimization
Production optimization refers to all the managerial actions that are taken to increase the productivity of a production facility without acquiring additional resources such as labor or equipment. This includes actions such as re-imagining the factory layout for a better flow of materials around the shop floor, balancing the assembly line to make sure all employees have a similar workload or making adjustments to the product itself so it’s easier to manufacture.
Managing each of the areas of the scope of production management is complex and requires the execution of a variety of actions from the production management team and the organization as a whole. These are known as the functions of production management.
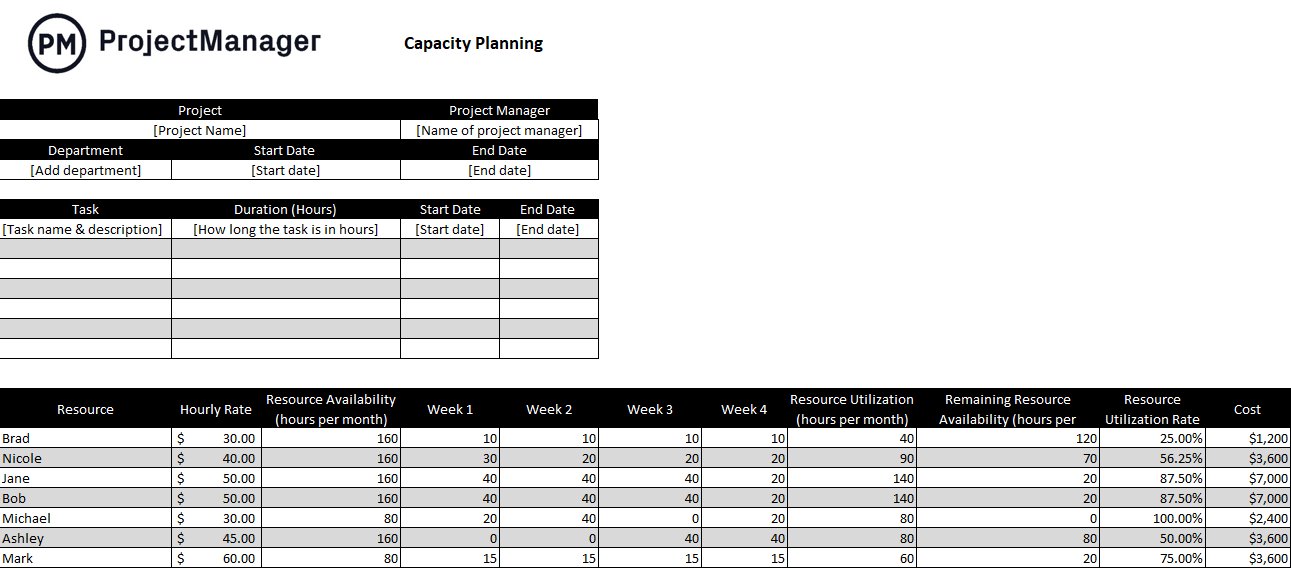
Free Capacity Planning Template
This free capacity planning template helps ensure that your manufacturing team distributes work efficiently across your team. Allocate work based on resource availability, calculate utilization rate and monitor labor costs to maintain profitability. Download it today for free.
Functions of Production Management
The functions of production management can be defined as all the actions an organization takes to manage its production process from the moment raw resources are acquired to the moment final products are delivered to customers.
Here are some examples of key functions of production management.
- Shop floor management: The shop floor is the physical area of a production facility where products are manufactured. An important function of production management is establishing the factory layout, standard operating procedures, safety guidelines and overseeing other factors that affect productivity at the shop floor level.
- Inventory management: Manufacturers must manage three main types of inventories: production inventory, work-in-process inventory and product stock. Maintaining these inventories optimally ensures that production can continue uninterruptedly and customer demand is met while minimizing warehouse and production costs.
