As the creation of products and services has become more extensive and varied, the manufacturing industry has become more competitive. There are many things to keep an eye on such as material requirements planning, supply chain management and inventory control. Operations continue to become more complex, meaning manufacturing companies require more thorough production planning.
A production plan is the best way to guarantee you deliver high-quality products or services as efficiently as possible.
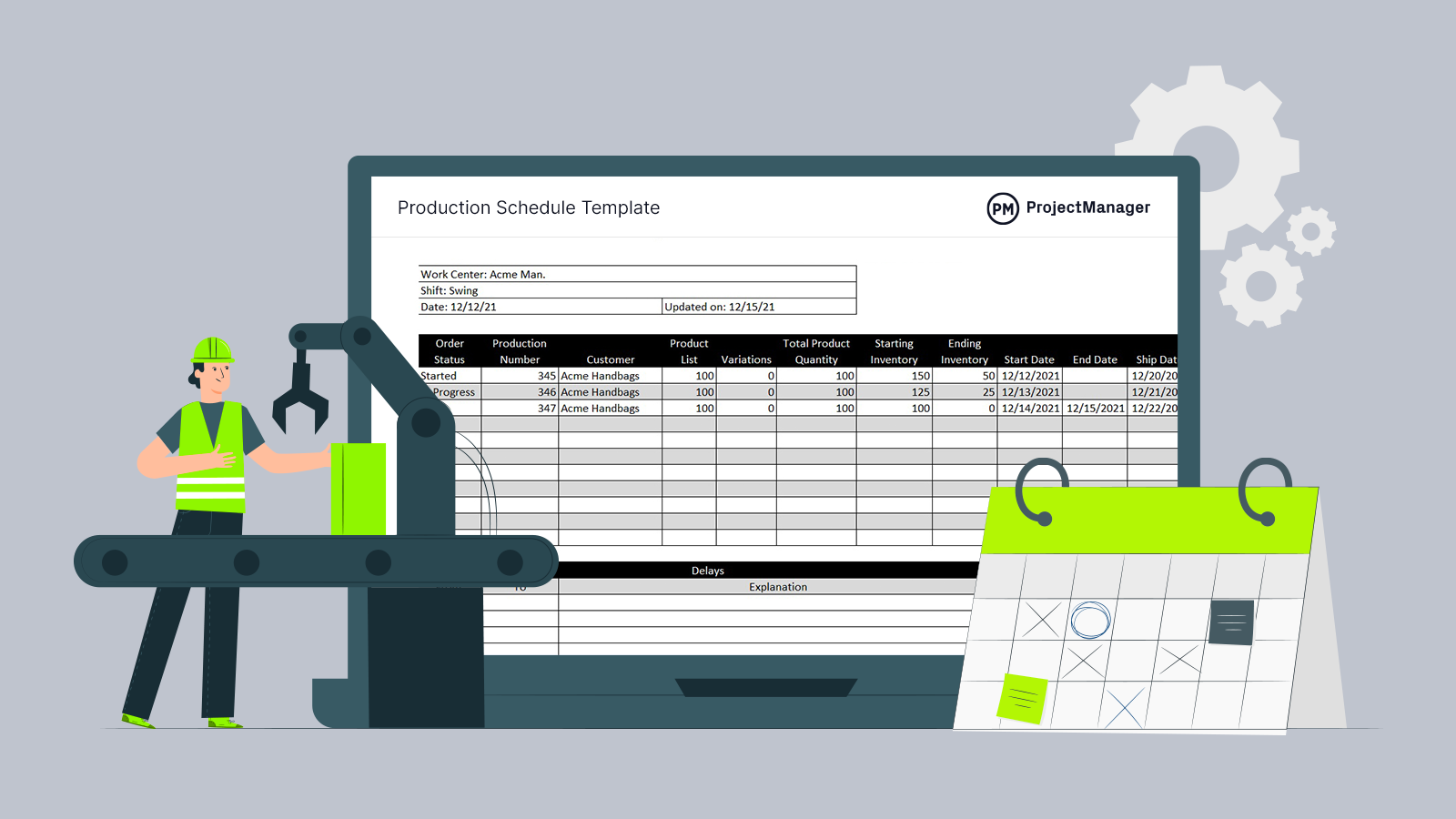
Get your free
Production Schedule Template
Use this free Production Schedule Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
What Is Production Planning?
Production planning is the process of deciding how a product or service will be manufactured before the manufacturing process begins. In other words, it’s how you plan to manage your supply chain, raw materials, employees and the physical space where the manufacturing process occurs.
Production planning is important for manufacturers as it affects other important aspects of their business such as:
- Supply chain management
- Production scheduling
- Material requirements planning
- Production lead time
- Capacity planning
ProjectManager is project management software that helps manufacturers cover every aspect of production planning. Plan with Gantt charts, execute with kanban boards and manage resources along the way. No other software offers sophisticated project and resource management features in one intuitive package. Get started today for free.
