Production scheduling is part of the pipeline that starts with sourcing and planning. Is it the most important part? Every part is important! If you don’t have the materials, you can’t manufacture a product. If you don’t have a plan, you’ll never get your goods to market on time.
But for now, let’s focus on production scheduling. We’ll define both production scheduling and a production schedule and define what production scheduling is not. Then we’ll explain what to consider in production scheduling and how the process can benefit your projects.
What Is Production Scheduling?
A production schedule is a plan that helps facilitate the process of delivering products to customers and the marketplace. It’s part of the larger supply chain in manufacturing and includes everything from procurement of raw materials and labor and logistics to the costs involved and a production timeframe.
Manufacturers need to address production scheduling before they begin the manufacturing process. This might sound obvious, but production scheduling informs the costs involved in producing a product, such as the production itself and labor. Therefore, financial resources must be allocated for every step in your production cycle.
It’s essential to consider when to introduce your product to the marketplace. You want to do so quickly without negatively impacting quality, so many work backward from a deadline. That means understanding how long production will take and the timeline to transport finished goods to distributors. This requires balancing resources to have what you need when you need it.
That’s a lot of different pieces to coordinate. ProjectManager is award-winning project management software with robust Gantt charts to map your production schedule. Our Gantt charts allow you to manage your resources and costs in real time. All four task dependencies can be linked in the production schedule to avoid costly bottlenecks. Once you have your production scheduling planned, set a baseline to capture that plan. Now you can compare the planned schedule to the actual schedule when in production to help you stay on track. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
Production Scheduling Process
To balance production orders with the availability of resources in a cost-effective manner, manufacturers apply the production scheduling process to their production facilities. It provides a better way to allocate resources, operations and processes when creating goods and services.
By following the steps below, manufacturers can adjust their production scheduling to reflect resource availability and client orders. However, your production schedule must be accurate in terms of the resources available to reap the benefits of production scheduling.
1. Production Planning
Everything rests on this step. Here, you’ll figure out the course of the entire production. Managers will look over production budgets, a demand plan, and the number of raw materials that will be required. There are two types of plans, static and dynamic, the former thinking that everything will follow the plan’s timeline and the latter believes everything can change. The dynamic plan is recommended as change is part of any execution of a plan.
2. Production Routing
Now with the plan done, you’ll want to determine the path the production will follow. This is routing. That is, how the raw materials are procured and then made into a finished product. The idea behind production routing is to determine the more economical sequence of operations in the production process.
3. Production Scheduling
This is when you determine the date and time that the production operation must be completed. There are three types of production scheduling, master scheduling (which defines the entire process from start to finish), manufacturing or operation scheduling (for routing raw materials) and retail operation scheduling (to get the finished product from the manufacturing facility to stores). You’ll want to include a contingency plan to respond to issues that negatively impact your schedule.
4. Dispatching & Execution
Once you’ve scheduled production, it’s time to share the plan with everyone involved. Assign the order of jobs, instructions and other production information that’s important for execution. Execution is when staff works together to ensure that the sequence of the production schedule is followed and deliverables meet deadlines. This means monitoring and removing bottlenecks that might delay production orders.
What Is a Production Schedule?
A production schedule is an integral part of production scheduling. The production schedule is a list of all the products that are to be manufactured. That list also notes where and when each product will be made.
The production schedule is very detailed and includes everything from raw materials to logistics and what processes will be used to run a smooth production line. Managers will also explore potential bottlenecks so they can avoid issues. The production schedule is reviewed throughout the manufacturing process and revised as needed to keep production running on time.
Related: Best Production Scheduling Software
Not only managers but sales teams benefit from a production schedule. Sales can use the production schedule to keep the manufacturing team updated on the demand for the product. And, of course, managers can keep sales aware of what product is available.
Get your free
Production Schedule Template
Use this free Production Schedule Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
What Should Be Included In a Production Schedule?
When creating a production schedule these elements must be included to help the project be delivered on time: forecasted production volume, production timeline, lead times, resource requirements, production tasks and processes and estimated project costs. Let’s review each of these.
Forecasted Production Volume
This refers to the anticipated quantity of products or services that will be produced within a specific time. This metric is essential for planning and resource allocation to ensure production meets demand. It includes quantitative estimates, demand analysis, production capacity, schedule alignment and adjusting as necessary when monitoring and reviewing production.
Production Timeline
This detailed schedule outlines the sequences of tasks and milestones required to complete a project within a specified time. This roadmap helps teams understand what needs to be done and when it has to be completed. To do this, tasks have start and end dates, milestones are added to define important dates and help monitor progress.
Lead Times
Lead time in a production schedule can refer to a few different things. For example, there is procurement lead times, which refers to the time required to acquire materials or equipment. Production lead time is the time needed for each step in the production process. Finally, delivery lead times are the time needed to ship the finished product or deliver services.