- Supply chain management: Supply chain management consists of managing each step in the process of acquiring supplies from external vendors. The main objective is to get the highest quality supplies at the lowest cost possible and ensure supplies are punctually delivered to the production facility.
- Capacity planning: Production capacity is a measurement of the quantity of products organizations can produce based on its available resources such as human resources, equipment and raw materials. However, the production capacity of an organization varies as it manufactures goods, so you must constantly monitor your resource utilization so you understand your production capacity to either take on new production orders or reject them if necessary.
- Equipment maintenance: Equipment maintenance is the process of keeping production equipment in optimal conditions without interrupting the production cycle. The main objective is to minimize costs and equipment downtime, improve productivity and ensure that the company complies with regulatory standards.
- Facility location: Choosing the location of the production facility itself is important in production management because it significantly affects the operating costs of a business. To choose an optimal location, manufacturers use linear programming formulas to find the location that minimizes the costs of transporting supplies and finished goods from and to the production facility and maximizes profit.
- Order management: The order management process consists of receiving, prioritizing and scheduling production orders based on the purchase orders that are received from customers. There must be an order tracking system in place so you can deliver orders on time and make accurate production schedules.
- Quality management: To manage the quality of products, manufacturers must first define the quality standards that their products should meet and then establish quality assurance procedures, guidelines and tools to ensure quality control.
- Warehouse management: Any organization that manufactures products needs a warehouse to store its various inventories such as production supplies, equipment, machinery, work-in-process and finished goods. Storing these items costs money, so it’s important to streamline the warehouse operations to minimize operational costs.
- Production tracking and reporting: There are many production key performance indicators (KPIs) you can use to monitor how effective, profitable and resource-efficient your manufacturing process is. Then you need to establish a production reporting process to keep your stakeholders informed.
Production management is the process that oversees turning production inputs, such as raw materials, resources and costs, into production outputs, which are whatever products or goods a company produces. It involves phases that include planning, scheduling, control and maintenance in service of producing quality and quantity on time and within the budget.
Therefore, production management is concerned with every aspect of production. This means it works with managing all materials necessary for production, including inventory or warehousing of those materials, the design of the product or goods, utilization of equipment inventory, monitoring performance and more. The overall goal is to achieve the objectives of the company’s production strategy.
What Does a Production Manager Do?
A production manager is responsible for overseeing each of the areas of production management: production planning, budgeting, scheduling, control and optimization. To do so, production managers collaborate with a variety of decision-makers and leaders within an organization such as department managers from sales, product development or even marketing.
Here are some of the main responsibilities of a production manager:
- Create and maintain a master production schedule prioritizing the purchase orders and manufacturing contracts that are the most profitable for the company
- Make a production budget based on the forecasted customer demand and establish minimum inventory levels
- Define the shop floor layout and take other production optimization actions to improve the efficiency of the production process
- Act as the liaison between the production management department and the rest of the organization
- Establish safety management procedures, equipment and tools to ensure the safety of production workers and compliance with regulatory requirements
Other Production Management Roles
Depending on the manufacturing, there can be one or more production management roles. The larger the operation, the more likely production manager will have others working under them to share the responsibilities. Smaller companies could have a production manager who handles all the tasks related to the field. Let’s look at three main roles that can be found in production management.
- Production planner: Focuses on the planning and the use of production resources to make sure that supplies, resources, costs and timelines all work together.
- Production supervisor: Responsible for production equipment, staff and processes on the production floor, including scheduling, activities and troubleshooting.
Production Management vs. Operations Management
We’ve mentioned operations management in passing, but it deserves a section of its own to make the distinction between it and production management. Production management, as defined above, deals with the activities that lead to the creation of a finished product. It takes raw material as input and product as output. Operations management is a larger discipline made up of the administration of the produced goods of a company but also services for its customers
Production managers make design, quality, quantity and cost decisions as they relate to the production of the product. Operations management is more concerned with product design, quality, quality, process design, location, manpower, storage, maintenance, logistics, inventory management, waste management and more. Operations management has a larger set of responsibilities than production management.