Why Is Production Planning Important?
If a manufacturing operation wishes to expand, that evolution demands careful production planning and scheduling. Someone must take on the responsibility of managing resources and deciding how they’ll be allocated. This process is a big part of capacity planning—how much can be made in a certain period, with the available resources?
Without production planning, it’s easy to use too much of a resource for one product and not leave enough for another, or fail to schedule your resources properly, which results in delays that affect your overall production management process. It’s just as easy to let resources go to waste. These issues indicate a lack of efficiency in your production planning process.
Production planning is the best way to ensure resources are used appropriately, products and services are high-quality and nothing goes over budget. In most organizations, a production manager manages the production planning process.
What Does a Production Planner Do?
A production planner is a team leader who oversees the production planning process, which defines how an organization will approach major areas of production management such as production scheduling, resource capacity planning, production control and production budgeting to manufacture products.
To better understand what a production planner does and the importance of this role in any manufacturing organization, let’s dive into each step of the production planning process.
10 Steps of the Production Planning Process
The production planning process consists of an organization’s actions to make a production strategy that allows it to manufacture products most efficiently and profitably. Here are 10 key steps you should follow when planning your production process.
1. Use Production Forecasting Methods for Estimating Customer Demand
The first step of the production planning process is to forecast the customer demand for your product for a future period like a year or a quarter. To do so, manufacturers rely on quantitative and qualitative techniques such as Delphi method, historical analogy method, moving average method and the analysis of business data and sales forecasts.
This process is known as demand planning, which helps manufacturers be better prepared to meet the demand for their products and manufacture the right quantity so they can minimize production and operational costs.
2. Gauge Your Production Capacity
The term production capacity refers to the maximum quantity of product a manufacturing company can produce based on its available production resources such as raw materials, labor, equipment and machinery.
Once you better understand the customer demand for your product, you’ll need to gauge the total quantity of product that needs to be manufactured and then evaluate if your production capacity is sufficient.
3. Map Out the Shop Floor Layout
Now think about the steps of the production process itself. Outline the production tasks that must be executed to transform raw materials, parts and components into a final product and the physical route that those elements will follow to move across the shop floor. This will allow you to pick a production floor layout that minimizes the time and effort required from your employees.
4. Make a Production Budget to Find the Optimal Production Volume
The next challenge in the production planning process is determining the exact number of units to manufacture to keep up with customer demand and maintain your desired stock levels.
This requires a production budget, a document used to calculate the number of units that should be produced by a company to meet the customer demand for a period such as a month, quarter or even a year.
Creating a production budget involves assessing the current product inventory, the production capacity, sales forecasts and the ending inventory that should remain at the end of the period. Once you analyze these variables and use the production budgeting formula, you’ll know the required production level for a given time.
5. Choose a Production Costing Technique
Choose a costing method for your production process such as activity-based costing, process costing, job costing or simply standard costing. Each has its pros and cons depending on your organization’s particular characteristics.
6. Create a Production Schedule
Now it’s time to make a production schedule that allows your organization to create a stock inventory, deliver products to distribution channels, fulfill customer orders and meet the obligations of any manufacturing contracts the organization has in place for the production timeline you’re planning for.
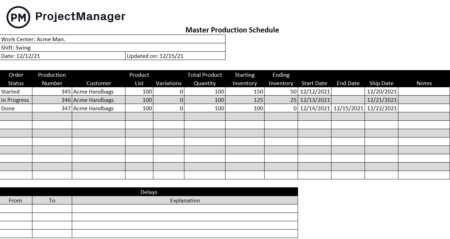
7. Establish a Production Control System
Next, it’s important to establish standard operating procedures and key performance indicators and use a variety of production control tools to create a system that allows you to track the production process to ensure your products meet quality standards and are manufactured on time and under budget.
8. Set Production Reporting Guidelines
After you’ve decided what KPIs will be used to monitor the efficiency of your production process, you’ll need to determine what types of reports will be used to communicate these metrics with stakeholders and the frequency in which they’ll be produced.
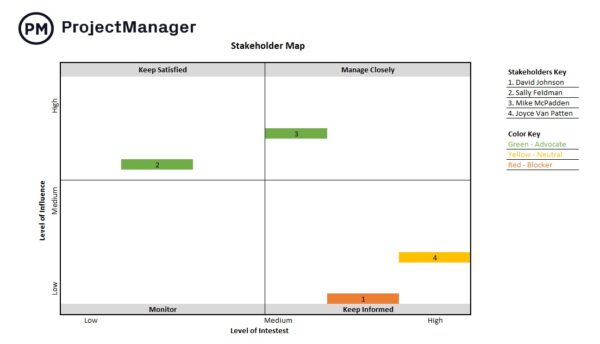
The documentation from each of these production planning stages, such as the production budget and production schedule are gathered in a larger document called the production plan.
What Is a Production Plan?
