What Is Logistics Management?
Logistics management is the process of managing the activities that are required to transport goods from its source to the final customer. That process involves a series of logistics activities such as order processing, material handling, packaging, warehousing, transportation and customer service management.
The logistics management process is used for tangible goods such as raw materials, finished products, equipment and machinery to food or other consumable items. A person who works in this field is called a logistician or logistics manager.
Logistics Management vs. Supply Chain Management
Logistics management is a subset of the larger supply chain management. Supply chain management plans, implements and controls the efficient flow of storage, goods, services and related information from the point of origin to the point of consumption. This is done for the purpose of meeting the requirements of customers.
Logistics management in business works across industries. It aims to manage the fruition of project life cycles, supply chains and resultant efficiencies. As businesses grow more complex and expand into a global marketplace, business logisticians have evolved into something called supply chain logisticians.
With logistics management in manufacturing, the focus is twofold: inbound logistics for internal functions and outbound logistics for the external flow from the point of origin to the point of consumption. Logisticians focus on inventory management, purchasing, transportation, warehousing, consultation and the organization and mapping of these processes.
Get your free
Inventory Template
Use this free Inventory Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
Different Types of Logistics Management
Here’s a quick overview of the main types of logistics management, each emphasizing a different aspect of the supply chain management process.
Inbound Logistics Management
Inbound logistics management refers to the logistics activities that are necessary to transport materials, equipment and machinery from a supplier to a production facility.
Production Logistics and Management
Production logistics management manages the transportation of goods during the production process. This involves the staging of materials from production warehouses to the production line at the right time to streamline the production process.
Outbound Logistics Management
Outbound logistics management is the opposite of inbound logistics. It involves the transportation of goods from the production or distribution center to the final customer.
Third-Party Logistics Management
Third-party logistics management refers to the outsourcing of logistics management activities. Third-party logistics management can involve outsourcing inbound or outbound logistic activities.
Supply Management Logistics Management
This involves the planning, procuring and coordinating materials that are needed at a certain time at a particular place for the production of a task. This includes transportation of the materials as well as a place to store them. Additionally, evaluating the level of supply at the different stages of the process is required to ensure the needs of the customer are met, for example delivering materials to a construction site or parts for a manufacturing plant.
Distribution Logistics Management
This takes stored materials and transports them to where they need to go. The issues in this involve moving materials; including loading, unloading and transportation, as well as keeping track of the stock and how it’s used. This type of logistics management controls the movement of supplies from a central warehouse to the stores that sell the product to the public.
Customer Service Logistics Management
Customer service logistics management consists of ensuring products are delivered on time and damage-free to ensure customer satisfaction. To do this, organizations use logistics management tools and techniques to track customer interactions along the logistics management process of order processing, handling, transportation and delivery of goods.
Reverse Logistics Management
This is about the management of reclaiming materials and supplies from the customer back to production. For example, reverse logistics management is concerned with the return of unwanted or unused products from the end customer seeking a refund.
To model, analyze, visualize and optimize this complex logistical puzzle, the use of logistics management software is often used. ProjectManager has planning tools such as Gantt charts, kanban boards, timesheets and real-time dashboards to help you manage the tasks in your logistics management process. Get started for free today.
The Logistics Management Process: Logistics Activities
Logistics management is a process that consists of logistic activities, also referred to as functions that allow organizations to implement the types of logistics management explained above.
1. Warehousing or Warehouse Management
A warehouse is a physical place where goods are stored when they come out of production. However, warehouse management can be strategically used by companies to excel in the market. For example, the location of a warehouse can play a significant role by allowing companies to deliver their products faster than their competitors. Warehousing automation can also help companies cut labor costs.
2. Order Processing & Fulfillment
Order processing and fulfillment is the process of receiving an order, ensuring payment terms have been met, checking the production capacity and availability of stock and preparing the order for transportation. Another important aspect of order processing & fulfillment is to document transactions and make sure the warehouse inventory is updated whenever an order is fulfilled.
