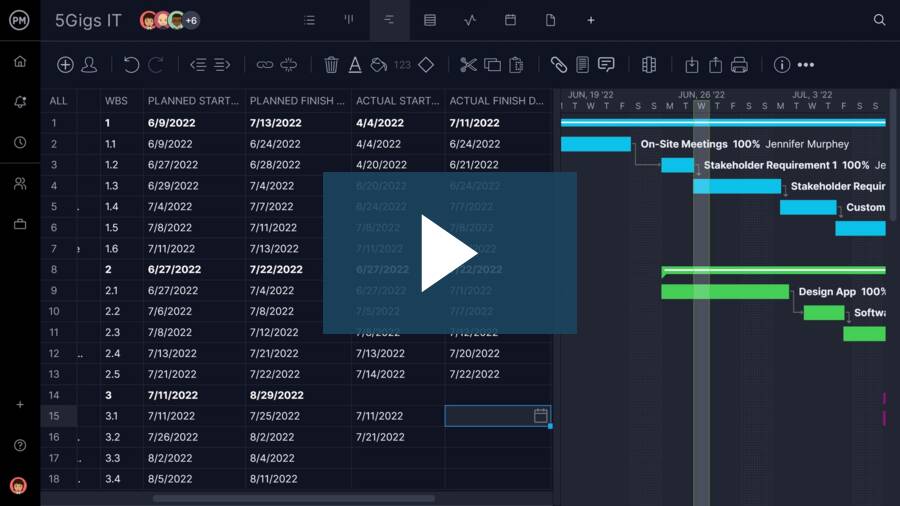
Manufacturing is a complex process. It requires balancing production capacity, inventory levels, material requirements and other aspects to fulfill orders. Once you’ve aligned these project aspects, you need to schedule your production.
Creating a master production schedule is crucial in ensuring your supplies match demand. A robust master production schedule also supports your sales force and strengthens your capacity to meet the needs of your customers.
What Is a Master Production Schedule?
A master production schedule (MPS) outlines which products will be manufactured and when they are made. This schedule outlines the various processes and resources needed to make production move forward smoothly while identifying potential bottlenecks and creating plans to avoid them.
A master production schedule is critical in manufacturing, as it can be the difference between an organization making a profit or experiencing a loss in revenue. To make sure you don’t miss anything, there are several data sources you can use as input for the development of a master production schedule. Here are some of the most commonly used ones.
- Aggregate planning: This method allows organizations to create manufacturing plans that focus on uninterrupted production in periods from six to 18 months. Using aggregate planning as input is a great way to create a master production schedule.
- Stock inventory level: You’ll need to know your current inventory levels to create an efficient production schedule that minimizes inventory costs down and meets customer demand.
- Production capacity: This is the maximum output that can be achieved by your organization in terms of manufactured goods. It’s essential to know this before creating a master production schedule.
- Material requirements planning: This is a system that’s used to calculate the components and materials necessary to manufacture a product. The basic inputs include a master production schedule, inventory status file and bill of materials.
- Sales forecasts: Provides estimates of future customer demand, which will help to determine how much product is needed to be produced. With master production scheduling, this demand is translated into a detailed plan for production, specifying what to produce, in what quantities and when. It helps companies optimize inventory levels, reduce costs and improve customer satisfaction.
Get your free
Master Production Schedule Template
Use this free Master Production Schedule Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
Master Production Schedule (MPS) vs. Production Schedule
The master production schedule and production schedule are similar. However, they serve different but related purposes. For example, an MPS outlines the products needed to be produced, including the quantity and when they are needed as determined by demand forecast and inventory levels.
This usually covers a longer timeframe, often months ahead, which provides a high-level overview of production goals. In terms of strategy, MPS helps in planning resources, managing lead times and aligning production with sales forecasts.
A production schedule, on the other hand, focuses on more details and specifies actual production activities for a shorter timeframe than the MPS, usually daily or weekly tasks.
It includes specific details such as work orders, labor assignments, machine schedules and materials needed. That’s because a production schedule is used for day-to-day operations and execution of the project plan outlined in the master production schedule.
