- What Is a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)?
- Why Use a WBS In Project Management?
- Components of a Work Breakdown Structure
- Work Breakdown Structure Examples
- Work Breakdown Structure Software
- Work Breakdown Structure Templates
- Must-Have Features of WBS Software
- How to Create a WBS in ProjectManager
- Benefits of Using a Work Breakdown Structure In Project Management
- When to Use a Work Breakdown Structure?
- Who Should Use a Work Breakdown Structure?
- Types of Work Breakdown Structure
- Types of Work Breakdown Structure Charts
- Work Breakdown Structure Best Practices
- WBS in Project Management Documents
- Work Breakdown Structure Variants
What Is a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)?
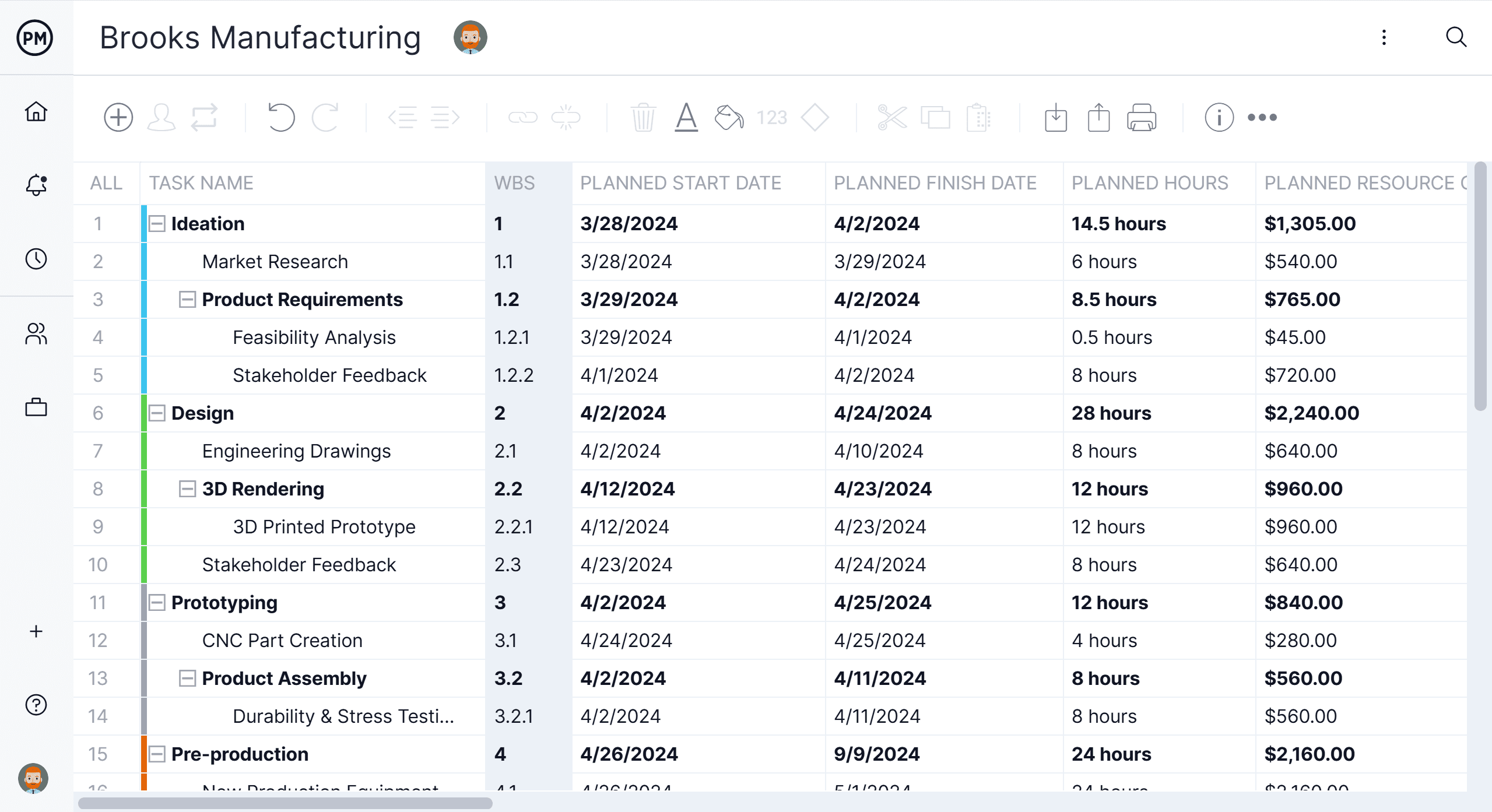
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is a visual, hierarchical and deliverable-oriented deconstruction of a project. It is a helpful diagram for project managers because it allows them to break down their project scope and visualize all the tasks required to complete their projects.
All the steps of project work are outlined in the work breakdown structure chart, which makes it an essential project planning tool. The final project deliverable, as well as the tasks and work packages associated with it rest on top of the WBS diagram, and the WBS levels below subdivide the project scope to indicate the tasks, deliverables and work packages that are needed to complete the project from start to finish.
Project managers make use of project management software to lay out and execute a work breakdown structure. When used in combination with a Gantt chart that incorporates WBS levels and task hierarchies, project management software can be especially effective for planning, scheduling and executing projects.
ProjectManager is an online work management software with industry-leading project management tools like Gantt charts, kanban boards, sheets and more. Plan using WBS levels in our tool, then execute with your team via easy-to-use kanban boards and task lists. Try it for free today.
ProjectManager’s online Gantt charts feature a column for the WBS code—learn more
Why Use a Work Breakdown Structure In Project Management?
Making a WBS is the first step in developing a project scope baseline and a project schedule. It defines all the work that needs to be completed (and in what order) to achieve the project goals and objectives. By visualizing your project in this manner, you can understand your project scope, and allocate resources for all your project tasks.
A well-constructed work breakdown structure helps with important project management process groups and knowledge areas such as:
- Project Planning, Project Scheduling and Project Budgeting
- Risk Management, Resource Management, Task Management and Team Management
In addition, a WBS helps avoid common project management issues such as missed deadlines, scope creep and cost overrun, among others.
In other words, a work breakdown structure serves as your map through complicated projects. Your project scope may include several phases or smaller sub-projects—and even those sub-projects can be broken down into tasks, deliverables, and work packages! Your WBS can help you manage those items, and gain clarity into the details needed to accomplish every aspect of your project scope.

Get your free
WBS Template for Excel
Use this free WBS Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
Get the templateComponents of a Work Breakdown Structure
A work breakdown structure is built from several key elements that define, organize and clarify a project’s scope. These components break the final deliverable into manageable parts, explain how work is structured and provide the detail needed for estimating, scheduling and assigning responsibilities. Together, they create a clear hierarchy that helps teams understand the project’s full scope and how each piece contributes to the overall outcome.
- WBS Chart: A WBS chart is the visual diagram that displays all components of the work breakdown structure. It shows the project’s scope broken into progressively detailed levels—final deliverable, project deliverables, sub-deliverables and work packages—helping teams clearly see how the entire project is organized.
- WBS Dictionary: The WBS dictionary is a companion document that defines each element shown in the WBS chart. It describes deliverables, work packages, boundaries and key details so stakeholders share the same understanding of what each component includes—and what it does not.
- Final Deliverable: The final deliverable sits at the top of the WBS and represents the completed outcome of the project, or in other words the delivery of the project itself. Everything beneath it in the hierarchy contributes to producing this end result, from major deliverables down to the detailed work packages.