Resource Requirements
When referring to resource requirements in a production schedule, this means anything that is needed to execute the tasks. Therefore, resource requirements run the gamut from materials, such as raw materials or inputs required for production, personnel, equipment and machinery to the budget.
Production Tasks & Processes
This encompasses all the activities and steps required to complete the project. Each step in the production process must be broken down into tasks and the sequence of those tasks defined. It can also include material sourcing, supplier coordination, equipment setup, workflow planning and more.
Estimated Production Costs
Ensure that all production costs are covered, including direct material costs, such as raw materials, direct labor costs, as in wages and manufacturing overhead costs that range from utilities, maintenance and other factory-related expenses. There are also variable costs that fluctuate with production volume and fixed costs that are constant.
Who Should Participate in the Production Scheduling Process?
Many professionals are involved in the production scheduling process. They include the production managers, production scheduler, procurement team, inventory manager, production engineering team, marketing and sales team and maintenance team. We’ll briefly describe each below.
Production Manager
The production manager is responsible for overseeing the production process, including realistic timelines and coordinating resources. They establish objectives and create the schedule, monitoring and adjusting that schedule as needed, ensuring quality deliverables and reporting to make insightful analyses.
Production Scheduler
A production scheduler oversees the production scheduling process, managing production schedules and allocating resources strategically to ensure that his organization can respond to customer orders at any point. To do so, production schedulers must constantly collaborate with production managers, production planners and cross-functional teams to ensure the production process is as efficient as possible.
A production scheduler must demonstrate working knowledge in key areas of production management such as production planning, optimization and control but also managerial skills such as resource planning, workflow management, team management and project scheduling.
Procurement Team
The procurement team is involved in material sourcing, identifying suppliers and vendor management to ensure the necessary materials, components and services are acquired in a timely and cost-effective manner. They work closely with production planners and analyze production forecasts. Procurement teams are responsible for creating and managing purchase orders.
Inventory Manager
The inventory manager ensures that the necessary materials and components are available when needed. They do this through material planning, which involves demand forecasting and tracking stock levels to prevent stockouts. They also oversee work-in-progress and finished goods.
Production Engineering Team
This technical team provides expertise to ensure processes are designed, optimized and maintained for efficient production. They develop production processes and analyze workflows to minimize bottlenecks and improve efficiency. The team assesses the production capacity of equipment and resources to determine how much can be produced and identify constraints that could impact the schedule.
Marketing and Sales Team
The marketing and sales team provides insights related to customer demand, market trends and promotional strategies. They provide demand forecasting, schedule new product launches and collect customer feedback to gather insights and manage expectations.
Maintenance Team
The maintenance team ensures that equipment and materials are operating smoothly and efficiently. They plan preventive maintenance for equipment and schedule all maintenance activities. The maintenance team also monitors equipment performance, performs emergency repairs and collaborates with production managers to understand production schedules and identify critical periods when equipment must be operational.
Production Schedule vs. Production Plan
Production scheduling and production planning work together but they are separate processes. In fact, sometimes a manufacturer will use one instead of both depending on the type of production they’re doing.
There are differences between the two and it’s important to understand what those differences are. One way to look at it is that production planning is a general overview of when a product is made, but a production schedule is a far more detailed look into that process.
Production Schedule vs. Master Production Schedule (MPS)
A master production schedule (MPS) details what, when and how many products a manufacturer will produce in the long term across the entire organization, usually covering weeks, months or even quarters. It links the demand determined by sales to the capacity a company has to make multiple production runs for all its production lines. Therefore, the master production schedule helps create a realistic plan that avoids overstocking warehouses but maintains on-time delivery.
A production schedule shares many qualities with the MPS, but the main difference is that its scope is much more specific as it focuses on individual production runs or batches of products and is meant to be used at a shop floor level for guiding everyday production processes and activities.
How to Make a Production Schedule
Production schedules vary from one organization to another depending on the production scheduling tools you use, the level of detail you’d like to include and the specific characteristics of your manufacturing process. Having said that, here are five general steps any organization should follow when making a production schedule.
1. Estimate Customer Demand
Before you make a realistic production schedule, you’ll need to forecast the future customer demand for your product so you have a better idea of the ideal production volume your organization should manufacture to ensure there’s enough product supply for fulfilling customer orders.
Various demand planning techniques and business analytics tools can make an accurate sales forecast for your business. Sales forecasts can be made for various time frames such as quarterly, monthly or yearly.
2. Measure Your Production Capacity
Once you’ve created a sales forecast, you’ll then need to measure your production capacity, which refers to the organizational resources such as raw materials, labor and capital assets that your organization uses to manufacture goods and evaluate whether there are enough resources to meet customer demand and manufacture products on time.