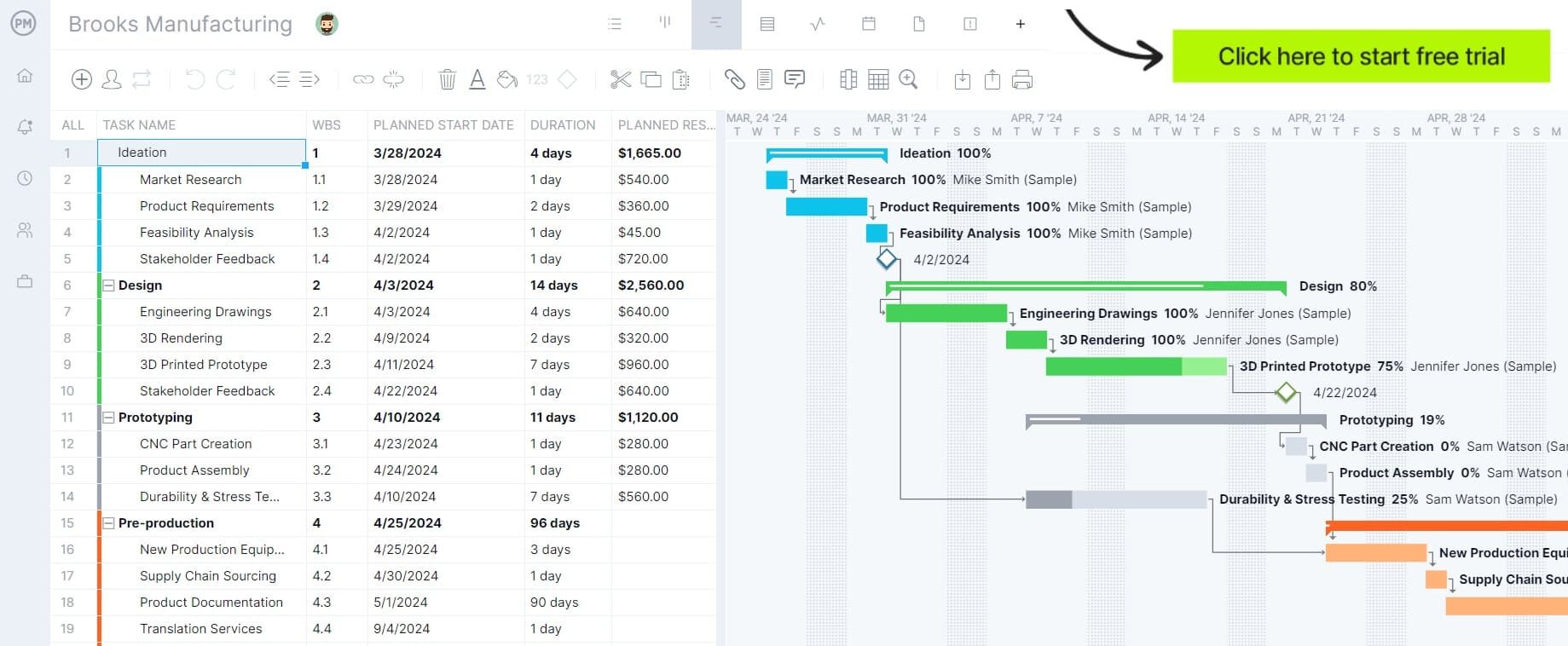
One of the easiest ways to make a master production schedule is using an online Gantt chart. ProjectManager offers an award-winning Gantt that is flexible and collaborative for your whole team. Schedule tasks across the timeline, linking dependent tasks to avoid bottlenecks in the manufacturing process. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
Why Should You Use a Master Production Schedule?
Having a plan that can forecast the demand for your product over a period is the primary purpose of a master production schedule. However, there are other key roles an MPS plays in manufacturing and production planning.
The main functions of a master production schedule include:
- Planning: Balancing market demand to materials, labor and the capacity of your equipment to deliver the goods.
- Make adjustments to schedule: Schedules need to have a contingency for unexpected delays or mistakes that stop the flow of products.
- Prevent stockouts: Planning for capacity requirements to maintain the output of production.
- Improve efficiency and control costs: The better the plan, the more likely you’ll stay on schedule and identify potential efficiencies.
- Facilitate order fulfillment: It does this by aligning with demand, inventory management, resource allocation, lead time management and being flexible and responsive to changes.
Another function is to keep your commitments to your customer base. Manufacturing only works when it serves its customers on time and within budget.
When you have the right master production schedule process, your demand flows smoother, lead times improve, communication is standardized, requirements are prioritized and production is stabilized.
How to Create a Master Production Schedule
When making a master production schedule, you need to follow a process to fulfill the function of the schedule. The best way to do that is by following these steps.
- Start with a demand plan, which maps the demands that your master production schedule is going to respond to.
- Identify the raw materials you’ll need and secure a supply chain to deliver those materials to your production.
- Develop a proposal of the master production schedule to make sure the schedule can meet its requirements.