A production plan is a document that describes how production processes will be executed, and it’s the outcome of the production planning process. It describes the human resources, raw materials and equipment needed and the production schedule that will be followed.
The person responsible for production planning must also be very familiar with the operation’s inner workings, project resources and the products/services they produce. This usually entails collaborating with people on the floor, in the field or in different departments to create products and deliver services.
Production Plan Example
The best way to illustrate this process is through an example. When you set out to create a production plan, make sure to follow these steps to make it as robust as possible.
Sales Forecast
Making a sales forecast greatly helps you decide which product planning method is best for your operation given your production capacity. You’ll need to use diverse sales forecasting techniques to better understand what will be the future demand for your product. From here, you can estimate which resources are required and how they’ll be used in the manufacturing process to begin the production capacity planning process.
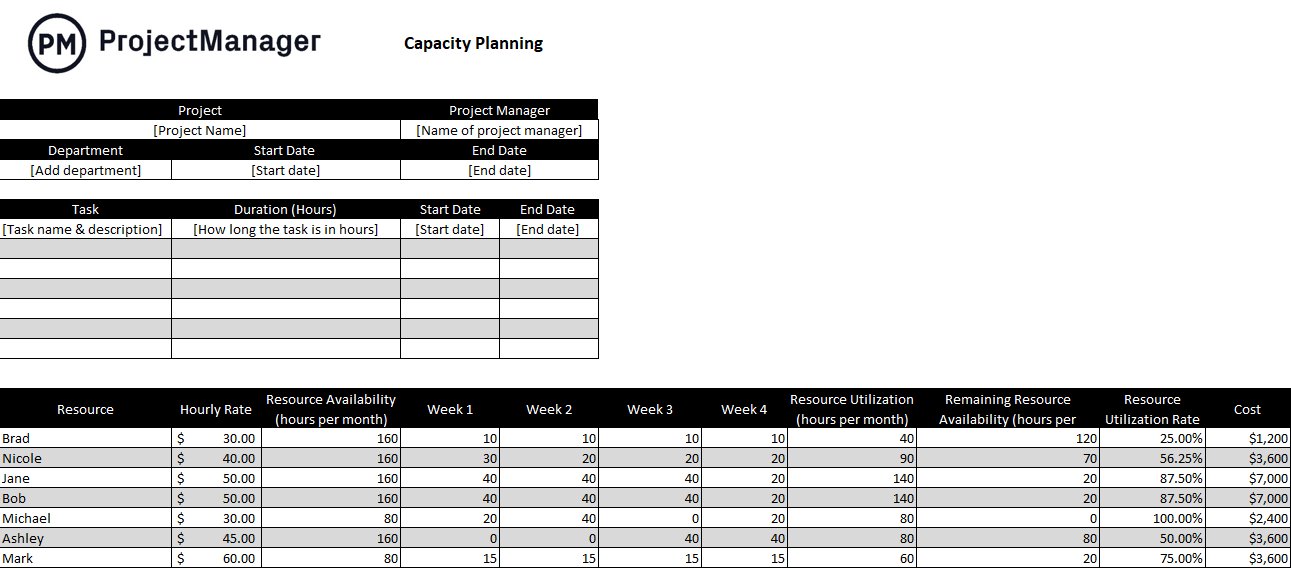
Inventory Management Plan
Accessing inventory is about more than simply taking stock: you should make an inventory management plan for your production inventory and work-in-progress inventory so that you don’t experience shortages that might halt production or let things go to waste. For this step, focus on the inventory control and inventory management techniques you can use to handle inventory in the most efficient way possible.
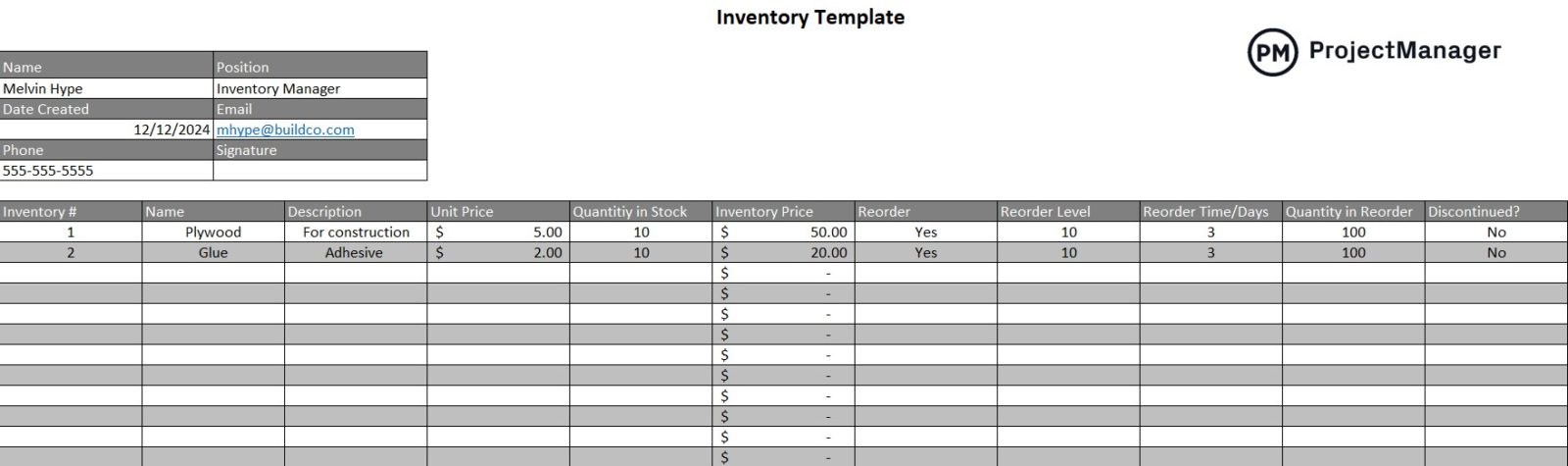
Production Budget
Most manufacturers use the production budgeting formula below to make a production budget that indicates the ideal production volume based on a starting inventory, sales forecasts, production capacity and expected ending inventory levels.