- Work Streams: Work streams are parallel areas of effort that run through the project, often cutting across multiple deliverables. They group related work performed by specific teams or functions, helping organize the WBS in a way that reflects how work actually gets done.
- Project Deliverables: Project deliverables are the major outputs required to complete the final deliverable. Each deliverable breaks the project into manageable sections of scope and becomes the foundation for creating sub-deliverables and work packages beneath it.
- Sub-deliverables: Sub-deliverables break a larger deliverable into more specific components. They provide another layer of detail in the WBS, helping clarify the structure of the work before it is decomposed into the work packages that teams will execute.
- Work Packages: Work packages are the lowest level of the WBS and represent the smallest units of scope that can be assigned, estimated and tracked. Each work package groups related tasks that contribute to a sub-deliverable or deliverable, making project planning and execution manageable.
- Planning Packages: Planning packages represent portions of scope that are understood at a high level but not yet broken into detailed work packages. They allow project teams to estimate costs, and make a project budget early, while leaving room to refine the breakdown as more information becomes available.
- WBS Levels: WBS levels represent the depth of decomposition in the structure—from the final deliverable at the top, to deliverables and sub-deliverables in the middle, down to work packages at the bottom. Levels help readers quickly understand where each component fits in the hierarchy.
- WBS Codes: WBS codes are hierarchical identifiers assigned to each component in the structure. They make it easy to reference elements, show how pieces relate to one another and support reporting, traceability and organization across all levels of the WBS.
- Control Accounts: Control accounts group related work packages under a management control point. They enable performance measurement, cost tracking and reporting at meaningful chunks of the project, often aligning with major deliverables, work streams or functional areas.
- Cost Accounts: Cost accounts tie elements of the WBS to budget categories used for estimating and tracking project spending. They link financial management to the scope structure, making it easier to monitor costs, compare planned versus actuals and control budget performance.
If you prefer a visual and verbal explanation of this information on work breakdown structures, watch this video.
The best way to understand how these work breakdown structure components interact with each other, is to look at a work breakdown structure example.
Work Breakdown Structure Examples
Here are two work breakdown structure examples, showing the two most commonly used types of work breakdown structure in project management.
Tree Diagram Work Breakdown Structure Example
This work breakdown structure example illustrates how a large project—such as building a commercial office building—can be organized into clear, manageable components. At the top sits the final deliverable, which represents the completed outcome of the project. From there, the work is broken into work streams, or major areas of effort that run in parallel throughout the project. These streams reflect the real way teams work: design teams focus on drawings, field crews handle site preparation, MEP specialists manage electrical and plumbing systems, and so on.

Beneath each work stream is a deliverable, which defines a tangible output required to complete that portion of the project. Deliverables are further decomposed into sub-deliverables, providing an additional layer of structure that clarifies what each deliverable includes. Finally, each sub-deliverable breaks down into a work package, the smallest unit of scope that can be assigned, estimated, tracked, and completed by a project team.
By showing five vertical chains—one for each work stream—the diagram demonstrates how the entire project scope can be decomposed consistently from top to bottom. Each column represents a logical slice of work, making it easy to see how individual work packages roll up into sub-deliverables, how those sub-deliverables support the deliverables, and how all deliverables together contribute to the final building.
This visual structure helps stakeholders understand the overall project plan, ensures nothing is overlooked, and provides a solid foundation for scheduling, estimating, budgeting, resource planning, and progress tracking.
Build a work breakdown structure Gantt chart diagram in ProjectManager in just a matter of minutes. Get started for free today.
A Gantt chart with WBS codes in ProjectManager. Learn more
List Work Breakdown Structure Example
As discussed above, a WBS doesn’t need to be shown as a visual chart to be effective. It can also be represented as a structured outline that lists each level of the hierarchy. The work breakdown structure example below shows the same commercial office building project using a list format, with each level of decomposition clearly identified. This format is easy to scan, works well in project documentation, and can be used directly in tools that support hierarchical lists or WBS coding.
1.0 Commercial Office Building
1.1 Design & Engineering
1.1.1 Architectural & Structural Plans
1.1.1.1 Finalize Building Layout
1.1.1.1.1 Produce Approved Floor Plan Drawings
1.2 Site Preparation
1.2.1 Site Survey
1.2.1.1 Topographic Analysis
1.2.1.1.1 Complete Topographic Survey
1.3 Structural Work
1.3.1 Foundation Construction
1.3.1.1 Concrete Footings
1.3.1.1.1 Pour Concrete Footings
Because of their simplicity and effectiveness, list-based work breakdown structures are usually implemented in project management software like ProjectManager.
Work Breakdown Structure Software
Making work breakdown structures manually is a time consuming task, especially when projects are constantly changing, so using a project management software like ProjectManager is ideal for busy teams across industries. Here’s a quick video showing how to make a WBS with ProjectManager.
Software facilitates the process in several different ways. Some use a network diagram and others use a Gantt chart. All of them, however, are a visual representation of the project, literally breaking down the various stages and substages needed to assemble the final project deliverable.
Work Breakdown Structure Templates
If you’re not ready to take the plunge and use ProjectManager’s work breakdown structure software, but you’re still interested in seeing how using this tool can help you construct a sturdier plan for your next project, don’t worry. We have an intermediate step you can take.
Work Breakdown Structure Template for Excel
This free work breakdown structure allows users to break down the scope of a project into work streams, deliverables, sub-deliverables and work packages using a list or a tree diagram.
Work Breakdown Structure Template for Google Sheets
We’ve also created a work breakdown structure template for Google Sheets, for those teams that prefer to collaborate online.
Visit our library of free project management templates to access over 100 free templates for Word, Excel and Google Sheets, including a free WBS template to get you started off right. If you decide to try out our project management software, we offer a free 30-day trial. You can upload the project work breakdown structure template into ProjectManager, and it automatically creates a new project in our software. Now you can use that template to plan, schedule, monitor and report on your project.
Must-Have Features of WBS Software
There are many types of work breakdown structure software available, so when you’re looking for one to help you plan your project, be sure it offers these features:
Break Tasks Down
Deliverables are important to define, as are the tasks that get you there—but most tasks require being broken down further in order to complete them. That’s where subtasks come in. They’re part of a more complex task, and you want that feature in your WBS software.