If this isn’t the case, you should invest in your manufacturing facilities to expand your production capacity. If that’s not possible, try production optimization techniques such as re-thinking your shop floor or balancing the workload of assembly line stations.
3. Make a Production Budget
Based on your sales forecast and production capacity, you can now make a production budget, which is a document that allows you to estimate the ideal number of units that should be produced to meet customer demand and also maintain optimal product stock inventory levels.
4. Optimize Production Routing
Production routing consists of defining the route that materials, parts and components will take across the production floor as they’re transformed into final products by production workers. The main objective of the production routing process is to identify the most efficient route in terms of time, effort and cost. By defining the production route, you can also accurately measure how long it’ll take to make your products.
5. Schedule Production Activities
At this point, you should clearly understand the quantity of product that needs to be manufactured, how much it’ll cost and how long it’ll take. Now, you’re finally ready to schedule production orders to meet the production budget you’ve defined.
Production Schedule Example
Various tools can make a production schedule, from a simple spreadsheet or task list with production order details and due dates to more advanced production scheduling tools such as Gantt charts.
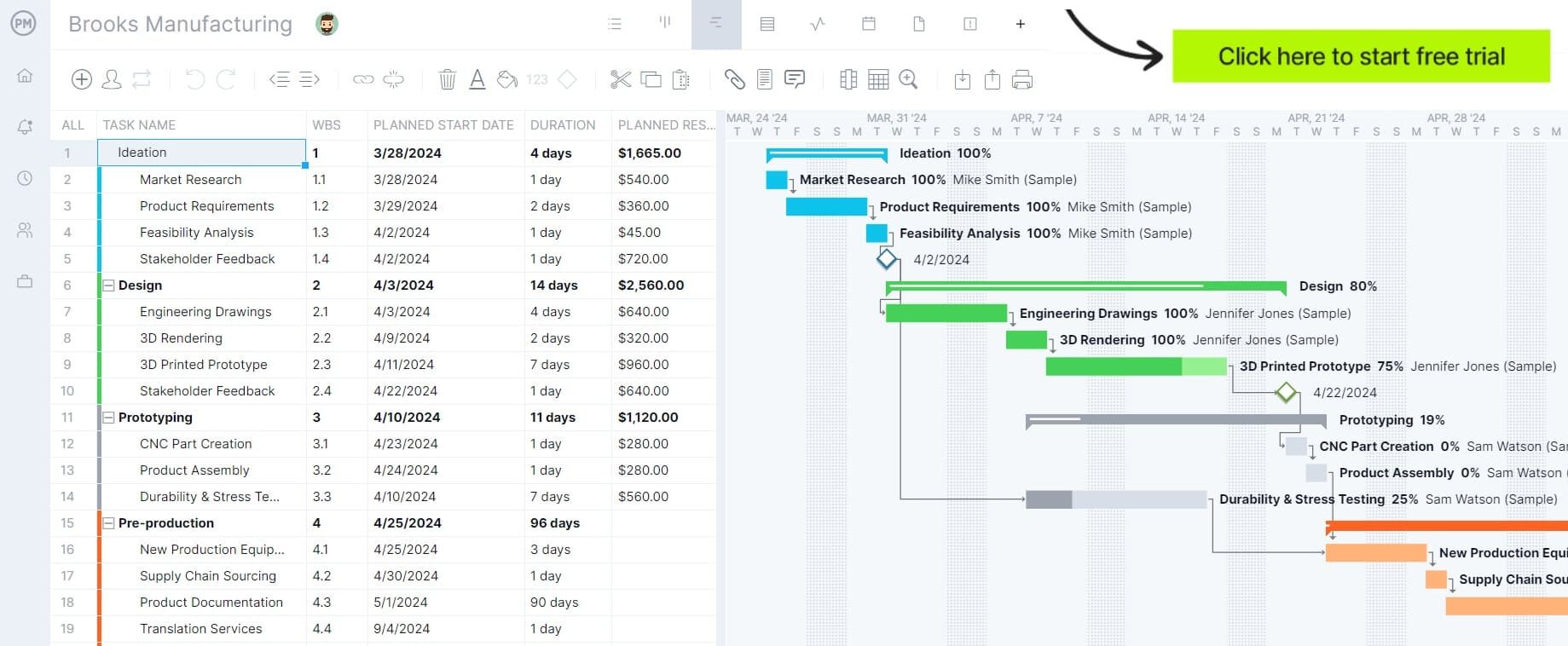
Here’s an example of what a Gantt chart production schedule looks like. On the left side, you can list the major stages of your production process, which in this case are “design,” “prototyping” and “pre-production” among others. To complete these production processes, the team must execute many smaller tasks, such as 3D rendering, CNC machining and durability testing.