Another difference is where production managers and operations managers are employed. You’ll find production management only in companies that produce goods and products. But operations management is common to all organizations, whether they’re manufacturers, service providers, banks, hospitals and so forth. That’s because production management is concerned with delivering the right quality, quantity and price for products, while operations management is about utilizing an organization’s resources efficiently to meet its customers’ needs.
Benefits of Effective Production Management
Production management ideally is going to do more than its mandate to deliver the right amount of quality products for a price acceptable to customers. However, running a smooth production will provide a company with added benefits that help it stand apart from its competition and increase its profitability. Here are a few ways production management does that.
1. Reduces Lead Time
Reduced lead time is the process of minimizing the time it takes to manufacture something and deliver it to a merchant or customer. Production management reduces lead time by removing unnecessary tasks, waste and waiting time not only in the production cycle but also in the supply chain.
2. Minimizes Costs
Production management helps reduce the costs associated with making products. It looks at various areas that can be cut or where a better deal can be made. These areas include material costs, whether that’s using different materials (and maintaining quality) or switching suppliers. It also seeks efficiency by using waste in the production cycle such as leftover materials. Automation is also a powerful tool for minimizing costs while consuming energy more efficiently is another area to reduce costs.
3. Efficient Inventory Management
Monitoring inventory is part of production management. This is done to ensure that you have enough supplies on hand to fulfill upcoming orders, which positively impacts the bottom line. It also manages inventory to ensure that there isn’t too much stock. Having to warehouse materials is expensive and that valuable space could be used for other more profitable ventures.
ProjectManager Helps With Production Management
ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that helps control schedules, activities and costs related to a company’s production of goods. Our software has tools that help you plan schedules and activities with robust Gantt charts, which also manage resources and costs to keep your production on time and within its budget. But there’s so much more that can help you eliminate waste and maximize your production while maintaining quality control.