- Make any calculations necessary to see if it can meet the demands of your master production schedule draft. These calculations should continue throughout the process to make sure you’re always meeting demand.
- Once you’ve tested the draft and it meets your requirements, you can ensure that it aligns with your customer service, resources and the investment you’ve made into inventory.
- The next step is making sure you communicate the production schedule to everyone involved in the manufacturing process. You want to make sure your team is on the same page.
- Return to your schedule to see if your supply is balanced with demand. It should tell you whether you need to increase or decrease production. This ensures you produce the orders generated by your sales team and deliver them on time and with the expected quality.

What Should Be Included in a Master Production Schedule?
Before you make your master production schedule, you need a demand plan to understand what your customers want. A demand plan depends on accurate historical sales data, which helps you figure out what demand will be in the coming weeks. The demand plan must be regularly reviewed and updated.
It’s helpful to have what’s called a safety stock stored in case demand unexpectedly spikes. This will carry you through the period while you update your master production schedule. Don’t neglect to replenish your safety stock after you use it.
When it comes to master production scheduling, each company will have its guidelines, but at a basic level, a master production schedule will include these parts.
- Forecasted demand: This forecast determines what products need to be produced, in what quantities and when. This helps to ensure that production aligns with anticipated sales, which helps companies meet customer demand while optimizing inventory levels.
- Product list: A listing of all the products you make, including quantities and the timing for each production run. This helps production align with demand forecasts and operational capabilities by providing a clear roadmap for manufacturing.
- Production start and end dates: These dates help to define the timeline for when production should begin and when it should be completed each time. This helps align with demand and manage resources more effectively, facilitating smoother operations and timely order fulfillment.
- Planned production value: This is the number of units you’re going to manufacture each week. Be sure to include how many units of each variation are made up of the total number.
- Actual orders: Actual orders from customers can influence the master production schedule and be reflected in adjustments or updates to it. They provide real-time data that can lead to modifications in the schedule.
- Customer: The master production schedule is influenced by the customer and their needs, market trends and actual orders. To effectively meet customer expectations, companies often adjust the MPS.
- Beginning and ending inventory levels: The beginning inventory represents the amount of inventory available at the start of the planning period and serves as a baseline for determining production needs. Ending inventory is the desired inventory level at the end of the planning period, which helps ensure there’s enough stock to meet future demand without overproducing.
- Available to promise units: This refers to inventory available to fulfill customer orders after accounting for existing commitments. It incorporates assessing inventory levels, managing customer expectations and planning production.
- Safety stock: Though not typically detailed in the MPS, it’s an important consideration when developing that schedule. Safety stock is the extra inventory kept on hand to mitigate risks associated with demand variability and supply chain disruptions.
- Work in progress: Not explicitly detailed in the MPS, it’s an important factor when planning production for scheduling production runs and managing lead times.
- Production costs: Again, not usually included in the MPS, but it’s closely tied to financial considerations when evaluating feasibility, optimizing production and reporting on costs.
- Variation sublist: You want a column with variations, such as sizes or colors to document and manage supporting systems or processes. It can influence how the MPS is developed or adjusted.
- Dates: Any schedule must have dates to accurately forecast demand and delivery. It’s best to break your schedule into months and weeks and adjust as needed.
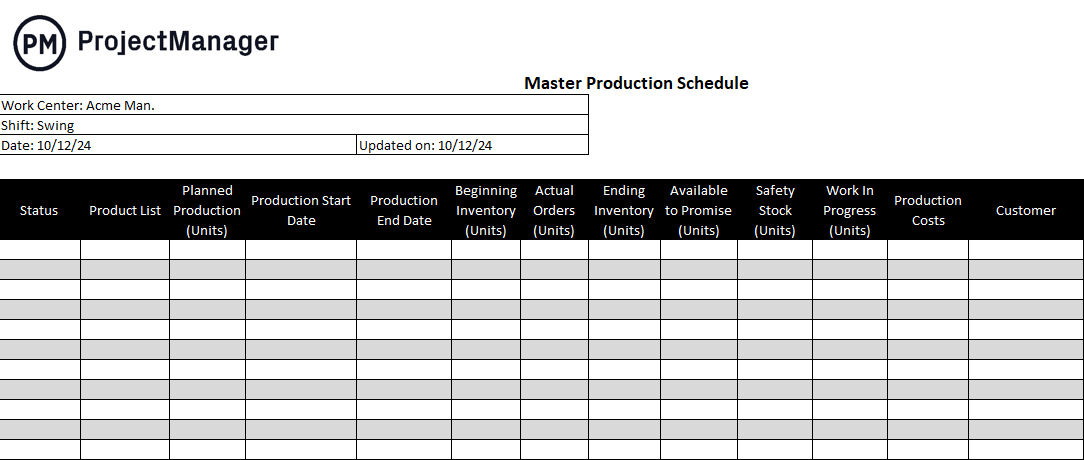
Master Production Schedule Example
To better understand the MPS, let’s imagine a real-world scenario. As illustrated in the schedule below, Acme Manufacturing is scheduling its swing shirt. Four widgets were created during this timeframe and are all in progress.