Required Production = Sales Forecast Expected Units + Desired Ending Inventory – Beginning Inventory
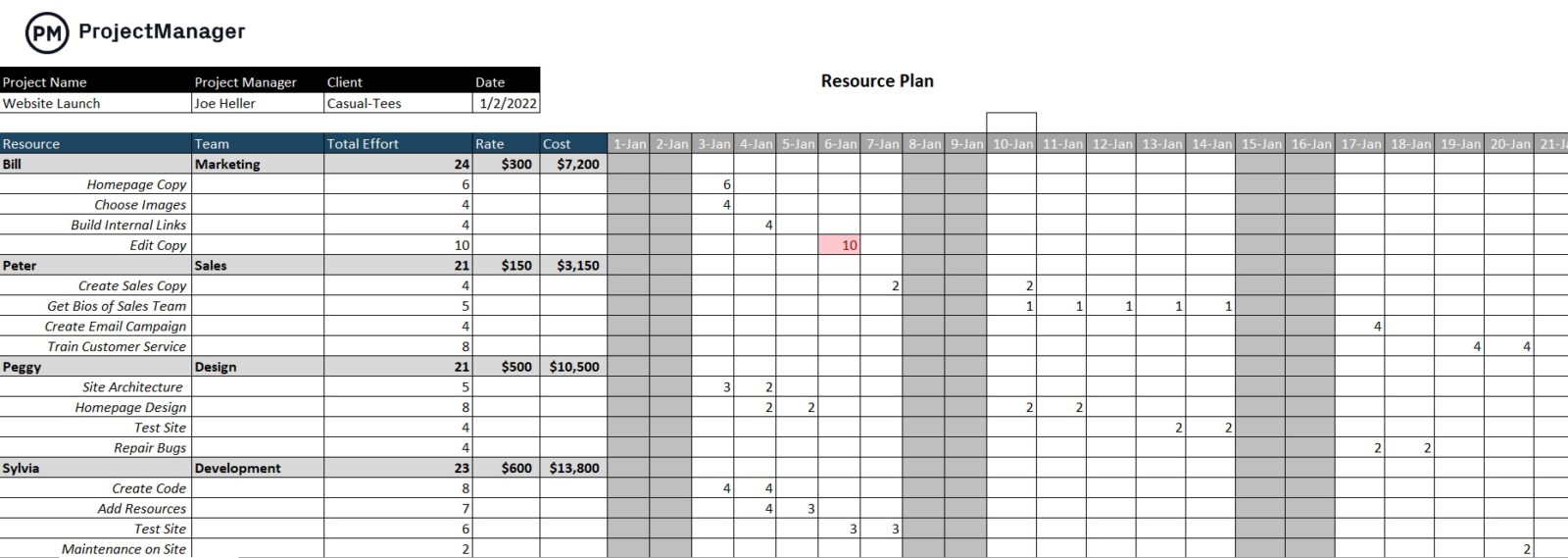
Resource Plan
A successful production plan requires you to be familiar with the resource planning details of the manufacturing process, which is why you’ll need to make a resource plan that outlines what resources such as labor, raw materials, equipment and any other capital assets are available for production and when they’re scheduled to be utilized.
Production Cost Estimate
Once you’ve determined what the required level of production is and the resources that will be needed, you’ll need to estimate the cost of production. It’s important to ensure the production process will be profitable before creating a production schedule.