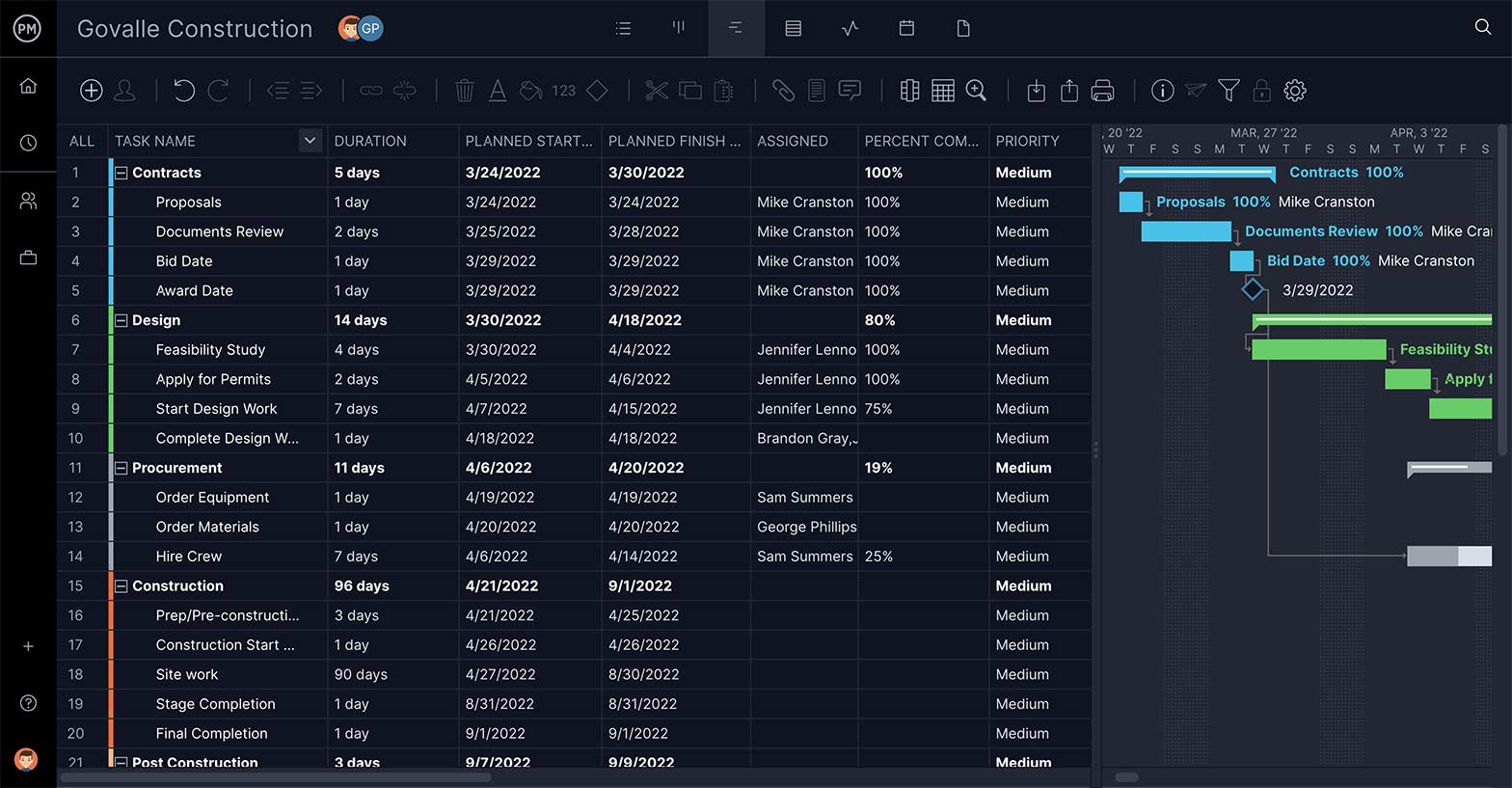
Link Dependent Tasks
Not all tasks are the same. Some can’t start or stop until another has started or stopped. These dependent tasks can create a bottleneck later in the project’s execution phase, unless you identify them early. Having a task dependency feature is essential.
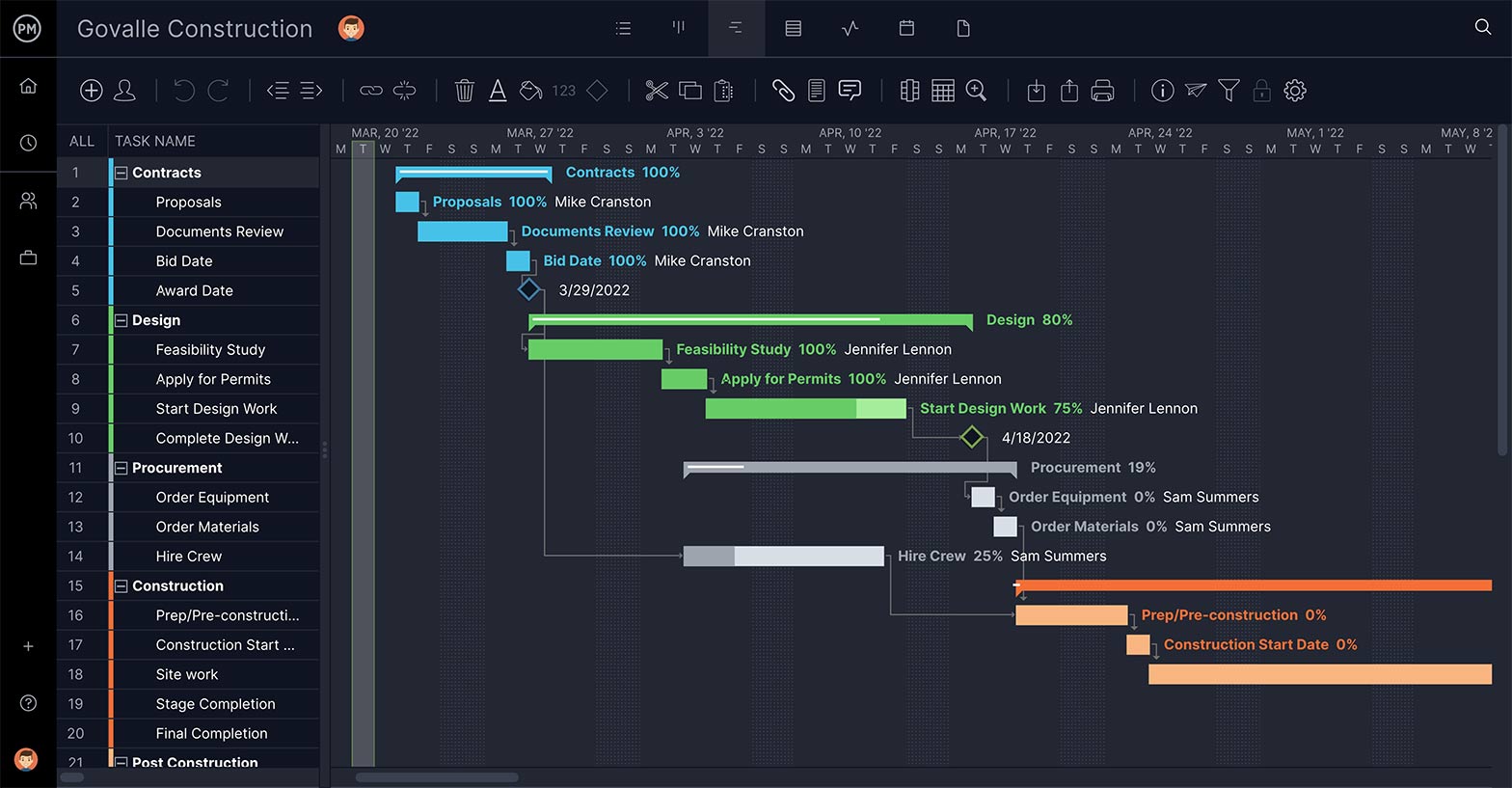
Set Task’s Priority and Duration
The point of WBS software is to build a feasible schedule. Therefore, you need features that feed into this process by defining the priority of the task, so you know which phase it goes with; as well as describing the task and estimating how long it will take to complete.