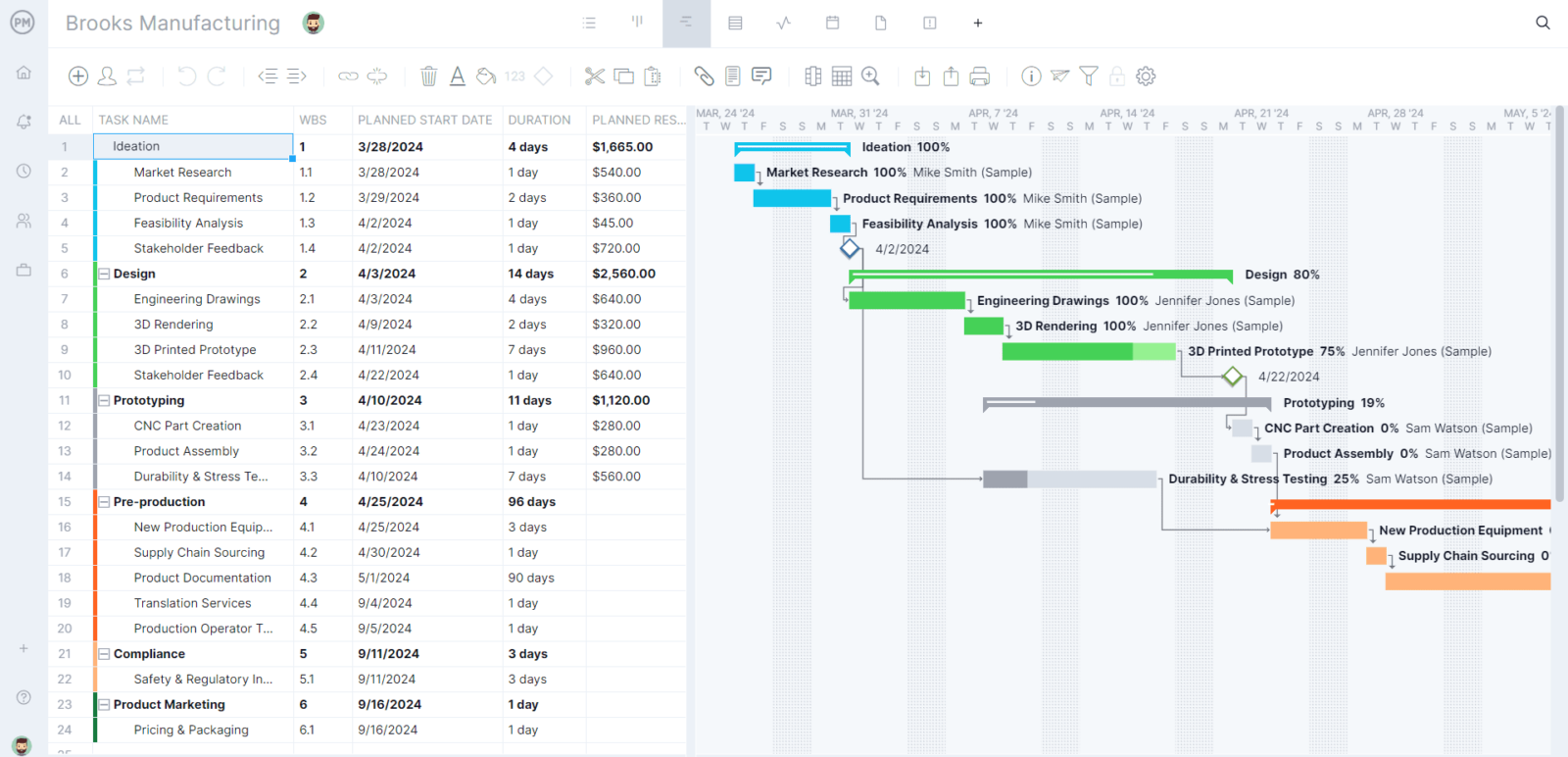
As you can see in our production schedule example image, a Gantt chart allows you to enter details about these tasks such as their due dates, duration, costs and more. On the right-hand side, there’s a visual timeline that shows bars to represent the duration of tasks over a calendar and allows you to track their percentage of completion and identify any dependencies between them.
If you prefer, use the visual timeline bars to represent each of your production orders to create a high-level view Gantt chart production schedule that allows you to check their progress and due dates at a glance. Or if you’re not ready for Gantt charts yet, you can use a manufacturing template for Excel to keep track of production orders.