The quantities range from 500-600 units that will be completed on average in four days as indicated by the production start and end dates. The beginning inventory level is listed as well as the actual orders and ending inventory. There’s even a safety stock level to address any fluctuations in demand or other changes to the schedule.
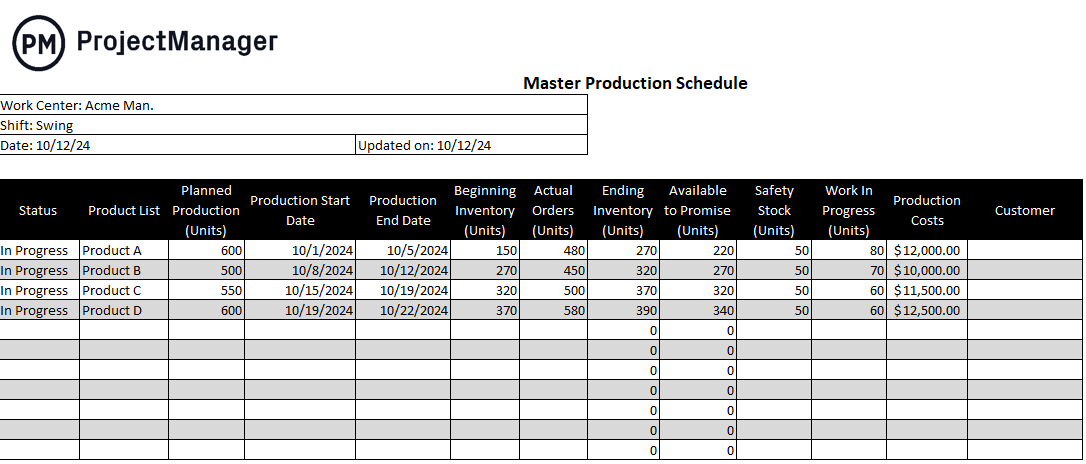
The work in progress is listed in units and the production costs for each item being produced are calculated at the end of the schedule. The MPS can be updated during production if necessary, and that information is listed on the MPS to ensure that everyone is working from the most current information.
Master Production Schedule Template
Our free master production schedule template is a great tool to get started with production planning. It can be easily customized to fit your business’s needs.
Related: 10 Free Manufacturing Excel Templates
Benefits of Using a Master Production Schedule
Using a master production schedule is a necessity for manufacturing businesses. The better you understand your manufacturing process, the better you can meet the changing demands of your customer base. Here are some of the main benefits of using one.
- Helps with demand planning
- Helps with inventory management
- Helps with production staffing
- Prevents stockouts
- Facilitates maintenance planning
- Helps create better estimates for procurement
A master production schedule also serves as a channel for communication between the sales and manufacturing teams. Because this is a continuous dialogue, the master production schedule is flexible and open to change as needed.
To summarize, it’s a plan for making whatever commodity your organization produces. It schedules the production process of that commodity but also includes the staffing and inventory that are required. The plan itself is determined by the demand for the product, and this information is provided by sales.
How ProjectManager Manages Your Master Production Schedule
ProjectManager is award-winning software that organizes work, teams and projects. Project management tools can help you plan, schedule and implement manufacturing processes more efficiently.
Use our online Gantt chart to create a master production schedule that lets you map tasks across a timeline while keeping track of costs and resources to make sure you’re never overspending. Even better, the dynamic Gantt chart is flexible and can be quickly edited to reflect changes in orders and capacity.
Gantt charts are planning tools that help you schedule tasks across a timeline. You can then link any dependent tasks to avoid bottlenecks in your manufacturing cycle. For example, if a strap needs to be stitched to the body of a handbag before the embroidery can be added, you identify this dependency and link the two tasks to keep production running smoothly.
See how to do that and more by watching this short video on how to schedule with ProjectManager.
The Gantt can also be shared, and because the project management tool is online, all data about your manufacturing process is collected in real time. If there’s a delay with needed materials, you can easily adjust the schedule.