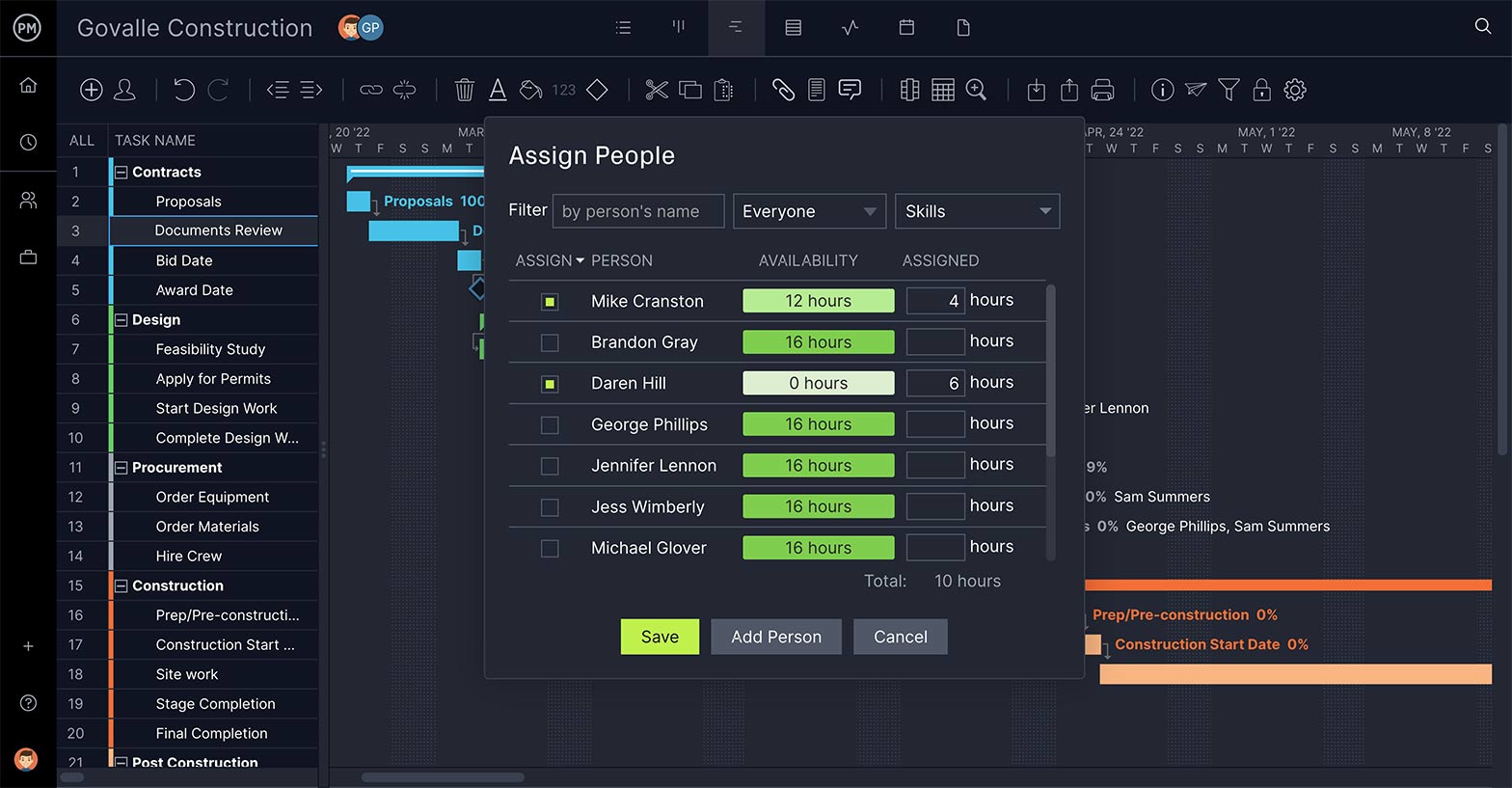
Keep Your Team Working
The WBS sets up your tasks and deliverables, but once the project is in the execution stage, it’s key that you have a way to allocate resources to your team to keep the tasks moving as planned. That includes a feature to make sure their workload is balanced.
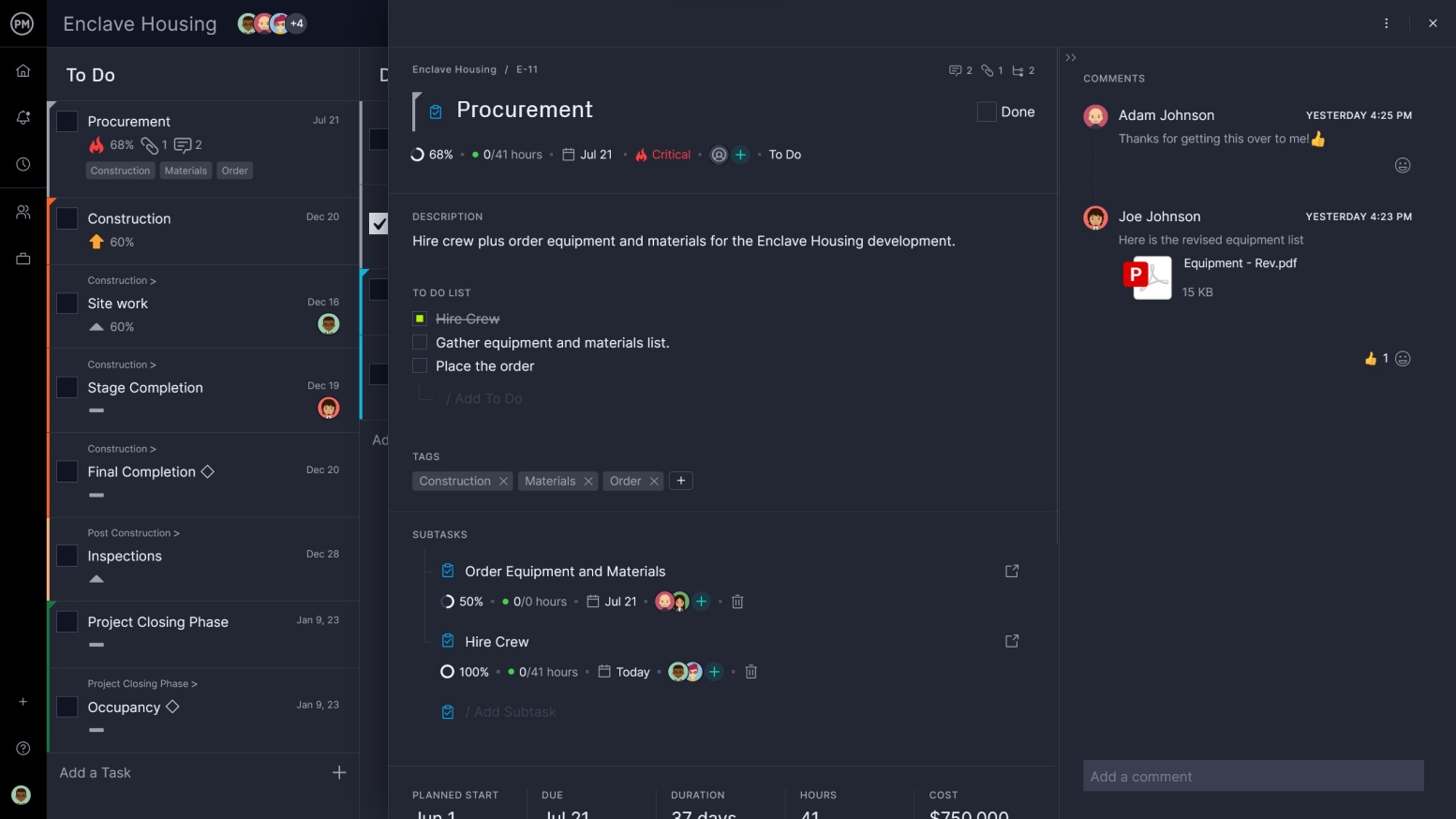
Get a High-Level View
Being able to monitor your progress is what keeps your project on schedule. A WBS software sets up the plan and you must have features to maintain it throughout all the phases of the project. Dashboards can give you a view of the landscape across several metrics.

Make Better Decisions
As you move from the planning to the execution stage, you’ll need a reporting feature that can deliver critical project data on progress and performance. This information will feed your decision-making and help you steer the project to a successful conclusion.