3. Material Handling
Materials handling refers to the movement of goods in a warehouse. Companies need to plan their warehouse layouts carefully to help their employees clearly understand where to find the products that are ordered by customers. Some warehouses for big companies can be large, so it’s important to plan carefully to avoid any logistic inefficiencies.
4. Packaging
In logistics management, the packaging doesn’t focus on the aesthetics of the product packaging for the final customers, but instead on how well the product is packaged for transportation in terms of storage space efficiency, breakage prevention, packing cost and ease of handling. If packaging meets these requirements, it can help companies save money and facilitate its logistics management process.
5. Transportation Management
Transportation is the process of delivering products or materials from their warehouse to the final customer. This is the most expensive logistics activity and therefore, is a step that should be planned carefully to minimize manufacturing costs. Logistic managers need to find the most efficient transportation schedule and method of transportation such as rail, truck water and air.
6. Inventory Management
Keeping an inventory of products at the warehouse is costly for businesses and may affect their profitability. For this reason, the goal of inventory control is to gauge customer demand to maintain an inventory level that satisfies it, but without causing overcosts. Some manufacturing methods such as lean manufacturing or just-in-time manufacturing allow businesses to manage their inventory costs.
The Distribution Network of Logistics Management
The various links and points of distribution in a logistics management network include the following:
- Factories that manufacture products
- Warehouses that store products
- Distribution centers to receive and return items for clients
- Transport to deliver the product
- Retail locations, from small to larger stores sell a product
These are the major hubs for the logistics of a product, though there can be vendors and intermediaries operating between these points.
Tips for Smart Logistics Management
Logistics management involves a lot of planning and the more steps, the better. By considering every stage of the product, its distribution and the return of materials and supplies, you’re more likely to increase efficiencies and increase revenues.
The larger the operation, the more complex and difficult the logistics management. Therefore, the more you need a strong logistics management plan. To be prepared and have the best plan possible, follow the below tips.
- Have a strong plan: Like any management, it succeeds or fails on the plan’s strength. The more thorough your plan, the less you’ll have to think on your feet. There will always be issues and only so many potential risks you can anticipate, but planning early and in detail can help mitigate delays and other obstructions to the clear flow of materials and supply.
- Make a plan B: No matter how good your initial plan is, there can always be something that comes along that it cannot manage. That’s why you need a contingency plan for every element of your logistics plans to respond to unforeseen problems that might arise. But it’s important to also know when to give up the original plan and move on to the secondary one.
- Hire a manager: It’s critical that this process has an experienced leader who can work with a variety of different parties, all of whom are involved in the logistics of the materials and supplies. That means interpersonal skills are a must. They should also have strong industry contacts to deal with any last-minute logistics changes in suppliers, etc.
- Automate: It goes without saying that automation is a built-in way to make workflow more efficient. They are so many processes that can be helped through task automation, from tracking to monitoring delivery to fleet and inventory management software.
- Learn from mistakes: This goes for almost everything. You’ll take missteps on your journey of managing logistics. That’s a given. What’s not assured is that you’ll learn from those mistakes, so they don’t happen again. Take time to look back on what you’ve done, where it worked and where it didn’t, and get feedback from your team.
Why Is Logistics Management Important?
The purpose of logistics management is about finding more efficient and effective ways to move resources and products from conception to completion and, finally, to the customer. But the driving force of these actions is to meet customer demand and provide the best service possible to retain customers and maintain their satisfaction by meeting their product requirements.
As customers demand better service, there’s a need to ship faster, more accurately and with a high level of quality. It’s through logistics management that customer satisfaction is achieved.
But that’s not the only benefit. It also helps to create visibility in the business’ supply chain. By analyzing historical data and tracking the real-time movement of goods, logistics managers can better the flow of materials and avoid potential disruptions.
Therefore, logistics management helps drive up revenue. It improves customer service and adds to the company’s good reputation and brand, which in turn creates new and more business. With more visibility into the supply chain, there’s the opportunity to save costs in operations, by controlling inbound funds, keeping inventory at the right level and organizing the reverse flow of goods.