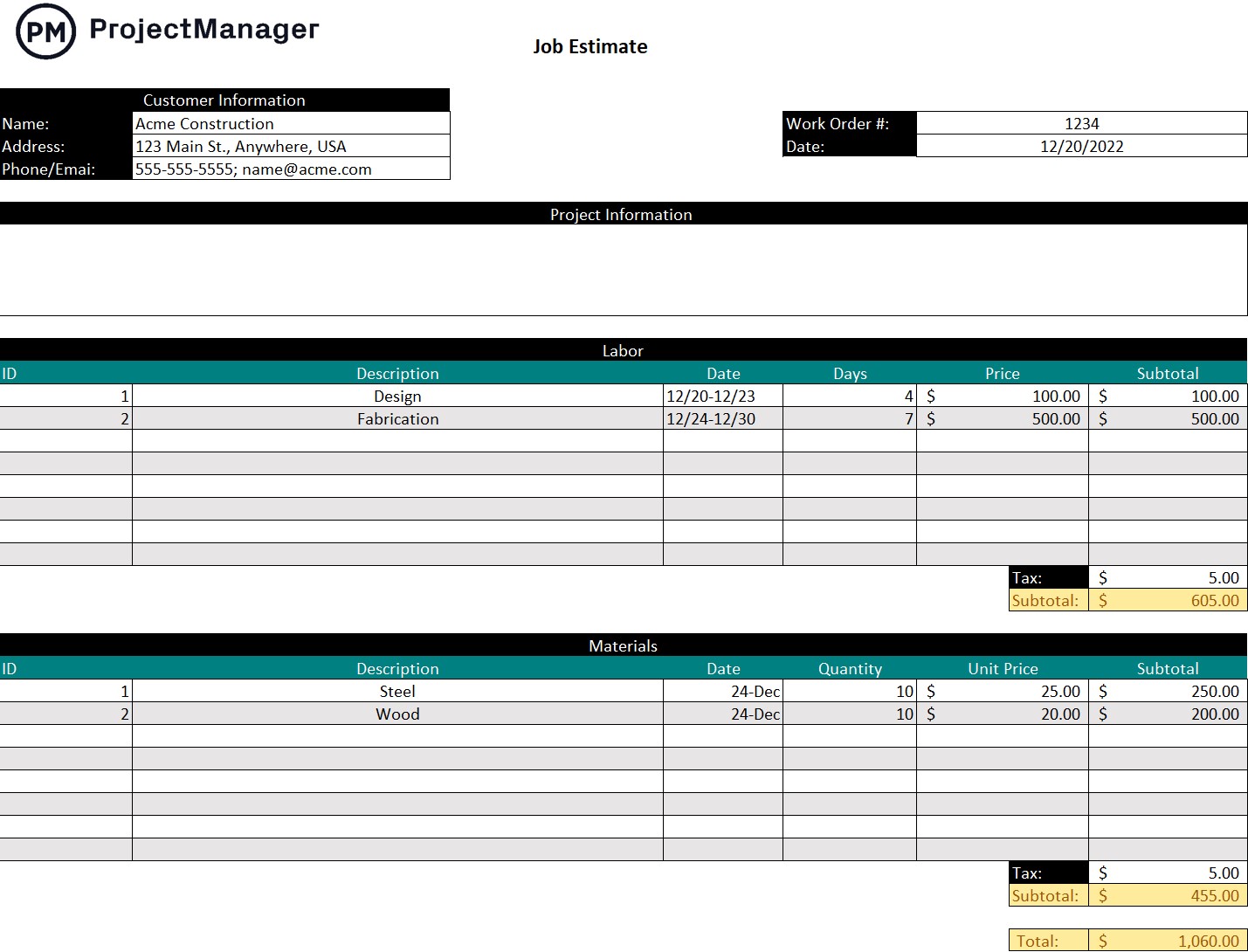
Production Schedule
As stated above, a production schedule is key to making sure your manufacturing team delivers products on time, but also guides efforts in other areas such as supply chain management and logistics management.