How to Create a WBS in ProjectManager
The purpose of work breakdown structure software in project management is to organize and define the scope of your project.
Using ProjectManager’s online Gantt charts to build your WBS is not only more efficient, it dovetails into every other aspect of your project, because of our robust suite of project management features.
Here’s a quick summary of how to create a WBS using a Gantt chart. Sign up for a free trial of our software and follow along!
1. Identify Project Deliverables
There are 5 stages in the project life cycle, initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and closure. Each of them produces deliverables that are required to produce the final deliverable, which is the completion of your project.
Identify the phases in your project to create more than a mere task list. Set them apart with our milestone feature on the Gantt chart tool. They can also be color coded to better differentiate the phases.
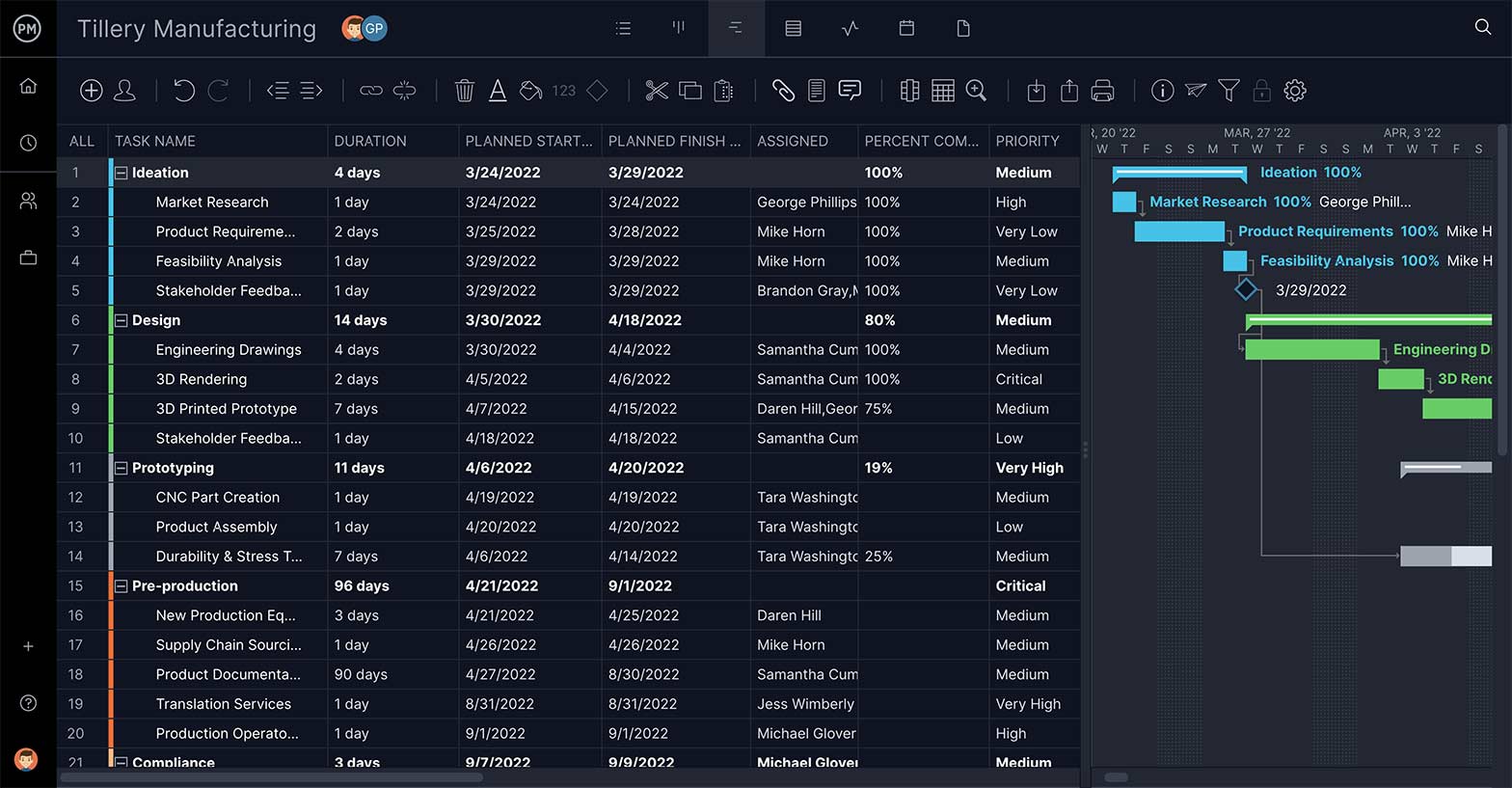
2. List Subtasks, Describe Tasks & Set Task Owner
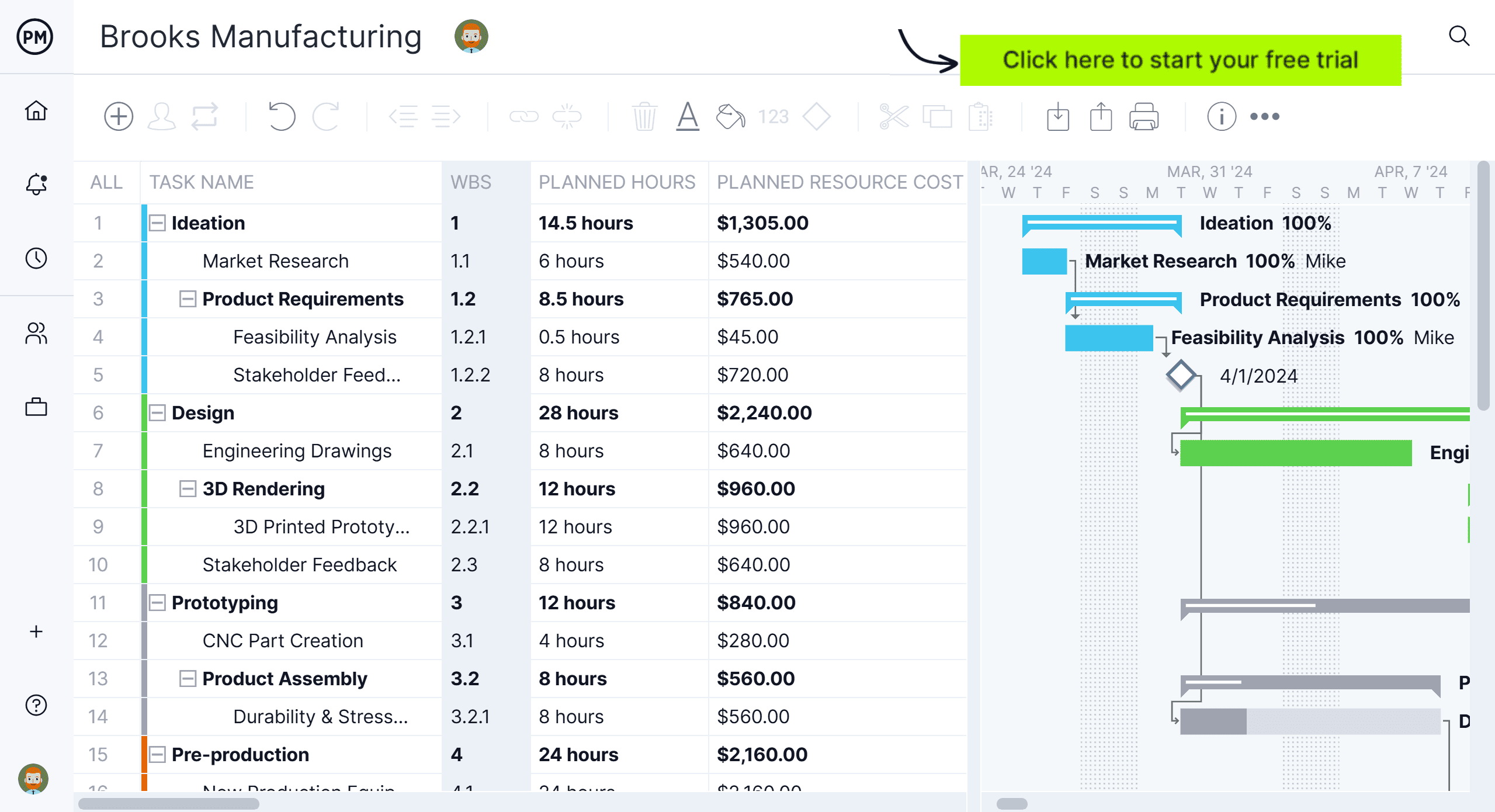
Subtasks are part of a larger, more complex task. In this case, your WBS work packages are perfect for this feature. Add summary tasks or work packages above the related tasks, which can be your project phases or project deliverables, depending on your WBS type preference and indent them. The image below shows our WBS example represented on a Gantt chart, showing the project phases and work packages associated with them.