Streamline Repetitive Work
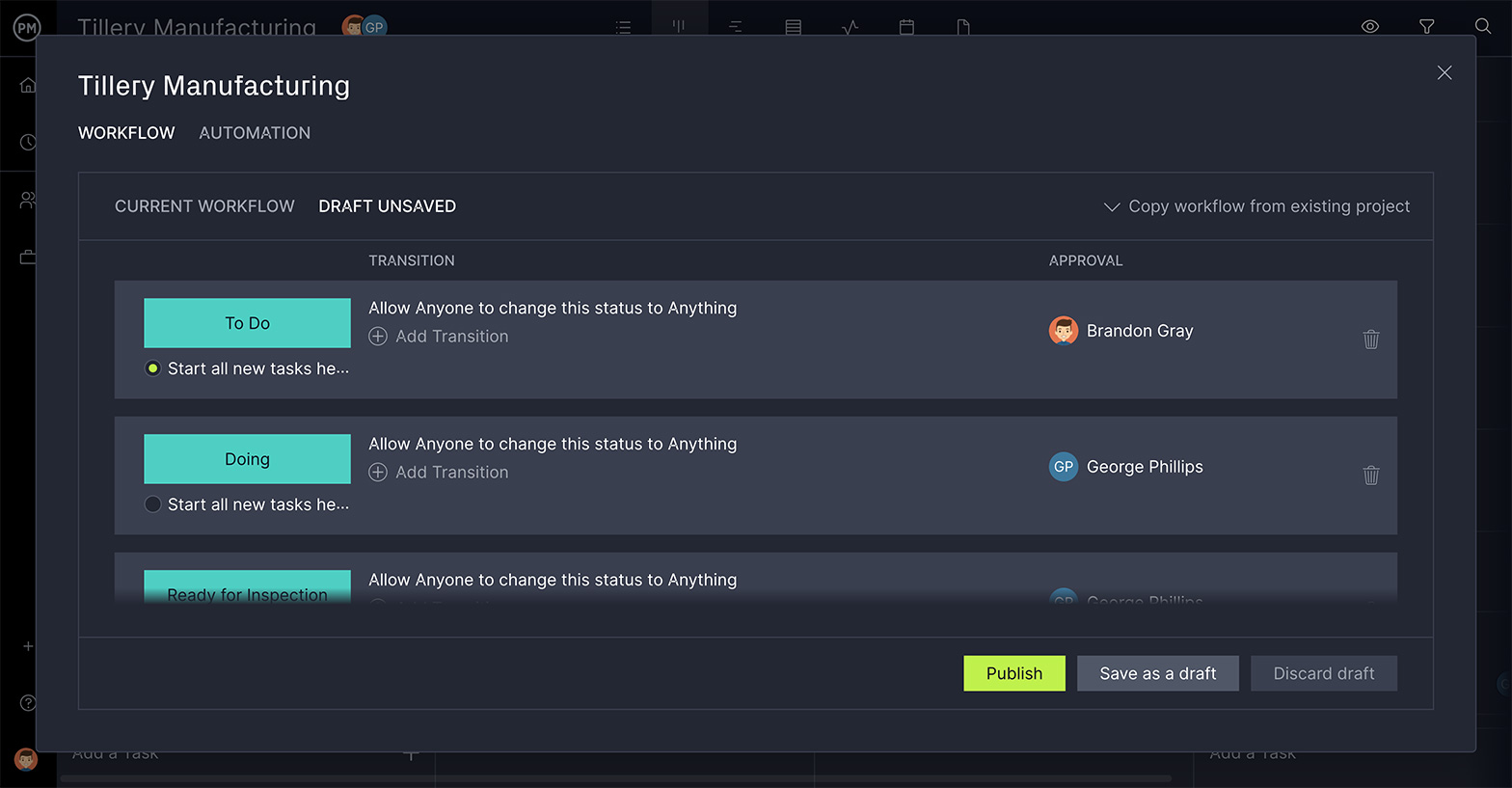
One way to reduce waste is to keep your teams focused on important tasks and automate busy work without compromising quality. You can automate workflows by setting up a trigger that automatically changes the status, assignee, tags and more. By designating someone who has the authority to approve the work, you can ensure that nothing moves forward until it meets your quality expectations. That streamlines the process without risking the quality of the products you’re producing.

Keep Production Teams Productive
Streamlining processes and having task approvals help, but a production manager needs to ensure teams are working at capacity without overburdening them with tasks. Our resource management features make it, first, easy to set team availability so you know who can work when, and, second, balance their workload so they work more productively. Use our color-coded workload page to see at a glance who has too much more and then re-allocate their tasks right from the page.
Production management relies on monitoring processes and tracking metrics, which can be done with our real-time dashboard and customizable reports. For a high-level view of time, cost and more, our live dashboards automatically capture and display easy-to-read graphs and charts. Filter reports on status, variance and more to go deeper into the data. Our tool also has multiple project views so managers can plan on Gantts and teams can execute the visual workflow of a kanban, robust task lists, calendars and more.
Related Production Management Content
There’s a lot to learn about each area of the scope of production management, which is why we’ve created dozens of blogs, templates and guides to help you streamline the production process of your organization.
- Production Schedule Template for Excel (Free Download)
- Production Tracking: Monitoring the Success of Your Manufacturing Process
- Production vs. Manufacturing: Key Differences
- How to Make a Production Flow Chart for Manufacturing Processes (Example Included)
- How to Make a Production Order for Manufacturing
- Batch Production: Examples, Advantages and Disadvantages
- Gestión de Producción: Guía Rápida para Gerentes
ProjectManager is online project management software that helps you plan, manage and track production in real time. Make production plans and schedules, monitor resources and costs and streamline your production cycle to get to market faster. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.