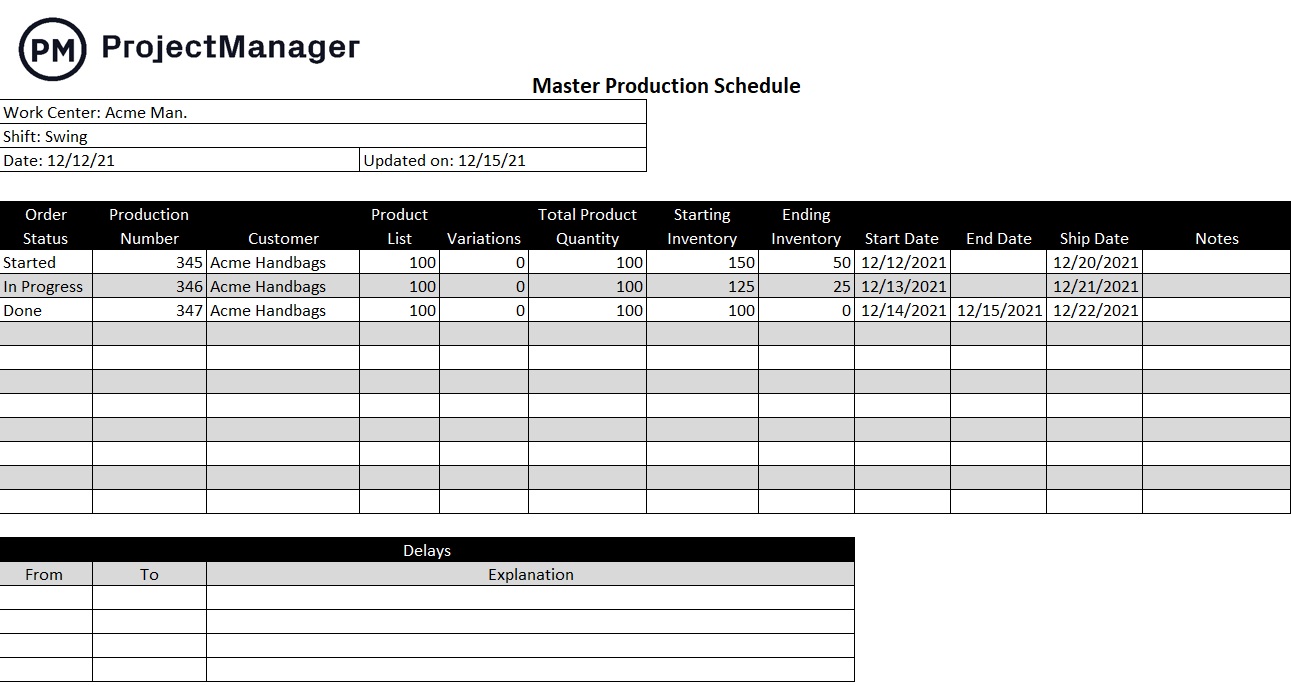
Production Schedule Template
This free production schedule template for Excel helps you schedule production orders and keep track of their status and due dates for manufacturing and shipping. It also allows you to keep track of the starting and ending inventory of finished goods after each production order to help you maintain optimum inventory levels.
Production Scheduling Techniques
Various production scheduling techniques can help you streamline your manufacturing process and efficiently use organizational resources. Here’s a quick overview of some of the most commonly used methods to make a production schedule.
Forward Scheduling
This production scheduling technique consists of manufacturing orders as soon as they’re received, or whenever resources become available. This ensures your production workers and capital assets have a high resource utilization rate but might make it difficult for your organization to accommodate new orders as production capacity is always limited.
Backward Scheduling
As its name suggests, this production scheduling method works in the exact opposite manner as forward scheduling. In a backward scheduling approach, manufacturers wait until the last day of the lead time to manufacture production orders. While it might seem counterintuitive, this allows them to use their production capacity strategically to take as many orders as possible.
Make-to-Order Production Scheduling
In a make-to-order production scheduling approach, manufacturers don’t keep an inventory of product stock so they only make the exact number of product units to meet customer orders.
Make-to-Stock
This production scheduling method is used by manufacturers who sell their products through physical distribution channels such as brick-and-mortar retail shops that hold inventories of product stock for sale. In a make-to-stock manufacturing approach, manufacturers constantly check stock inventory levels and schedule production orders to replenish them.
Finite Capacity Scheduling (FCS)
In a finite capacity production scheduling model, manufacturers schedule production orders based on their available production capacity. This conservative production scheduling approach helps ensure that organizations don’t take customer orders they can’t complete on time which is ideal for small to medium-sized manufacturing companies with limited resources.
Infinite Capacity Planning
The opposite of finite capacity scheduling, this method ignores production capacity constraints and consists of scheduling production orders based on their lead time but ignores resource constraints, which is a preferred method for larger organizations.
In this production method, resources utilized for a production order might be reallocated from one to another based on their lead time and due dates.
Key Factors to Consider In Production Scheduling
Because production scheduling is such a large job, it can seem overwhelming. It’s best to look at it as a collection of many smaller jobs or factors that contribute to production. Let’s look at some things you’ll need to consider when production scheduling.