3. Link Dependencies
Task dependencies are tasks that cannot start until another is finished or started. Link tasks that are dependent on one another by dragging one to the other. We link all four types of task dependencies. By identifying these tasks at this stage, you’ll avoid bottlenecks during execution.
4. Set Resources & Costs
Resources are anything that you need to complete the project phases, deliverables and work packages. They range from the people on your team to materials, supplies and equipment. Your WBS allows you to break down your project scope into work packages so that you can allocate resources and estimate project costs.
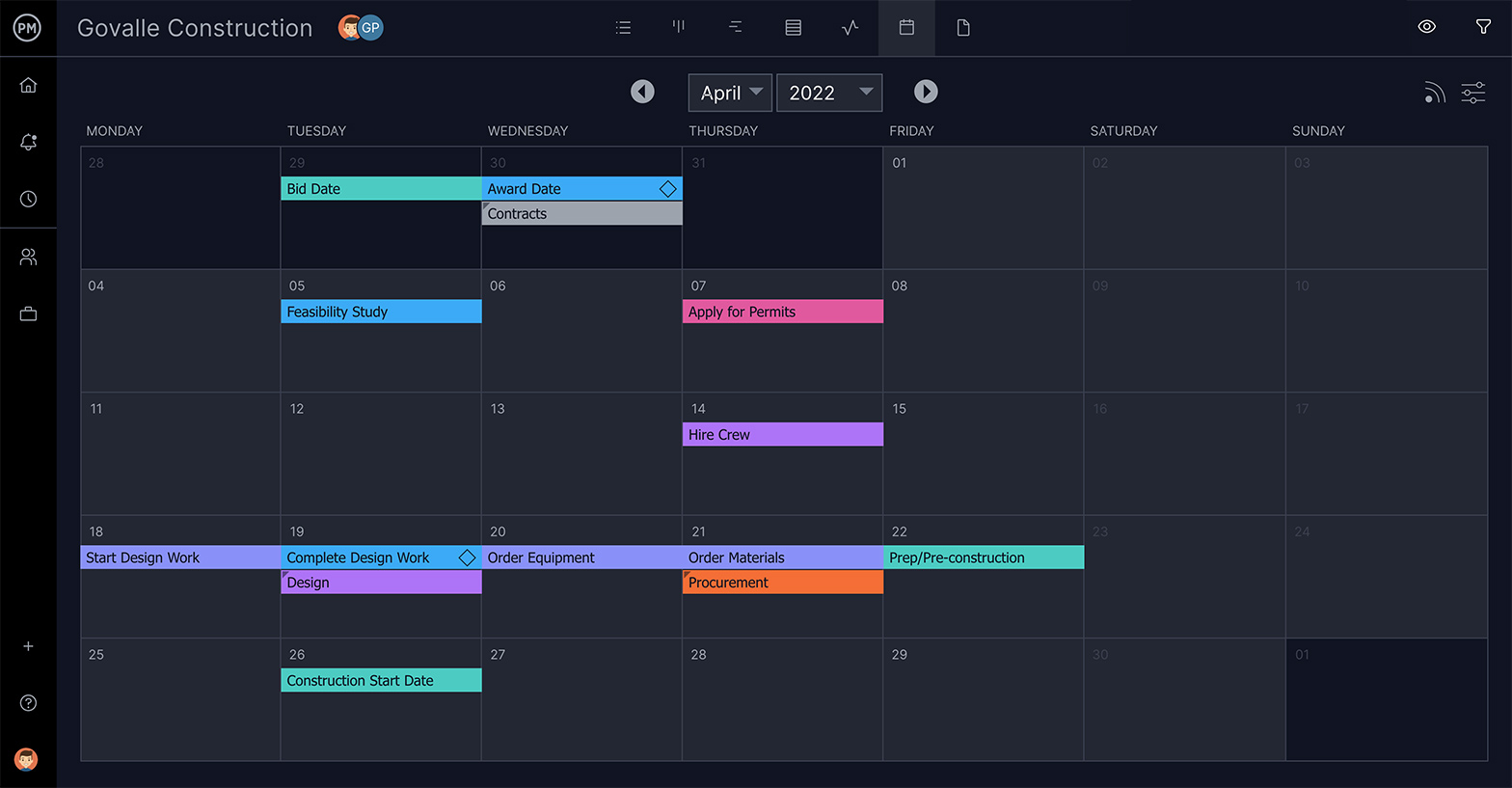
5. Add Start & End Dates & Estimated Completion
Every task has a start and an end date. Add the date when the task needs to start in the planned start date column and when it should be completed in the planned finished date. There’s also an estimated completion column for the amount of time you plan for the task to take.
6. Track Status of Control Accounts & Work Packages
Tracking is how to know if a project is performing as planned. That’s why a WBS has control accounts and work packages. When speaking of tasks, tracking tells you multiple things: logged hours, costs, priority, new communications, the percentage complete and how its actual progress compares to your planned progress.
7. Write Notes
Having a section in which to jot down notes is always advisable. While the WBS is thorough, there might be something you need to address that doesn’t fit into its rigid structure.