How ProjectManager Helps Your Logistics Management
Logistics is just planning with literal deliverables. Therefore, successful logistics managers understand the importance of a project management software tool to help them collect, organize and move items from one place to the next efficiently. ProjectManager is award-winning software that’s designed to improve the organization of projects and teams to maximum effect.
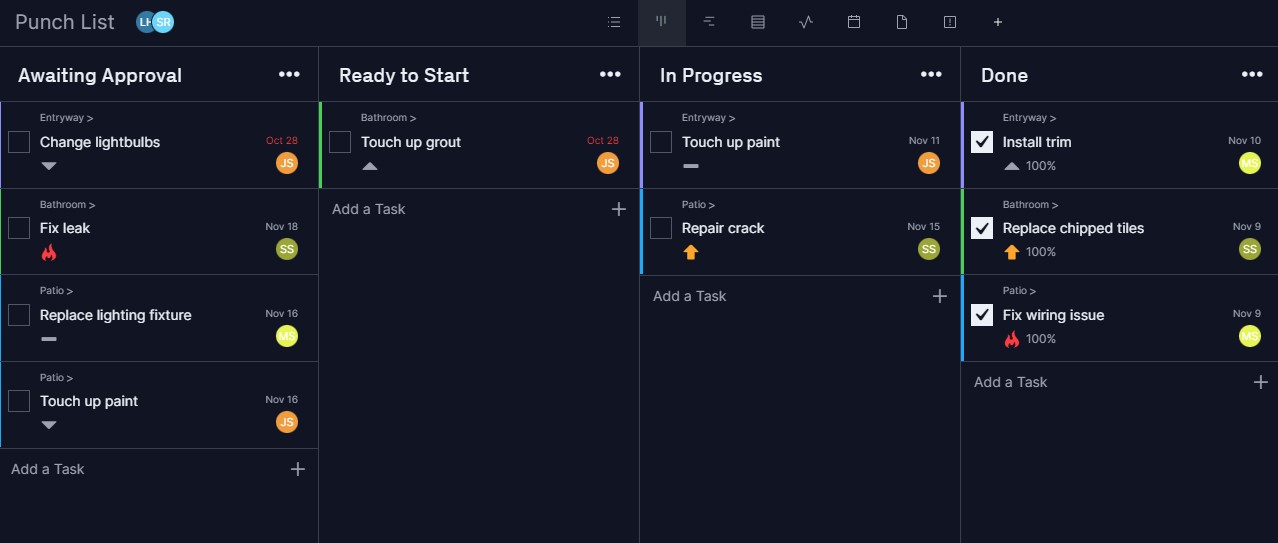
Track Progress With Kanban Boards
When you’re dealing with an overwhelming amount of shipping, priorities and deadlines, you need a way to see where those pieces are at any given time. Our kanban tool visualizes the movement of your shipments with cards representing each item and columns that show where it is in your shipping cycle.
Dashboards and Reporting Keep Things Moving Smoothly
Since our software is online, every time there’s a status update, it reflects across the tool. We have dashboard and reporting tools that provide more data and make managing logistics simple. For example, you can get a high-level view of your costs, variance, tasks and more. The data is crunched automatically and displayed in easy-to-read graphs and charts.
 Logistics management has many things to track and resources to schedule. As projects go, it’s one of the more complicated. ProjectManager is project management software that gives you the tools to manage logistics more efficiently through automation and real-time monitoring. Kanban boards for visual workflows, online Gantt charts for scheduling and a real-time dashboard to report on progress as it happens. See how it can remove bottlenecks from your supply chain by taking this free 30-day trial today.
Logistics management has many things to track and resources to schedule. As projects go, it’s one of the more complicated. ProjectManager is project management software that gives you the tools to manage logistics more efficiently through automation and real-time monitoring. Kanban boards for visual workflows, online Gantt charts for scheduling and a real-time dashboard to report on progress as it happens. See how it can remove bottlenecks from your supply chain by taking this free 30-day trial today.