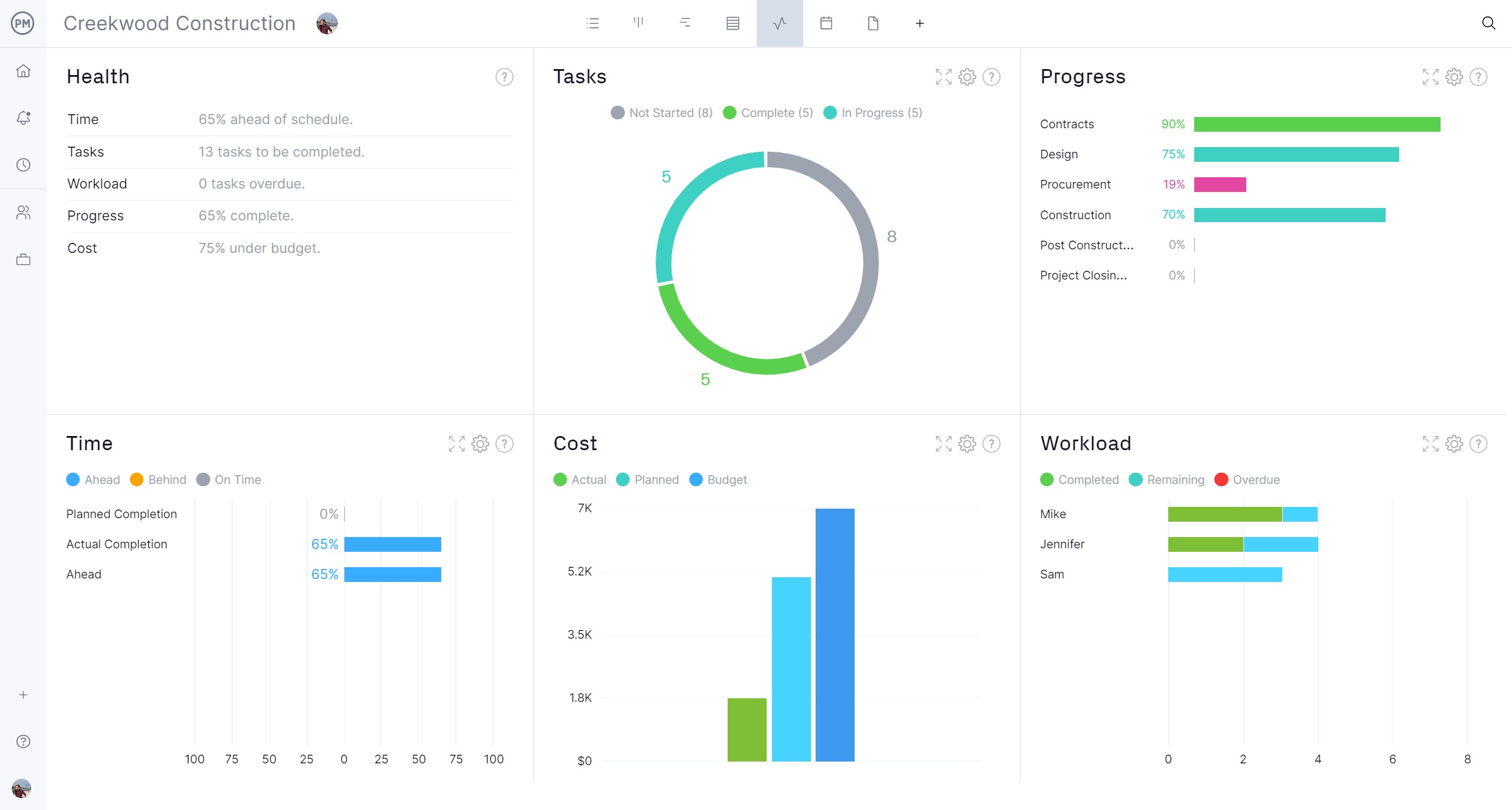
The master production schedule needs to reflect demand and supply. This means it also needs a tool that can give you a high-level view of your production. The real-time dashboard collects data and automatically calculates time, costs and other metrics to give you a high-level view of your production.
Related Content
We publish blogs, videos and guides that explain all the different aspects of production management. Here are a few of the ones that focus on production scheduling and other similar topics:
- Best Production Scheduling Software Rankings
- Production Management: A Quick Guide
- Production Planning in Manufacturing: Best Practices
- Production Scheduling Basics
- Production Schedule Template
ProjectManager is an award-winning tool that organizes your manufacturing to help you work more productively. Plan, schedule and adjust your master production schedule according to demand and capacity requirements. Get started for free.