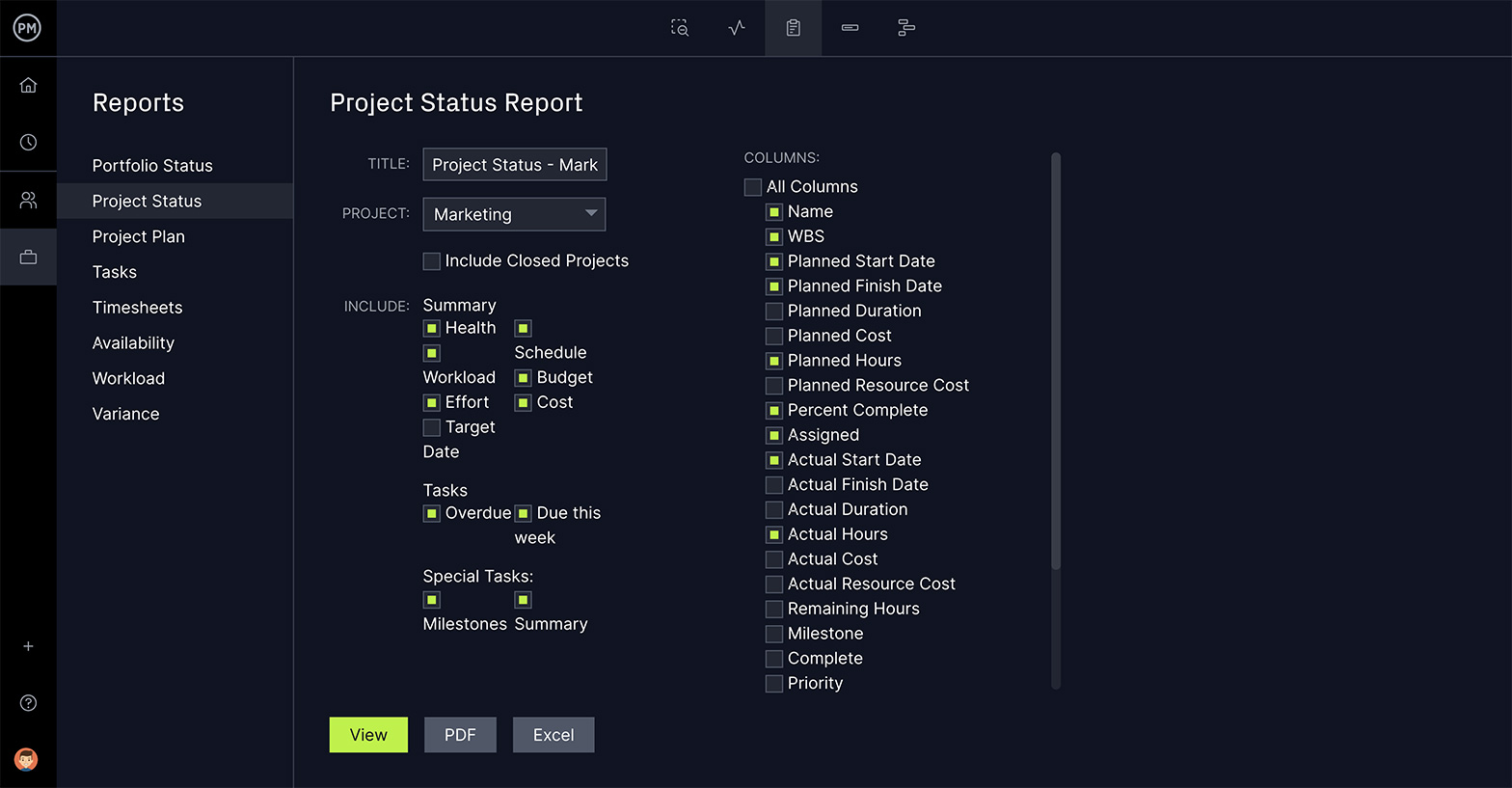
8. Generate Reports
Project reports pull data from the project to illuminate its progress, overall health, costs and more. Generate a report on your WBS by using our reporting tool. Our reports summarize your project data and allow you to filter the results to show just want you want. Reports can also be shared with stakeholders.

Benefits of Using a Work Breakdown Structure In Project Management
A work breakdown structure helps teams turn a broad project vision into a clear, structured plan. By decomposing the project scope into manageable components, the WBS improves coordination, strengthens estimating, clarifies responsibilities and supports more accurate planning across cost, schedule and resources.
These benefits make it easier to deliver predictable results and maintain control throughout the project life cycle.
Prevents Scope Creep
A work breakdown structure prevents scope creep by forcing a clear project decomposition tied directly to the scope baseline, scope statement and scope decomposition process. Each deliverable and work package is defined upfront, making scope validation easier and reducing the chance of unapproved work slipping in.
As teams plan project milestones and align expectations, the WBS becomes a reference point that keeps the project focused on authorized deliverables. This structured breakdown helps managers identify variations early and maintain tight control over what is—and isn’t—in scope.
Brings Clarity into the Resource Planning Process
The WBS brings clarity to resource planning by mapping work packages directly to the resources required to complete them. Once the scope is decomposed, teams can build a resource allocation matrix, identify resource breakdown needs and understand both material requirements and labor allocation for each part of the project.
This structured view eliminates guesswork and supports more accurate estimating, enabling managers to assign the right people, equipment and materials at the right time. As a result, resource planning becomes more predictable and aligned with actual project needs.
Helps with Cost Management and Project Budgeting
A detailed WBS provides the structure needed to build an accurate project budget baseline. Each deliverable and work package can be estimated individually, making cost planning more granular and reliable.
Because the WBS ties work directly to measurable outputs, teams can link budget items to specific components of the scope, improving cost tracking and forecasting. This clear alignment between work and spending allows managers to detect variances early, understand the financial impact of changes and maintain tighter control of the overall project budget throughout execution.
Facilitates the Implementation of the Project Scheduling Techniques
A well-defined WBS makes project scheduling techniques far easier to apply. With each work package clearly identified, teams can perform accurate activity sequencing, build a coherent project timeline and develop a complete project network diagram.
These structured relationships also support the precedence diagramming method, enabling the calculation of dependencies and durations. Once this information is in place, the critical path method can be implemented to determine the sequence of work that drives the overall schedule. This leads to more predictable and realistic project planning.
Build a work breakdown structure Gantt chart diagram in ProjectManager in just a matter of minutes. Get started for free today.

A Gantt chart with WBS codes in ProjectManager. Learn more
When to Use a Work Breakdown Structure?
A work breakdown structure is most valuable when teams need clarity, structure and agreement on what the project will deliver. It supports planning, estimating, documentation and control, making it useful from early scoping through execution and ongoing project monitoring.
When defining the project scope
A WBS is essential when teams are clarifying the project scope and identifying what the final deliverable includes. By breaking the work into structured components, it supports scope definition, avoids ambiguity and ensures everyone understands the boundaries of the project before detailed planning begins.
When estimating project time, cost, or resources
A WBS provides the detail needed to estimate time, cost and resource requirements with greater accuracy. Each deliverable and work package becomes an estimating unit, allowing teams to build realistic schedules, budgets and resource plans that reflect the actual structure of the work.
When a project is complex or involves multiple deliverables
The more complex the project, the more valuable the WBS becomes. It organizes multiple deliverables into a clear hierarchy, making it easier to visualize the overall structure, identify dependencies and divide the work into manageable segments that teams can plan and execute confidently.
When preparing documentation
A WBS is especially helpful when assembling essential project documents such as the statement of work, scope baseline or project schedule. Its structured breakdown of deliverables provides a foundation that supports clearer descriptions, measurable expectations and better alignment across all planning documents.
Who Should Use a Work Breakdown Structure?
A work breakdown structure is a versatile project management tool used across industries to break complex work into manageable components. Any team that needs structure, clarity, predictable planning or stronger coordination benefits from using a WBS to organize deliverables, support estimating and improve execution throughout the project life cycle.
Project Management Teams
Project management teams use a WBS to define scope, organize deliverables and structure work into clear components. It helps them build accurate schedules, budgets and resource plans while improving communication across all stakeholders involved in planning and execution.
- Project Manager
- Program Manager
- PMO Director
- Project Scheduler
- Project Coordinator
Construction Project Management Teams
Construction project management teams use a WBS to break the project into phases such as site preparation, structural work and finishes.
It clarifies responsibilities, supports subcontractor coordination, improves estimating and provides the structure needed for cost tracking, inspections and progress monitoring.
- Construction Project Manager
- Site Supervisor
- General Contractor
- Estimator
- Construction Scheduler
Event Planning Teams
Event planners use a WBS to organize venues, logistics, speakers, catering and attendee management. It ensures no task is overlooked and helps teams coordinate timelines, resources and vendor activities for smooth event delivery.