- Production capacity: The most output measured in units of output per period.
- Production forecasting: Projection of the number of finished products or subassemblies that’ll be produced in a specific period to meet forecasted sales.
- Production inventory: Everything that’s used in the manufacturing process.
- Required raw materials & components: Specific items in production inventory.
- Supply chain: A series of processes in the production and distribution of a product.
- Available equipment: Metric to measure the percentage of time a piece of equipment can operate.
- Operations management: The production schedule must stay up-to-date on what’s going on with the organization.
- Plant layout: This is important as the time it takes to transport materials and process them is part of the larger production schedule.
Production Scheduling Software
Production scheduling software helps manufacturers better schedule their production lines, including equipment and resources. It can automate certain activities to streamline work and define employees’ availability to make it easier to assign them to jobs.
It monitors and tracks the schedule to help managers catch issues and respond to them quickly to avoid any slowdown or delay or delivery. It can address customer demand and reduce lead time getting products into retail shops or eCommerce. Production scheduling software can help with workflows, timesheets and much more.
Choosing software to manage your production scheduling process can be difficult, which is why we’ve reviewed the best free and paid production scheduling software in our blog to help you make an informed decision.
ProjectManager Has Powerful Production Scheduling Tools
ProjectManager is award-winning scheduling software that helps managers plan, manage and track their jobs in real time. Live dashboards and customizable reporting tools allow managers to have transparency into the production line, whether getting a high-level view of costs, time and more or digging deeper into status reports, variance and other reports that can be shared with stakeholders to keep them updated.
Make Detailed Production Schedules with Gantt Charts
You can use ProjectManager’s Gantt chart to map all your production orders in one place and visualize their duration and due dates at a glance. In addition, you can zoom into the activities that need to be completed to transform your raw materials, parts and components into final products. You can track their percentage of completion, costs, task dependencies, priority and much more.
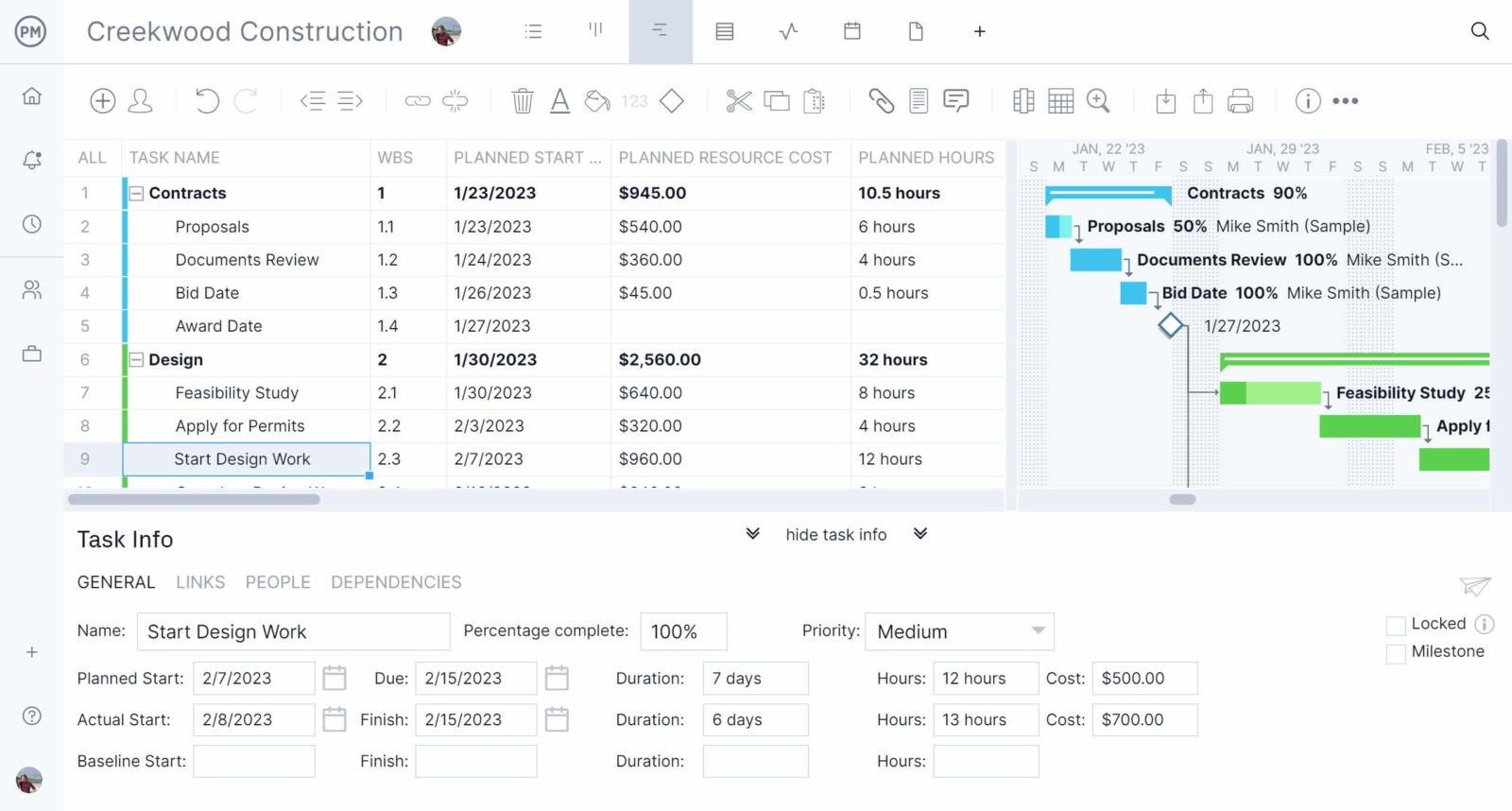
Create Production Workflows With Kanban Boards
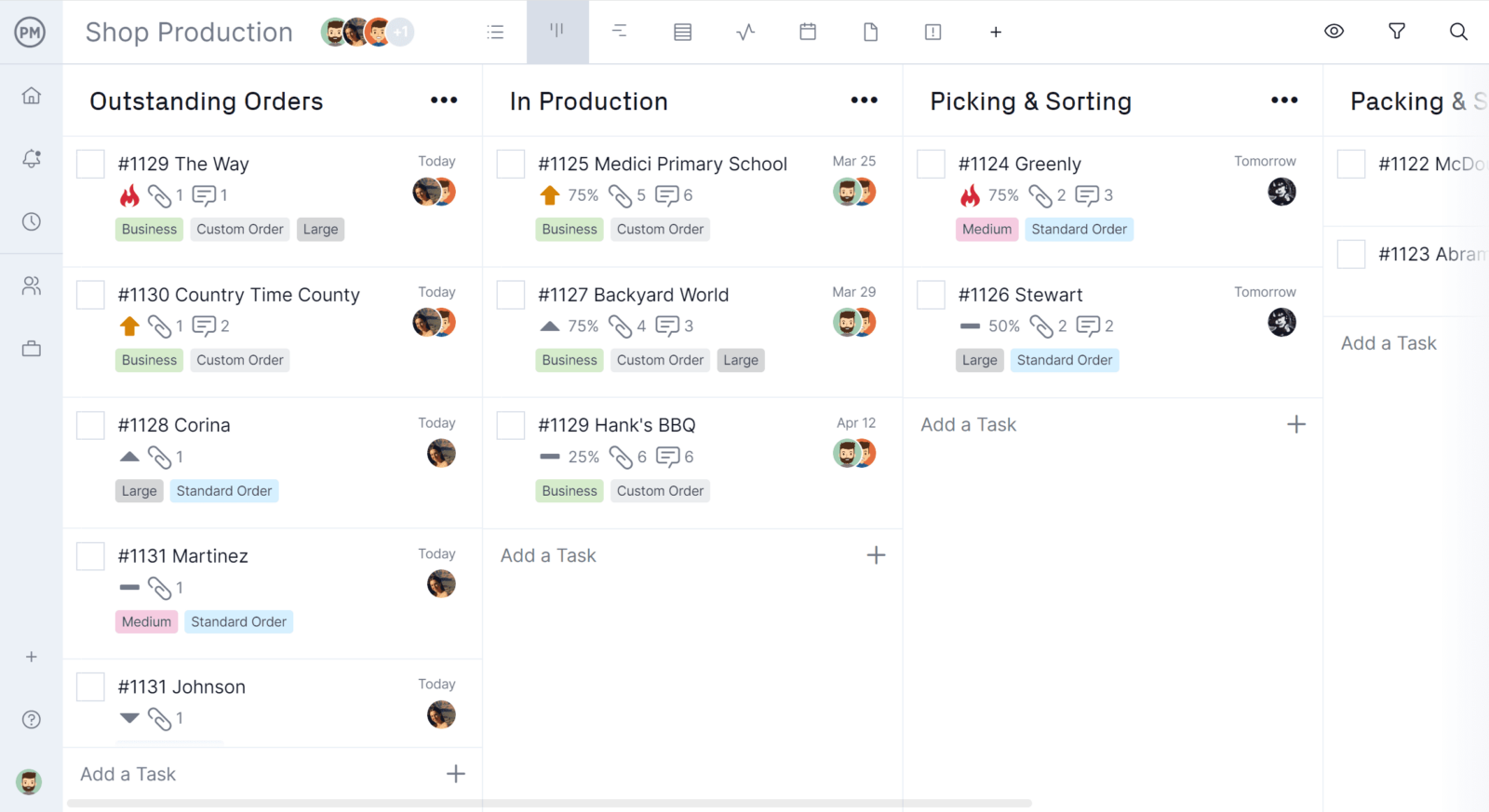
Creating custom workflows allows production to move from one activity to the next. You can even automate workflows by adding triggers that will change the status, assignee and more. To ensure that only quality moves forward on the production line, set task approvals and designate someone with authority to review and approve. Our software has multiple project views so the production scheduling of the Gantt chart is the same when you toggle over the kanban board, which makes it easy to visualize the workflow.