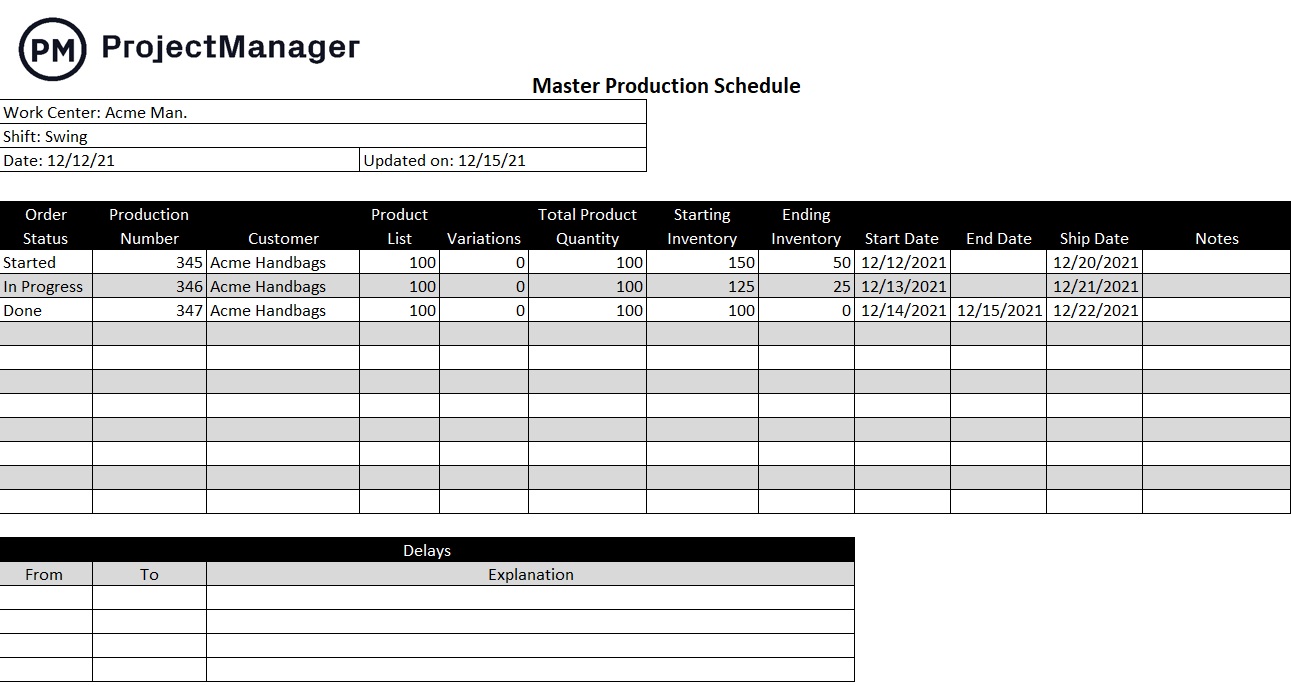
Production Control Plan
A production control plan should describe all the metrics, procedures, guidelines and tools that will be utilized to monitor how the results compare to the production schedule and resource management projections. This is something that should continually take place and be documented during the production process.
Types of Production Planning
Every operation is unique, and the same production plan isn’t right for everyone. To get the most from project planning, you decide which method is best for your manufacturing process. Here’s a quick intro to the different types of production planning.
Job Method
The job method is often used when manufacturing a single product, for which a unique production plan is created. This production planning method is generally used in smaller-scale productions, but it can also be applied to larger manufacturing facilities. The job method is especially advantageous when a production order requires specific customizations.
Batch Production Method
Batch production consists of manufacturing goods in groups, instead of being produced individually or through continuous production. This method is useful when manufacturing products on a large scale.
Flow Method
The flow method is a demand-based manufacturing model that minimizes the production lead time by speeding up the production line. The manufacturing process starts based on work orders, and once it starts, it doesn’t stop until all finished goods are produced. This is called continuous production and it’s achieved by using machinery and little intervention to minimize waiting time.
Process Method
The process method is more or less what most people picture when they think about production—an assembly line. With the process method, there will generally be different types of machinery that complete separate tasks to put together the finished goods.
Mass Production Method
The mass production method primarily focuses on creating a continuous flow of identical products. It’s similar to the flow method, but at a much bigger scale, which cuts production costs. When uniformity is just as critical as efficiency, use “standardized processes” to guarantee all products look the same.

Production Planning Best Practices
No matter what product or service is being manufactured, there are many tried-and-true best practices to increase your operational efficiency. When creating a production plan, keep these two in mind.
Make Accurate Forecasts
When you don’t properly estimate the demand for your product or service, it’s impossible to create a detailed production plan. Demand planning is never static. Consider buying trends from previous years, changes in demographics, changes in resource availability and many other factors. These demand planning forecasts are the foundation of skillful production planning.
Know Your Capacity
Capacity planning means knowing the maximum capacity your operation can manage—the absolute most of a product or service it can offer during a period of time. This is the only way to anticipate how much of each resource you need to create X amount of products.
When you don’t know the production capacity, your production planning is like taking a shot in the dark.
Common Production Planning Mistakes
Stay vigilant of common missteps as you go through the production planning process. Here are three mistakes often made during production planning. Luckily, they can be prevented.
Not Expecting the Unexpected
This means having risk management strategies in place if things go awry. The goal is to never have to employ them, of course, but it’s better to have them and not need them. Production planning is incomplete if it doesn’t anticipate risks, issues and changes. When you plan for them, you’re ready to problem-solve if and when they happen.
Getting Stuck Behind the Desk
You should work with intelligent production planning tools, but that doesn’t mean you should only rely on enterprise resource planning software for production planning and not oversee resources and manufacturing operations in person. When production planning is only done from behind a screen, the result won’t be as informed as it could be. The best production planning is active and collaborative.
Neglecting Equipment
To get the most from your equipment, you need to take care of it. This means tracking usage and keeping up with regular maintenance. This looks different depending on the industry and product or service, but the principle is the same: continually take care of your equipment before it becomes a problem that slows down production.