- Event Manager
- Logistics Coordinator
- Vendor Manager
- Marketing & Communications Lead
- AV/Production Coordinator
Marketing Teams
Teams that manage marketing operations use a WBS to structure campaigns into creative development, content production, distribution and tracking. It helps align cross-functional teams, clarify deliverables and plan timelines for coordinated, on-brand execution.
- Marketing Manager
- Campaign Strategist
- Creative Director
- Content Manager
- Marketing Operations Specialist
Product Development Teams
Product planning and development teams use a WBS to break features, prototypes and testing activities into manageable components. It improves coordination among design, engineering and QA teams while supporting clearer estimates and release planning.
- Product Manager
- UX/UI Designer
- Mechanical/Electrical Engineer
- Quality Assurance Lead
- Prototype/Testing Engineer
Software Development Teams
Software development teams use a WBS to decompose features, user stories and technical work into structured components. It helps organize development, testing and deployment tasks, making planning more predictable and improving collaboration across developers, testers and product managers.
- Software Project Manager
- Product Owner
- Lead Developer
- QA Engineer
- DevOps Engineer
Build a work breakdown structure Gantt chart diagram in ProjectManager in just a matter of minutes. Get started for free today.

A Gantt chart with WBS codes in ProjectManager. Learn more
Types of Work Breakdown Structure
There are two main types of WBS: deliverable-based, and phase-based. They depend on whether you want to divide your project in terms of time or scope.
Deliverable-Based Work Breakdown Structure
A deliverable-based WBS first breaks down the project into all the major areas of the project scope as control accounts and then divides those into project deliverables and work packages.
Phase-Based Work Breakdown Structure
The phase-based WBS displays the final deliverable on top, with the WBS levels below showing the five phases of a project (initiation, planning, execution, control and closeout). Just as in the deliverable-based WBS, the project phases are divided into project deliverables and work packages.
Process-Based Work Breakdown Structure
A process-based WBS organizes the project by major workflows or business processes of an organization rather than deliverables or phases. It decomposes the work into sequential or parallel activities—such as design, procurement, fabrication or testing—making it ideal for operational, manufacturing or service-driven projects where processes define how the work is executed from start to finish.
Time-Based Work Breakdown Structure
A time-based WBS structures the project around time periods or work cycles instead of deliverables or phases. It breaks the project into weeks, sprints, quarters or recurring activity blocks, helping teams manage repetitive work, forecast resource needs and align planning with schedule-driven execution, especially in agile, maintenance or long-duration programs.
Types of Work Breakdown Structure Charts
Once you’ve chosen a deliverable-based or phase-based WBS, you can also choose between different types of WBS diagrams. Let’s take a look at the main types of work breakdown structure charts.
- Work Breakdown Structure List: Also known as an outline view, this is a list of work packages, tasks and deliverables. It’s probably the simplest method to make a WBS, which is sometimes all you need.
- Work Breakdown Structure Tree Diagram: The most commonly seen version, the tree structure depiction of a WBS is an organizational chart that has all the same WBS elements of the list (phases, deliverables, tasks and work packages) but represents the workflow or progress as defined by a diagrammatic representation.
- Work Breakdown Structure Gantt Chart: A Gantt chart is both a spreadsheet and a timeline. The Gantt chart is a WBS that can do more than a static task list or tree diagram. With a dynamic Gantt chart, you can link dependencies, set milestones, even set a baseline. This is the most common version in project management software.
Work Breakdown Structure Best Practices
As you’re working on your WBS it is helpful to maintain some best practices. Here are some things to keep in mind.
- 100% Rule: This is the most important work management principle to construct a WBS. It consists in including 100% of the work defined by the project scope, which is divided into WBS levels that contain control accounts, project deliverables, work packages and tasks. This rule applies to all the levels of the WBS, so the sum of the work at a lower WBS level must equal the 100% of the work represented by the WBS level above without exception.
- Use Nouns: WBS is about deliverables and the tasks that will lead to your final deliverable. Therefore, you’re dealing more on the what than the how. Verbs are great for action, and should be used in your descriptions, but for clarity, stick to nouns for each of the steps in your WBS.
- Be Thorough: For a WBS to do its job, there must be no holes. Everything is important if it’s part of the course that leads to your final deliverable. To manage that schedule, you need a complete listing of every task, big and small, that takes you there.
- Keep Tasks Mutually Exclusive: This simply means that there’s no reason to break out individual tasks for work that is already part of another task. If the work is covered in a task because it goes together with that task, then you don’t need to make it a separate task.
- Go Just Deep Enough: You can get crazy with subtasks on your WBS. The WBS has to be detailed, but not so deep that it becomes confusing. Ideally, think maybe three or five at most levels.
Build a work breakdown structure Gantt chart diagram in ProjectManager in just a matter of minutes. Get started for free today.

A Gantt chart with WBS codes in ProjectManager. Learn more
WBS in Project Management Documents
A work breakdown structure can be included in a variety of project management documents across industries. Here are some of the most common uses of a work breakdown structure in project documentation.
Project Management Plan
Including a work breakdown structure in the project management plan strengthens clarity, alignment and control from the very beginning. The WBS defines what the project will deliver and breaks the scope into manageable components, making scheduling, estimating and resource planning far more reliable.
Because of its central role in organizing the work, the WBS can also appear in several subsidiary plans, which are listed below.
- Scope Management Plan
- Schedule Management Plan
- Cost Management Plan
- Resource Management Plan
- Risk Management Plan
- Procurement Management Plan
Scope of Work
A scope of work is a comprehensive document that explains your project scope, which is all the work to be performed. A WBS is the perfect tool to break down the scope of a project into work packages that are easier to control. On top of that, a work breakdown structure allows you to easily identify milestones, deliverables and phases.
Statement of Work
A statement of work is a legally binding document between a client and the organization who’s responsible for executing a project. It details project management aspects such as the timeline, deliverables, requirements of the project.
Work Order
A work order is similar to a statement of work, but it’s main purpose is to show the costs associated with each task. A WBS is essential for an accurate cost estimation.
Work Breakdown Structure Variants
Several breakdown structures complement the WBS by organizing different project elements—such as risks, costs, resources and responsibilities—using a similar hierarchical format. These variants support more accurate planning, clearer analysis and stronger project control.
- Risk Breakdown Structure (RBS): Categorizes project risks into hierarchical groups to improve risk identification, assessment and response planning.
- Cost Breakdown Structure (CBS): Breaks project costs into structured categories aligned with the WBS for budgeting and cost control.
- Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS): Organizes labor, materials, equipment and skills into resource categories for planning and allocation.
- Product Breakdown Structure (PBS): Decomposes the final product into its physical components or features for clearer product definition.
- Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS): Maps project work to responsible teams or departments to clarify ownership and reporting.
All our tools are geared to making your project more efficient and effective. See for yourself by starting your free 30-day trial of our software.
Work Breakdown Structure Resources
Templates
Articles
- Importance of a Work Breakdown Structure in Project Management: 10 WBS Benefits
- How to Create a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Step-by-Step
- How to Make a Resource Breakdown Structure
- Construction Work Breakdown Structure: A Guide to WBS for Construction Projects
- Sample Project Management Flow Chart
- WBS and Gantt Chart: How to Use This Project Management Duo
- Sample Project Plan For Your Next Project
- ¿Qué es Una Estructura de Desglose de Trabajo?
- Qu’est-ce qu’une structure de répartition du travail ?
- Was ist ein Projektstrukturplan (PSP)?
- Estrutura analítica do projeto (EAP): um guia rápido
Start your free 30-day trial
Deliver faster, collaborate better, innovate more effectively — without the high prices and months-long implementation and extensive training required by other products.
Start free trial