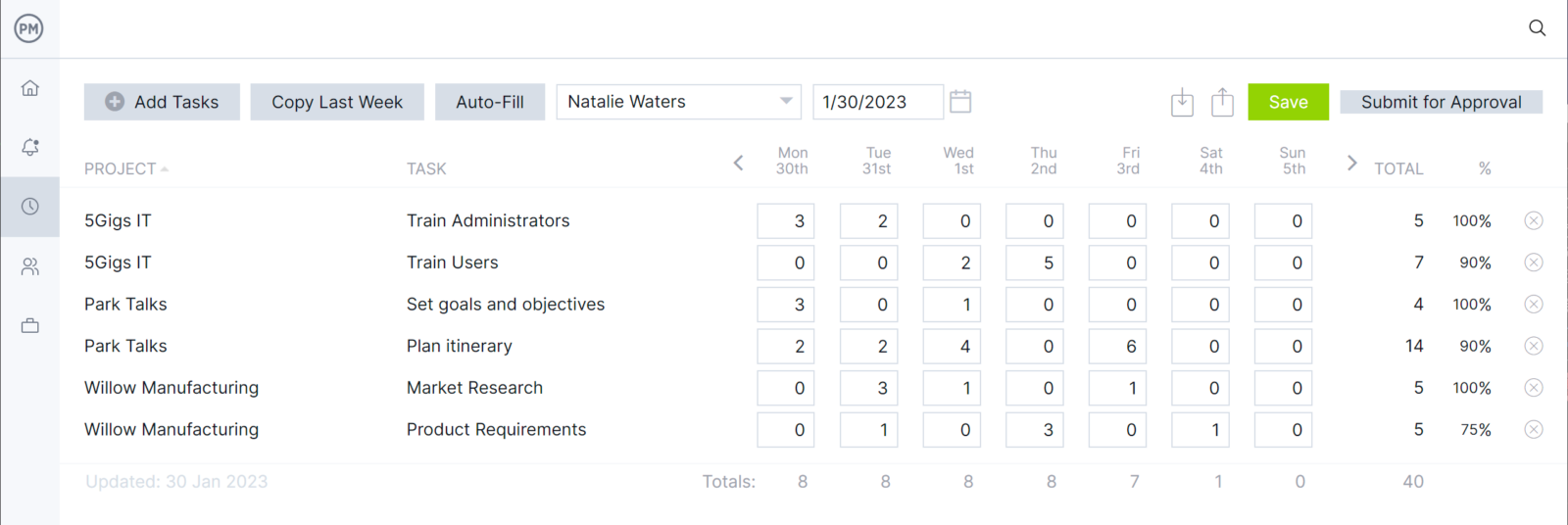
Track Resource Utilization With Timesheets and Workload Charts
Keeping track of your resources is essential to staying on a production schedule. Our software has resource management tools that can keep your production line working more efficiently. There are tools, such as secure timesheets, which do more than streamline payroll. They also show you a real-time picture of how complete each team member’s job is. You can set the availability of team members’ PTO, vacations and global holidays, which makes it easier to assign them work. Then our color-coded workload chart makes it easy to see who is overallocated. You can balance their workload from that chart to keep production on track.
As mentioned above, production scheduling must be flexible and adjust to changes. Our risk management features make it easier to identify risk and track issues in real time to ensure that there’s as little disruption as possible. Our collaborative platform makes it easy for everyone to share files, comment and more whether they’re on the production line or in the office. Manufacturers can benefit from all the features of our software.
Related Content
- Best Production Scheduling Software Rankings
- Best Production Planning Software Rankings
- Best Production Tracking Software
- Production Management: A Quick Guide
- Production Planning in Manufacturing: Best Practices
- Production Schedule Template
- How to Create a Master Production Schedule (MPS)
- Programación de producción: Cómo crear un cronograma de producción
- Planification du calendrier de production : les bases
- Produktionsplanung Grundlagen: Einen Produktionsplan erstellen
ProjectManager is online scheduling software that builds schedules and helps you execute them more efficiently. Use tools to plan, assign, track and report on all aspects of your production. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