Use ProjectManager for Production Planning and Scheduling
As the nature of manufacturing goods and services changes, you need modern tools to plan production and make schedules. ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that offers all the tools you need for excellent production planning and scheduling. With it, you can plan projects, create schedules, manage resources and track changes with one tool.
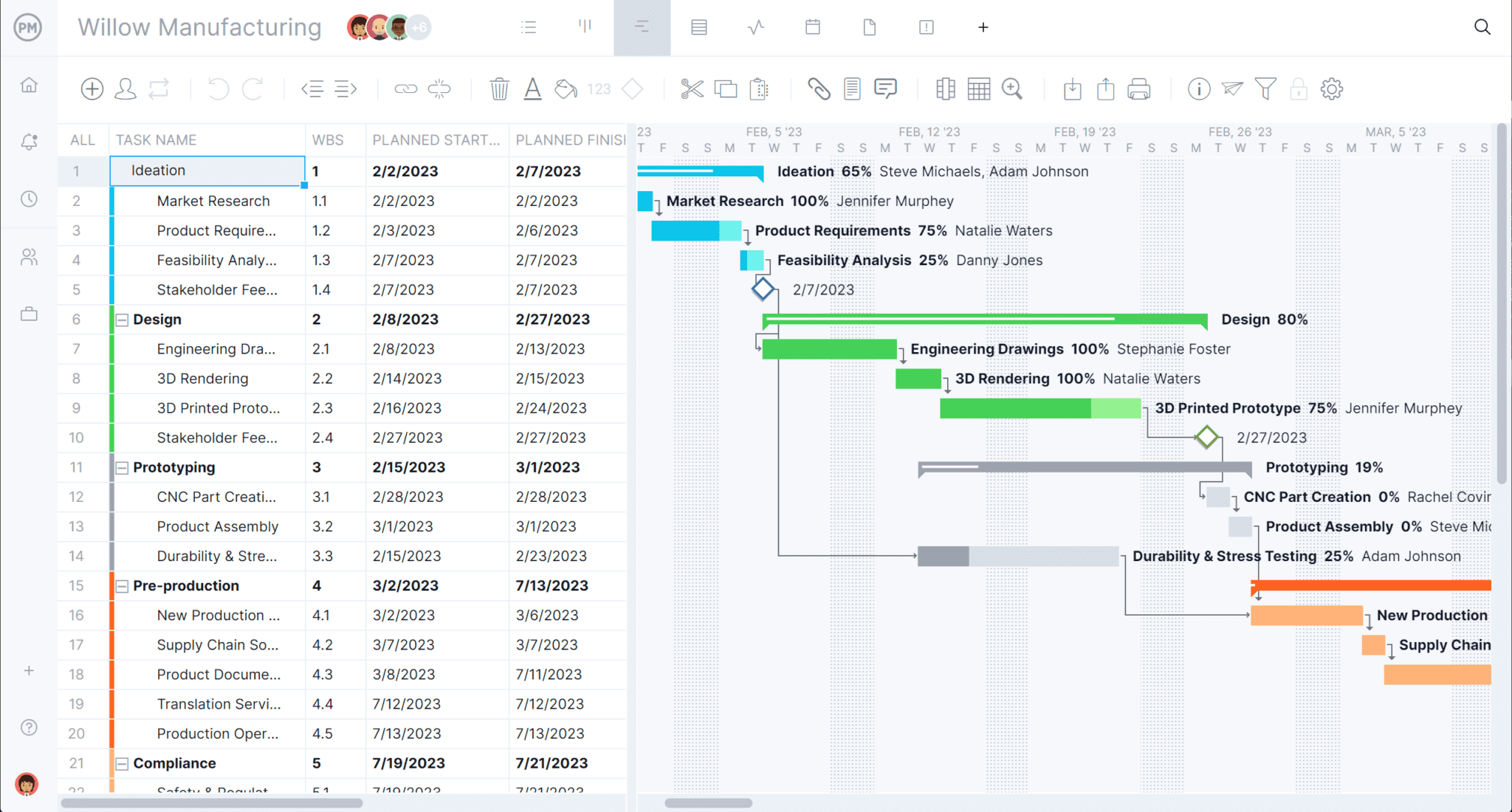
Plan With Gantt Charts
Manage your product manufacturing across a timeline with our Gantt chart view. With it, you can view your resources to help you track your cost of production to ensure you’re never overspending. You can then link any dependent tasks to avoid bottlenecks in your manufacturing.
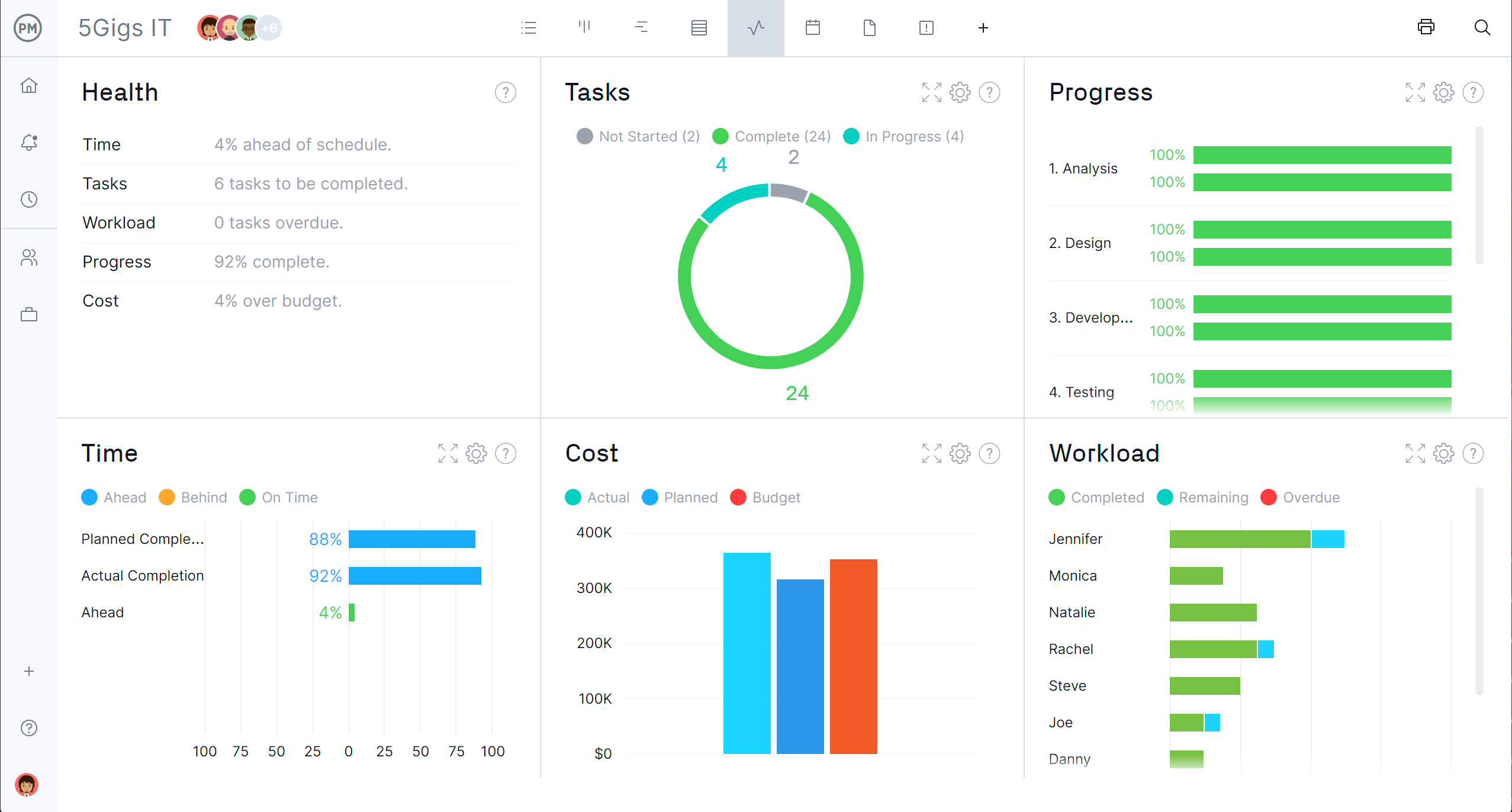
Get a Bird’s-Eye View
To keep your production plan on track, you need a high-level view to pinpoint setbacks before or as they occur. Our real-time dashboard collects data and converts it into colorful graphs and charts that give you at-a-glance analytics.
Easily Measure and Report Your Progress
Any operation will have stakeholders who want to be kept in the loop. ProjectManager’s project status reports make it easy to share key data points. They can be generated in a single click, making it simple to generate them before important meetings.
Related Production Planning Content
The production planning process involves many different activities such as estimating the quantity of goods to be produced, the resources needed, the production schedule and much more. That’s why we’ve created dozens of blogs, guides and templates on production management topics. Here are some of them.
- Production vs. Manufacturing
- How to Make a Production Flow Chart for Manufacturing
- Best Production Scheduling Software Rankings
- How to Create a Master Production Schedule (MPS)
- Production Schedule Template
- ¿Cómo Hacer un Plan de Producción? Principios de Planificación de la Producción
Manage every detail of your operation with ProjectManager’s powerful online project management tools. Our suite of tools is trusted by tens of thousands of teams, from NASA to Volvo, to aid them in the planning, scheduling, tracking and reporting on the progress and performance of their production plans. Our software lets you get out from behind your desk and make adjustments on the go. Try it for yourself for free for 30 days!

